Research Paper Final Draft
- 1. Research Paper Chambers 1 The Endogenous Cannabinoid System Our internal healing center By Jeremy Chambers
- 2. Research Paper Chambers 2 Jeremy Chambers Mary Karen Solomon April 8, 2015 Abstract The Endogenous Cannabinoid System The discovery of the Endocannabinoid System through marijuana research, has created a new market for pharmacotherapy and a different perspective of how the mammalian biology uses external and internal chemicals to process and fulfill certain functions in the brain and the peripheral organ systems. These functions are important for controlling mood, pain tolerance, and even digestion. The National Library of Medicine has several studies showing how the endo- cannabinoids interact with receptors to cause changes to help promote certain effects. This all began with the discovery of THC and how it interacts with the brain.
- 3. Research Paper Chambers 3 Research Outline Thesis: The ECS can potentially be the next big boom in medicine and possibly the key to curing most diseases and may legitimize the use of marijuana as a medicine. I. Marijuana has been used for medicinal purposes for thousands of years. A. 10,000 year old hemp baskets found in what is now Taiwan. B. 2737 BC Chinese text describe the use of the sativa plant for the relief of pain and cramps by the Emperor Shen Neng. C. 2500 year old mummy found with cannabis on her person. Mummy believed to be using it for her breast cancer symptoms. D. 2000-650 BCE: Cannabis (azaluu or gurgurru) mentioned in Assyrian pharma- copoeia at the library of Assurbanipal, E. 2,000-800 BCE Bhang (dried cannabis leaves, seeds and stems) is mentioned in the Hindu sacred text Atharvaveda (Science of Charms) as "Sacred Grass", one of the five sacred plants of India. It is used by medicinally and ritually as an of- fering to Shiva. F. In ancient India, the anxiety-relieving effect of bhang (the Indian term for mari- juana ingested as food) had been recorded more than 3000 years ago. G. The use of cannabis or hashish as a psychoactive substance reached Europe and the Americas through the Arab world in the 19th century.
- 4. Research Paper Chambers 4 H. Up until 1937, cannabis was a part of most of the world’s pharmacopeias but was then banned due concerns of the dangers of abuse. II. Research in the twentieth century has lead to more discoveries about the how cannabinoids interact with life. A. 1964: The discovery of tetrahydrocannabidiol (THC) structure and elucidation. B. 1988: Cannabinoid binding sites or receptors are found in rats brains lead to more research. C. 1991: the human CB1-R (receptor) is successfully cloned. D. 1992: the Endogenous CB1-R ligand and anandamide are discovered. E. 1993: CB2-R was found in the immune system and was successfully cloned. F. 1995: the second Endogenous cannabinoid is found called 2-AG (2-Arachi- donoylglycerol) and is more abundant in the brain than Anandamide(AEA). III. What is the Endogenous Cannabinoid System? A. The Endogenous Cannabinoid System is made up of the receptors CB-1 and CB-2 that are found to have some significant roles in multiple functions and chemical reactions and many cannabinoids such as the ones previously men- tioned, Anadimide and 2-AG are agonists that cause these reactions. B. The two receptors CB-1 and CB-2 are found primarily in the Central Nervous System as mentioned previously but are found throughout the Peripheral Ner- vous System as well. There is a third or CB-3 that is still under investigation.
