Human embryonic stem cells-a novel source for in vitro three dimensional oral mucosa
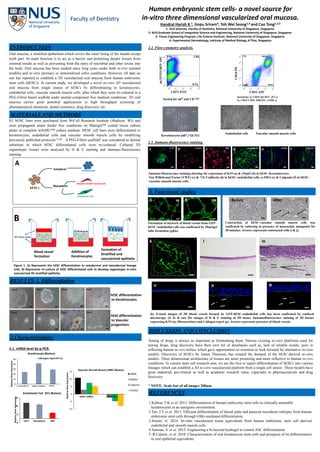
- 1. -5 5 15 25 CD31 VECadherin vWF RelativeGeneExpression Endothelial Cell (EC) Markers Human embryonic stem cells- a novel source for in-vitro three dimensional vascularized oral mucosa. Handral Harish K 1, Gopu Sriram4, Toh Wei Seong1,3 and Cao Tong1,2,3 1- Oral Sciences, Faculty of Dentistry, National University of Singapore, Singapore. 2- NUS Graduate School of Integrative Science and Engineering, National University of Singapore, Singapore. 3- Tissue Engineering Program, Life Science Institute, National University of Singapore, Singapore. 4- Experimental Dermatology, Institute of Medical Biology, A*Star, Singapore Oral mucosa, a stratified epithelium which covers the inner lining of the mouth except teeth part. Its main function is to act as a barrier and protecting deeper tissues from external insults as well as preventing from the entry of microbial and other toxins into the body. Oral mucosa has been studied since long years under both in-vivo (animal models) and in-vitro (primary or immortalized cells) conditions. However, till date no one has reported to establish a 3D vascularized oral mucosa from human embryonic stem cells (hESCs). In current study, we developed a novel in-vitro 3D vascularized oral mucosa from single source of hESCs by differentiating to keratinocytes, endothelial cells, vascular smooth muscle cells, after which they were tri-cultured in a PEG-Fibrin based scaffold under animal-component free medium conditions. 3D oral mucosa carries great potential applications in high throughput screening of pharmaceutical chemicals, dental cosmetics, drug discovery, etc. INTRODUCTION H1 hESC lines were purchased from WiCell Research Institute (Madison, WI) and were propagated under feeder free conditions on Matrigel™ coated tissue culture plates in complete mTeSR1™ culture medium. HESC cell lines were differentiated to keratinocytes, endothelial cells and vascular smooth muscle cells by modifying previously published protocols1,2 &3 . A PEG-Fibrin scaffold4 was considered as dermal substitute in which hESC differentiated cells were tri-cultured. Cultured 3D organotypic tissues were analysed by H & E staining and immuno-fluorescence staining. MATERIALS AND METHODS Mesoderm Ectoderm A Keratinocytes Vascular smooth muscle cells Endothelial cells Blood vessel formation Addition of Keratinocytes Formation of Stratified and vascularized epithelia B Figure 1. A) Represents the hESC differentiation to ectodermal and mesodermal lineage cells. B) Represents tri-culture of hESC differentiated cells to develop organotypic in-vitro vascularized 3D stratified epithelia. RESULTS-1. Differentiation Day0 Day2 Day5Day4 Day0 Day3 Day9Day6 hESC differentiation to Keratinocytes hESCdifferentiation to Vascular progenitors 0 10 20 30 40 50 Cytokeratin-14 α6Integrin ΔNp63 RelativeGeneExpression Keratinocyte Markers α6Integrin Hgh/CD71Lw 2.Characterization: 2.1. mRNA level by q-PCR. -10 -5 0 5 10 15 hESC-vSMCs hESC-EC RelativeGeneExpression Vascular Smooth Muscle (SMC) Markers αSMA SM22α Calponin PDGFβ Sorted for α6H and CD 71L Keratinocytes (α6H / CD 71L) α6INTEGRINAPC CD71 FITC Vascular smooth muscle cells Sorted for 1). CD34+&CD31+ (ECs) 2). CD34- CD31- PDGFb+ (vSMCs) Endothelial cells CD34-PE CD31-APC 2.2. Flow-cytometry analysis. ΔNP63K19 a b 2.3. Immuno-fluorescence staining. VE-CadherinVWF α-SMA Immuno-fluorescence staining showing the expression of K19 (a) & ΔNp63 (b) in hESC-Keratinocytes; Von Willebrand Factor (VWF) (c) & VE-Cadherin (d) in hESC-endothelial cells; α-SMA (e) & Calponin (f) in hESC- vascular smooth muscle cells. Formation of network of blood vessels from GFP- hESC-endothelial cells was confirmed by Matrigel tube formation (g&h). 4X Contraction of hESC-vascular smooth muscle cells was confirmed by culturing in presence of muscarinic antagonist for 30 minutes. Arrows represents contracted cells (i & j). k l Epidermis Dermis Blood vessels m (k) Z-stack images of 3D blood vessels formed by GFP-hESC-endothelial cells has been confirmed by confocal microscopy. (l) 4x & (m) 20x images of H & E staining of 3D tissue; Immunofluorescence staining of 3D tissues expressing K19 (n), fibronectin(o) and Collagen-type4 (p). Arrows represents presence of blood vessels. DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION Testing of drugs is always as important as formulating them. Various existing in-vitro platforms used for testing drugs, drug discovery have their own list of drawbacks such as, lack of reliable results, poor in reflecting human in-vivo milieu, which gave opportunities to scientists to look forward for alternative in-vitro models. Discovery of hESCs by James Thomson, has created the demand of the hESC-derived in-vitro models. Three dimensional architecture of tissues are more promising and more reflective to human in-vivo conditions. In current stem cell research area, we are the first to report differentiation of hESCs into various lineages which can establish a 3D in-vitro vascularized platform from a single cell source. These models have great industrial, pre-clinical as well as academic research value, especially in pharmaceuticals and drug discovery. * NOTE- Scale bar of all images 200µm. 1.Kidwai, F.K et al. 2013. Differentiation of human embryonic stem cells to clinically amenable keratinocytes in an autogenic environment. 2.Tan, J.Y et al. 2013. Efficient differentiation of lateral plate and paraxial mesoderm subtypes from human embryonic stem cells through GSKi-mediated differentiation. 3.Sriram, G. 2014. In-vitro vascularised tissue equivalents from human embryonic stem cell derived endothelial and smooth muscle cells. 4.Natesan, S. et al. 2012. Engineering a bi-layered hydrogel to control ASC differentiation. 5..B.Calenic. et al. 2010. Characterization of oral keratinocyte stem cells and prospects of its differentiation to oral epithelial equivalents. REFERENCES hESCs 3D Culture media n l c c e g Calponin Cytokeratin-19 Alpha 6 Integrin ΔNP63 3. Functional studies C d e f 10Xh o p AfterBefore i j