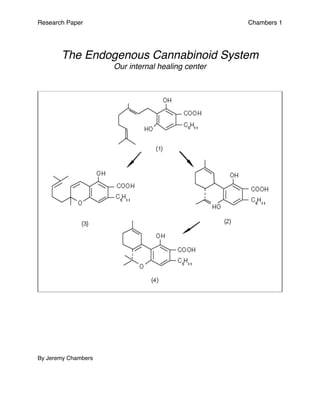
- 5. Research Paper Chambers 5 C. Anadimide (AEA) Like THC is a cannabinoid or ligand that is found in the Central Nervous System and the peripheral organs in rats and humans coupled with the CB-1R and CB-2R, suggesting it is an agonist for both receptor types. D. 2-arachi-donylglycerol (2-AG) is a ligand that needs more studies. 2-AG is found to be 200 times more prevalent in the human brain than AEA. The highest con- centrations were found in the brainstem, medulla, limbic forebrain, striatum, and hippocampus and the lowest in the cortex, diencephalons, mesencephalon, hy- pothalamus, and cerebellum. E. There are two classes of synthetics, the cannabinoid agonists (promote CB-1R and CB-2R affects) and cannabinoid antagonists (blocks the CB-1R and CB-2R affects). IV. There are many potential pharmacological therapies that are being explored using cannabis and the body’s own cannabinoid system. A. Soon after the discovery and synthesizing of marijuana’s THC, pharmaceutical companies raced to try to create a pharmaceutical drugs that use the same properties as THC to bind with the receptors causing similar affects. 1. Pharmaceutical companies like AbbVie inc. and Valeant Pharmaceuticals of North America, developed drugs that synthesized the effects of the cannabi- noids found in marijuana. 2. A Pharmaceutical company name Sanofi is developing a drug for weight loss in Europe.
- 6. Research Paper Chambers 6 3. Dronabinol (Marinol) is a synthetic THC and is a CB-1R and CB-2R agonist that is approved by the Food and Drug Administration that is used for cancer patients during chemotherapy as an antiemetic (anti-nausea) and appetite stimulant. 4. Nabilone (Cesamet) is a synthetic analogue of THC; it is a CB1-R and CB2-R receptor agonist that has been FDA approved as an antiemetic in chemo- therapy patients in whom all other therapy has failed. Unapproved use is em- ployed in patients with upper motor neuron syndrome who have spasticity-re- lated pain not controlled by conventional treatment. 5. Rimonabant (Acomplia or Zimulti) is a selective CB1-R receptor antagonist, with the primary role to centrally acting CB1-R receptors. Rimonabant was sold in Europe for the treatment of obesity. Due to depression as a side affect the drug was not approved in the US for sales. B. There has been a list of studies listed on the National Center for Biotechnology Information website and others that suggest cannabinoids found in marijuana have potential healing properties as well as the therapeutic uses. 1. “Extending pre-clinical research on cannabis-attributable immunomodulation, this study's CRP evidence points toward possible anti-inflammatory effects of cannabis smoking. More definitive evidence can be derived by combining pre-clinical research, studies of patients, and epidemiological research ap- proaches.”(NCBI, 2014).
- 7. Research Paper Chambers 7 2. Protective effects of cannabidiol on lesion-induced intervertebral disc degen- eration. 3. Cannabidiol improves lung function and inflammation in mice submitted to LPS-induced acute lung injury. 4. Cannabidiol (CBD) enhances the anti-cancer effects of THC on human brain cancer cells. 5. Cannabinoids are used in treatment of rare forms of epilepsy that do not re- spond to conventional medications. 6. CBD and THC are shown to cause cancer cells to commit suicide. V. Is Marijuana safe for consumption? A. Marijuana or the cannabis plant seems to be more safe than most food products. B. The lethal dose is higher than anyone could ever consume at one time.
- 8. Research Paper Chambers 8 Mary Karen Solomon English Composition II April 8, 2015 The Endogenous Cannabinoid System With the recent legalization of medical and recreational marijuana in some of the US states, there has been more attention brought to the internal system in the human body referred to as the Endogenous Cannabinoid System (ECS). This may sound like it has something to do with cannabis. That is because the discovery of delta-9-Tetrahy- drocannabinol or THC showed that it was binding with certain receptors in the human brain. Chemical structures including THC, are classified as cannabinoids deriving from the word cannabis. Our own body creates and maintains chemicals that generate or mimic the same responses that THC and other chemicals produced in marijuana. Since it is inside the body, it has been called the endo (latin for internal) cannabinoid system. The ECS can potentially be the next big boom in medicine and possibly the key to cur- ing most diseases and may legitimize the use of marijuana as a medicine. Up until the prohibition of cannabis in the early to mid twentieth century, marijuana or cannabis had a long history of medicinal uses showing that humans had been consuming it for millennia. The earliest evidence of man using the plant, dated
- 9. Research Paper Chambers 9 8,000+ BCE, was the use of hemp cord in pottery, identified at an ancient village site dating back over 10,000 years, located in the area of modern day Taiwan. This is not a medicinal use but correlates the relationship between humans and the plant. Carl Sagan, the famous twentieth century writer, found this to be a possible beginning point of civilization and believed that hemp had helped us along the way. Sagan was quoted, "It would be really interesting if in human history the cultivation of marijuana led generally to the invention of agriculture, and thereby to civilization” (The Dragons of Eden, 191). For the next 5,000 years or so, the Chinese were known to have eaten hemp seeds and oil using the plant to make textiles. In 2737 BCE or over 4,500 years ago, the Emperor of China, Shen Neng, listed Cannabis as a medicine. This is the first documentation of cannabis being labeled for medicinal purposes. In a Time Magazine article, Emperor Neng’s uses of the plant are described by author Patrick Stack as follows: As early as 2737 BC, the mystical Emperor Shen Neng of China was pre- scribing marijuana tea for the treatment of gout, rheumatism, malaria and, oddly enough, poor memory. The drug's popularity as a medicine spread throughout Asia, the Middle East and down the eastern coast of Africa (Stack, 2009). In 1993, archeologists, Andrey Letyagin and Andrey Savelov discovered a mummy from 2,500 years ago named Ukok (after the area she was found), that gives some insight into the treatment of ailments using cannabis. You see, Ukok was believed to have suffered from breast cancer and also to be a shaman. She was found with some herbs and cannabis in a container. The scientists that found her, believe she snorted
- 10. Research Paper Chambers 10 cannabis as remedy for her pain. They believe she lay for months in the same spot she died in as a result of her cancer (Holloway,2014). Soon after, in 2000 BCE, and all the way to 800 BCE, the Hindus used what they called Bhang (dried cannabis leaves and stems), which is listed in a sacred text, called the Atharvaveda (Science of Charms) as “Sacred Grass”. This is one of five sacred plants that were used ritually and medicinally as an offering to Shiva, or their God. That isn’t the first ancient text to mention it either, in 700-600 BCE, the Zoroastrian Zendav- esta, an ancient Persian religious text, calls it the “good narcotic”. This attitude towards cannabis seems to continue throughout most of ancient history, however, not in the 20th century US. Let’s fast forward to somewhere between the years 23 and 127. Gaius Plinius Secundus, also known as Pliny the Elder, wrote The Natural History and mentions hemp rope and marijuana’s analgesic properties, Hemp originally grew in the forests,1 where it is found with a blacker and rougher leaf than in the other2 kinds. Hempseed,3 it is said, renders men impotent: the juice of this seed will extract worms from the ears, or any insect which may have entered them, though at the cost of producing head-ache. The virtues of hemp, it is said, are so great, that an infusion of it in water will cause it to coagulate:4 hence it is, that if taken in water, it will arrest looseness in beasts of burden. A decoction of the root in water, relaxes contractions of the joints, and cures gout and similar mal- adies. It is applied raw to burns, but it must be frequently changed, so as not to let it dry (Plinius, 79).
- 11. Research Paper Chambers 11 A physician from Nero’s army named Dioscoride lists marijuana in his pharma- copeia. Shortly after that, Greek physicians prescribed marijuana as well from 130-200. In the year 200, The First Pharmacopeia of The East was published, listing marijuana as an analgesic and in that same year it was used by a Chinese surgeon named Hua T’o for that purpose. “Hua Tuo, Wade-Giles romanization Hua T’o(flourished c. late second century CE–early third century), Chinese physician and surgeon who is best known for his surgical operations and the use of mafeisan, an herbal anesthetic formulation made from hemp”. (encyclopediabritannica.com, 2014). History suggests that the Far East was and has been ahead of the West when it comes to using nature as medicine. However, in 1964, an Israeli physician and Hebrew professor named, Dr. Raphael Mechoulam had made a discovery that would change the future of marijuana. This wasn’t easy though. Since the US led prohibition of marijuana, other countries followed suit. In 1963, Dr Mechoulam had used his friendship with one of the top investigators of the national police in Israel to give him some samples for his research. They gave him several kilos of seized Lebanese hashish, not knowing what it would be used for. Hashish and cannabis have the same 480 chemicals but are processed differently(Le- ichman, 2012). Mechoulam discovered cannabidiol or CBD with what was given to him. The following year the good doctor was the first to synthesize one other main ingredient in marijuana, delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol or THC. After this discovery and through col- laborative research with other scientist, we now know that THC (known for its psychoac- tive qualities), is used to be a key ingredient that activates certain chemicals and reacts with receptors. Protecting against illnesses and helping with symptoms, such as nau- sea, and pain is something that humans have know for many years.
- 12. Research Paper Chambers 12 According to an article on the website leafscience.com, in 1982, Dr. Mecholaum was quoted saying that if marijuana were legal, it would immediately replace 10-20% of all pharmaceutical medicines. In 1988 he identified the binding sites in rats brains for cannabinoids. Dr. Mechoulam’s lab also made history in 1992, when one of his col- leagues became the first to discover a THC-like chemical in the brain called anan- damide (based on the sanskrit for “complete joy”)(emedicine.medscape.com, 2015). The same group discovered in 1995 the second known endocannabinoid in the human body called, 2-Arachidonoylglycerol or 2-AG. Anandamide is found primarily in the brain and 2-AG is found in the central nervous system and in more abundance in the brain than AEA. One can see why they call Dr Mechoulam the father of cannabinoid re- search. So now we know that the ECS consists of receptors and ligands. The receptors are CB-1 and CB-2 and the ligands are AEA or anandamide and 2-AG or 2-Arachi- donoylglycerol. This helps break down the structures and with the advancement of technologies, we may discover how these receptors and ligands interact with each other and other chemicals of the body. First of all, what is a cannabinoid? Better yet, what is an endocannabinoid? Where does this word come from? To know this, we must look back to Dr Mecholaum’s re- search to really understand what these are. Dr Mecholaum discovered THC and how it interacts with the human body. He found that THC binds with specific receptors in the brain that he dubbed CB-1 R (cannabinoid receptor type 1). Later he found more of these and a second type or CB-2 R. So, since then the classification of ligands that in- teract with the CB-1 and CB-2 receptors have been called cannabinoids.
- 13. Research Paper Chambers 13 The body produces its own ligands that bind to these receptors. This has been found true in rats as well as humans. The idea is that all animals produce their own in- ternal cannabinoid structures. Endo is the scientific or Latin word for internal, so an en- docannabinoid refers to ligands that work similarly to cannabinoids found in marijuana or the cannabis plant. What is a ligand? According to the Gene Homes Reference website, “A ligand is a protein that attaches (binds) to another protein called a receptor; receptor proteins have specific sites into which the ligands fit like keys into locks. Endogenous ligands are those that are produced in the body, not those introduced into the body, such as certain drugs (ghr.nlm.nih.gov, 2015). Our bodies produce several different types of ligands. There are two classes of ligands (endocannabinoids); there are the cannabinoid ago- nists (promote CB-1R and CB-2R affects) and cannabinoid antagonists (blocks the CB- 1R and CB-2R affects). The main ligands in focus, are anandamide or AEA and 2-AG. Anandamide is an agonist and is found in the Central Nervous System, specifically, the brain. However, it is found in the peripheral organs like the liver and pancreas as well. The name comes from the sanskrit word ananda, meaning “joy, bliss or delight” and amide. This particular ligand, has been shown to influence appetite regulation, mood, pleasure, and even the aiding of digestion in rat studies, giving it more potential for pharmaceutical purposes. Research is showing that anandamide levels are increased during female ovulation and correlates positively with estradiol and gonadotrophin levels, making scientists think that these two processes regulate the levels of anandamide. In 1996, anandamide was found in chocolate along with two other substances that mimic anandamide’s effects.
- 14. Research Paper Chambers 14 Researchers also found anandamide and other endocannabinoids in the fruit fly which was previously thought to have too small of a structure to house them. 2-AG or 2-Arachidonoylglycerol is found abundantly in the central nervous system. 2-AG is an antagonist ligand that needs to be more studied. 2-AG is found to be 200 times more prevalent in the human brain than AEA. The highest concentrations were found in the brainstem, medulla, limbic forebrain, striatum, and hippocampus and the lowest in the cortex, diencephalons, mesencephalon, hypothalamus, and cerebel- lum. It is an ester, like anandamide, formed from the omega-6 fatty acid arachidonic acid and glycerol. “Unlike anandamide, it is present at relatively high levels in the central nervous system; it is the most abundant molecular species of monoacylglycerol found in mouse and rat brains (~5-10 nmol/g tissue). Detection of 2-AG in brain tissue is compli- cated by the relative ease of its isomerization to 1-AG during standard lipid extraction conditions. It has been found in maternal bovine and human milk.”(wikipedia.com, 2015). Similar to anandamide, it is found to inhibit the bodies immune system, pain management, and inflammatory processes. It is also believed to have a neuroprotective role. In rats, research shows that induced closed head injuries, the levels of 2-AG is in- creased; also, giving higher doses shows a reduction of inflammation and overall ede- ma and a reduction in cell death. All of these traits are leading into the pharmaceutical application and syn- thesizing of the ligands in cannabis such as THC, and the ligands in our ECS. There have been a few pharmaceuticals available in the US and abroad for treatment of ail- ments like HIV. Dronabinol (Marinol) is a synthetic THC and is a CB-1R and CB-2R ag- onist that is approved by the Food and Drug Administration that is used for cancer pa-
- 15. Research Paper Chambers 15 tients during chemotherapy as an antiemetic (anti-nausea) and appetite stimulant. Some have reported that the feelings are not the same as with cannabis; however, the outcomes are similar. Nabilone (Cesamet) is a synthetic analogue of THC; it is a CB1-R and CB2-R receptor agonist that has been FDA approved as an antiemetic in chemo- therapy patients in whom all other therapy has failed. Unapproved use is employed in patients with upper motor neuron syndrome who have spasticity-related pain not con- trolled by conventional treatment. Another Pharmaceutical company named Sanofi is developing a drug called Rimonabant (Acomplia or Zimulti) which is a selective CB1-R antagonist, with the primary role of centrally acting CB1-R. Rimonabant was sold in Eu- rope for the treatment of obesity. Due to depression as a side affect, the drug was not approved by the FDA in 2007, who cited that the French company did not show that the drug was safe for sales in the US. There has been a list of studies listed on the National Center for Biotechnology Information website and others that suggest cannabinoids found in marijuana have po- tential healing properties as well as the therapeutic uses. Extending pre-clinical research on cannabis-attributable immunomodula- tion, this study's CRP [inflammation marker] evidence points toward possible anti-inflammatory effects of cannabis smoking. More definitive evidence can be derived by combining pre-clinical research, studies of patients, and epidemiolog- ical research approaches.(NCBI, 2014). There are studies of induced disc degeneration that show that Cannabidiol (CBD), a ligand found in cannabis, has neuroprotective properties and inflammatory re-
- 16. Research Paper Chambers 16 duction elements. Here is one explanation of the specific study listed on the National Library of Medicine. Disc degeneration is a multifactorial process that involves hypoxia, inflam- mation, neoinnervation, accelerated catabolism, and reduction in water and gly- cosaminoglycan content. Cannabidiol is the main non-psychotropic component of the Cannabis sativa with protective and anti-inflammatory properties…The ef- fects of intradiscal injection of cannabidiol (30, 60 or 120 nmol) injected immedi- ately after lesion were analyzed acutely (2 days) by MRI. The experimental group that received cannabidiol 120 nmol was resubmitted to MRI examination and then to histological analyses 15 days after lesion/cannabidiol injection. The needle puncture produced a significant disc injury detected both by MRI and his- tological analyses. Cannabidiol significantly attenuated the effects of disc injury induced by the needle puncture. Considering that cannabidiol presents an ex- tremely safe profile and is currently being used clinically, these results suggest that this compound could be useful in the treatment of intervertebral disc degen- eration.(nbi.nlm.nih.gov, 2014) Cannabidiol (CBD) also improves functions and reduces inflammation of lungs in mice with acute lung injuries. The study listed in National Library of Medicine shows when lipopolysaccharide is injected into the airway of mice and then treated with CBD administered by injection into their abdomen, there are great improvements with reduc- tion of inflammation. The study concluded with the following statement, ”Therefore the present and previous data suggest that in the future cannabidiol might become a useful therapeutic tool for the attenuation and treatment of inflammatory lung diseases.”
- 17. Research Paper Chambers 17 Cannabinoids are used in treatment of rare forms of epilepsy that do not respond to conventional medications. Charlotte’s Web is a medication made from cannabis plants and administered in liquid form or what is called hash oil. Its popular name refers to Charlotte Figi, the child with Dravet syndrome (a rare form of epilepsy) whose who was having up to 100 seizures per day and no relief from any standard pharmaceutic. As soon as she took her first dose, her parents claim that they could see instantly that she was better. Her seizures were reduced to only one a day. Charlotte’s web is grown in Colorado by the Stanley brothers and sold in their dispensary in Colorado Springs. GW Pharmaceuticals, a British company, has developed a medication as well, called Epidiolex, also taken in liquid form as a tincture or oil. It is high in CBD and contains no detectable THC. GW Pharmaceuticals has obtained per- mission from the Food and Drug Administration to make Epidiolex available as an Investigational New Drug (IND) by application from physicians wishing to prescribe it. Currently about a dozen physicians across the United States have submitted such IND applications to the FDA; none are in Colorado. GW Phar- maceuticals plans to conduct clinical trials using Epidiolex later this year. (epilepsycolorado.org,2014) Today, the internet is full of information. When one types in the search menu for Cannabis vs Cancer, or what does cannabis do to cancer cells, there are alarming claims that cannabis sativa cures cancer. Is this true? There is some resounding evi- dence pointing to the science that proves the agonist THC and antagonist CBD tend to bind to the CB-1 and CB-2 receptors in cancer cells and reprogram them to self de- struct. There was one particular site that explains it well and describes it in words that
- 18. Research Paper Chambers 18 most can comprehend. Biochemist Dennis Hill who has worked in cancer research for ten years and claims to have cured his own cancer states the following on his website. In every cell there is a family of interconvertible sphingolipids that specifi- cally manage the life and death of that cell. This profile of factors is called the “Sphingolipid Rheostat.” If endogenous ceramide(a signaling metabolite of sphingosine-1-phosphate) is high, then cell death (apoptosis) is imminent. If ceramide is low, the cell is strong in its vitality…The cancer cell dies, not be- cause of cytotoxic chemicals, but because of a tiny little shift in the mitochondria. Within most cells there is a cell nucleus, numerous mitochondria (hundreds to thousands), and various other organelles in the cytoplasm. The purpose of the mitochondria is to produce energy (ATP) for cell use. As ceramide starts to ac- cumulate, turning up the Sphingolipid Rheostat, it increases the mitochondrial membrane pore permeability to cytochrome c, a critical protein in energy syn- thesis. Cytochrome c is pushed out of the mitochondria, killing the source of en- ergy for the cell. There is not much material to either prove or disprove his allegations; however, one could admire the journey he has taken. There are other scholarly studies that show similar effects. One study from the National Library of Medicine titled “Inhibition of glioma growth in vivo by selective activation of the CB(2) cannabinoid receptor” involves the most malignant types of cancer cells with some strong supporting evidence. The cannabinoid being used is a pharmaceutical grade called JWH-133 and is available at a price of 10 mg for $235.00. The study concluded that there is support a therapeutic ap-
- 19. Research Paper Chambers 19 proach for the treatment of malignant gliomas devoid of psychotropic side effects. JWH- 133 is a CB-2 receptor agonist and it does not do anything to the CB-1 receptors. Curiosity asks, is marijuana safe for consumption? If one were to look that question up on the internet, webmd.com states that other than the well know side effects one should feel, like unsteady gate, memory loss, dry mouth, and increased appetite to name a few, there is little evidence to show what long terms effects are other than what some research has shows to be increase in depression and possibly psychosis. “There is some evidence that occasional pot smoking can have harmful effects on the body, al- though the science is still too new to prove anything.”(webmd.com, 2015) "We're learning new things every day," says Matthew J. Smith, PhD, a research assistant professor at the Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine. "Before we can really understand the effects of marijuana, further research is needed.”(webmd.- com, 2015) It is virtually impossible to overdose on marijuana or at least there has never been an overdose death linked to using marijuana. New research is finding the results and it is very interesting. In rats given high doses of THC their brains in turn, produce higher levels of a brain hormone called pregnenelone which reacts with the same receptors and lowers or reduces the actions of THC. Webmd study author is quoted with the fol- lowing; “When the brain is stimulated by high doses of THC, it produces pregnenolone – a 3,000 percent increase – that inhibits the effects of THC.” According to author William Breathes from the West Word marijuana is less lethal than nicotine.
- 20. Research Paper Chambers 20 For THC, there are varying figures, ranging from 1,260 milligrams of THC per kilogram of body weight down to 666 mg/kg. Even going with the lowest fig- ure, a 175-pound man would have to consume more than 53 whole grams of pure THC all at once. And pure THC isn't something you are going to find in even the purest shatter oils and waxes produced. If we're talking commercially pro- duced edibles, then you would probably die from an overdose of salt (3,000 mg/ kg) or sugar (1,100 mg/kg) before even coming close to the threshold for mari- juana. Need more perspective? Caffeine has an LD50 of 192 mg/kg, and nicotine is around 60 mg/kg. Alcohol doesn't necessarily have an LD50 that translates well, but if just .4 percent of your roughly 160 ounces of blood contains booze, you're not likely to wake up. Even synthetic, marijuana-derived pharmaceuticals have higher LD50 ratings than natural marijuana. So, marijuana is essentially safer than most food products? To put it into other terms, one would have to smoke approximately 1,500 pounds, in 15 minutes, in or- der to produce a lethal reaction. Another thing, the CB1 receptors are found primari- ly in the brain and have not been any found in the brainstem. The part of the body that controls breathing and circulation. So, the effects of TCH don't reach the vital organs and nerve centers that control life.
- 21. Research Paper Chambers 21 The relationship between humans and marijuana have been symbiotic for thou- sands of years and some say civilization was started with marijuana cultivation. Mar- ijuana has been revered as a way to reduce the amount of prescription drug use throughout the world and shows strong evidence that it could help heal many people throughout. The raw form of marijuana has been used in the past for medicinal pur- poses and with newer research, has been shown to interact with the human body like no other substance on the planet. The endocannabinoid system was discovered because of the research into cannabis sativa and THC. One might think that the more scientist learn about the different ligands in and out of the body, the better the chances look for furthering the health of our species. Jeremy Chambers
- 22. Research Paper Chambers 22 Bibliography "A History of Medical Cannabis Research and the Endocannabinoid System." YouTube. YouTube. Web. 17 Feb. 2015. <https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bK0ZDkRcG58>. Web. 13 Feb. 2015. <https://hempshopper.com/es/hemp-history-ce/133-77-79-ce>. "Cannabis and the Endocannabinoid System - Part 1." YouTube. YouTube. Web. 12 Mar. 2015. An interesting video that gives a non bias view into the cannabinoid research. The host is a physician and has his Ph D and MD. Gives insight as to the details about the process of cannabinoid production in the plant and gives molecular and genome ap- proach. "Cannabis Cures Cancer." Cannabis Cures Cancer. Web. 7 Feb. 2015 Rick Simpson the author of his own journey gives his personal story from diagnoses to complete remission using only cannabis oil. Has become a sort of Hallmark and re- source for many who are looking for safe alternative treatment of cancer. “Dear Stoner: How Much THC Equals a Lethal Dose?” Westword. 17 July 2014. Web. 4 April 2015. The article gives the reader real numbers and perspective on the US government’s own data on the safety of cannabis compared to other food products. "Dennis Hill: Bio Chemist Cured His Prostate Cancer Using Cannabis Oil (MORE"En- dogenous Ligands Gene Family." Genetics Home Reference. Web. 4 Mar. 2015.
- 23. Research Paper Chambers 23 This is another great source though it is not a peer reviewed study, showing the per- sonal stories and testament of the curing capabilities on cannabis agains cancer. “Endocannabinoids ." Endocannabinoids. Web. 7 Feb. 2015. <http://emedicine.med- scape.com/article/1361971-overview>. A well done peer reviewed article that gives conclusions to studies and detailed infor- mation on the background and current information on the endocannabinoid system. "Epilepsy/Seizure Disorder." Medical Marijuana. Web. 3 Mar. 2015. A peer reviewed study showing the correlations between the seizure patient’s relief of symptoms and the anti convulsion acts of the cannabis plant material. "How Cannabis Oil Works to Kill Cancer." Www.CureYourOwnCancer.org. Web. Though there is some advertisement on the web page this is a personal testament from a medical patient who had brain cancer and beat it with cannabis oil after all other conventional medicine failed. "Hua Tuo | Biography - Chinese Physician and Surgeon." Encyclopedia Britannica On- line. Encyclopedia Britannica. Web. 8 Feb. 2015. <http://www.britannica.com/ EBchecked/topic/1530857/Hua-Tuo>. Informative documentation giving the reader a better understanding that cannabis has been used in ancient China for medicinal purposes for thousands of years and specifi- cally with Hua Tuo and the Pharmacy he created. "JWH 133." Tocris Bioscience. Web. 25 Feb. 2015. " National Center for Biotechnology Information. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Web. 5 Mar. 2015
- 24. Research Paper Chambers 24 This site shows many peer reviewed studies in rats who cannabinoids have certain anti-inflammatory effects and how they interact with cancer cells and other diseases. PACHER, PÁL, SÁNDOR BÁTKAI, and George Kunos. "The Endocannabinoid System as an Emerging Target of Pharmacotherapy." Pharmacological Reviews. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Web. 12 Feb. 2015. <http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/ PMC2241751/>. A vast source of peer reviewed studies for different diseases and ailments in relation to the treatments in rats using cannabis or cannabinoids more specifically. "Scientist Who Discovered THC Receives Honorary Degree." Leaf Science. 5 Dec. 2013. Web. 17 Feb. 2015. <http://www.leafscience.com/2013/12/05/scientist-discov- ered-thc-receives-honorary-degree/>. Gives more credibility to the physician who began the studies into THC and the recep- tors that bind. Gives the reader a better understanding of the pioneering research that has begun to change the way people think about marijuana. ”The Israeli Pharmacologist Who Kick-started Marijuana Research." ISRAEL21c. 13 May 2012. Web. 16 Feb. 2015. <http://www.israel21c.org/people/the-israeli-pharma- cologist-who-kick-started-marijuana-research/>. An article that asks Dr. Mecholaum about his history from his perspectives that give the reader a true insight as to what his opinions about the cannabis plant. "The 10,000-year World History of Hemp and Cannabis." The 10,000-year World His- tory of Hemp and Cannabis. Web. 14 Feb. 2015. <http://www.advancedholis- tichealth.org/history.html>.
- 25. Research Paper Chambers 25 A large collaboration of historical events marking the relationship between hu- man beings and the cannabis plant. "WE UNDERSTAND A PATIENT'S NEEDS." AbbVie. Web. 8 Mar. 2015. A look from the Pharmaceutical company’s own website that shows the compounds, side effects and purpose of the drugs that are produced. "2-Arachidonoylglycerol." Wikipedia. Wikimedia Foundation. Web. 3 Mar. 2015. Open source that gives details of the structure of the endocannabinoids to help relate them to every day life. "5 New Cannabis Discoveries That You Won’t Hear About in the Corporate Media." Waking Times. Web. 2 Mar. 2015. Another eye opener that helps the reader understand that there are many new discov- eries happening almost daily.
