Revision for Test #1
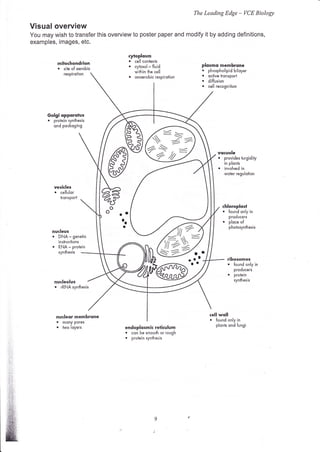
- 1. The Leading Edge - VCE Biology Visual overview You may wish to transfer this overview to poster paper and modify it by adding definitions, examples, images, etc. cytoplosm mitochondrion o cell conlents . . cytosol - fluid plosmo membr<rne site of oerobic within the cell o phospholipid biloyer respirotion . onoerobic respirotion o octive tronsport . diffusion . cell recognition vqcuole o provides turgidily in plonts . involved in woier regulotion vesicles . cellulor konsport chloroplost o found only in producers . 4r ?j ploce of pholosynhesis nucleus . ,: o DNA - genetic inskuctions RNA - proiein synhesis )u2> S7: / ribosomes . found only in producers r protein nucleolus synthesis nucleor membrone cell woll . mony Pores . found only in . h,vo loyers endoplosmic reticulum plonts ond fungi . cqn be smoolh or rough o protein synthesis
- 2. - VCE Biology The Leading Edge a The chemical nature of i cell .ig . The cell theory states that all living things are made up of cells, that the cell is the -s smallest living unit, and that new cells are made from pre-existing cells. . lil . The structure of a cell depends on its specific function, but most cells have a few basic t:t .3 things in common. All contain DNA within the cytoplasm, all of which is then enclosed :'E :,,i by'a plasma membrane. ::,* . There are two main cell types: r prokaryotic cells (bacteria and cyanobacteria) do not contain membrane-bound ,'lj . organelles. The DNA is a single chromosome in the shape of a ring =fj . eukaryotic cells have many different membrane-bound organelles within the { cytoplasm, including a nucleus that contains several strand-like chromosomes. 3 Comparison of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Eukaryote Prokaryote mitochondrion endoplasmic ribosome iell membrane reticulum Four elements, carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O) and nitrogen (N), make up 99% of all organisms by weight. Atoms are the basic unit of all matter. Molecules are two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds, and compounds are molecules containing more than one atomic element. Organic compounds always contain carbon, and most also contain hydrogen. Molecules that do not contain carbon are inorganic compounds. Some very simple compounds containing carbon are also considered to be inorganic. lmportant inorganic molecules include water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, nitrogen and minerals. Atoms within a molecule are bound together by strong forces called atomic bonds. The different properties of these bonds determine how the molecules move and interact within the cell. Write definitions for the following words: DNA prokaryote inorganic compound cytoplasm eukaryote organic compound plasma membrane lnorganic molecules Water . Most living organisms are about 70-90% water. . Water is very cohesive (interconnected), has a high heat capacity (good at limiting heat transfer) and is an excellent solvent for polar molecules. Oxygen and carbon dioxide . Oxygen is needed to release energy from food molecules (in respiration). . Carbon dioxide is the main source of carbon for organic compounds (by photosynthesis). l0
- 3. The Leading Edge - VCE Biology Nitrogen o Nitrogen is 'fixed'from the atmosphere (by bacteria in the soil or plant roots) into compounds that can be used by other organisms. Minerals . Small amounts of various minerals are used with organic molecules, e.g. enzymes. Organic molecules Large organic molecules made up of chains of many smaller sub-units (monomers) are called biomacromolecules or polymers. Carbo hydrates/polysacch arides . most abundant organic compounds in nature o major source of chemical energy . energy stores for plants and animals, e.g. starch and glycogen respectively o used in structural components of cells o part of DNA and RNA . combine with lipids and proteins to make membranes. Carbohydrates are made up of C, H and O. ln simple carbohydrates, the general formula is Cn(H2O)r, e.g. glucos€ CoHrzOo. The sub-units of carbohydrates are monosaccharides, 'single sugars' (e.9. glucose, galactose and fructose). Disaccharides, 'two sugars', are formed when two monosaccharides are joined together and a molecule of water lost. Polysaccharides, 'many sugars', are long chains or polymers of sugar sub-units. Lipids . non-polar (charge not separated) hydrophobic (water-hating) molecules . fats and oils store energy o phospholipids are essential components of membranes . steroids (hormones and vitamins) are made from lipids Lipids are made up of C, H and O. The sub-units are fatty acids, both unsaturated (one or more double carbon bonds) and saturated (all single carbon bonds, maximum possible hydrogen atoms in the molecule). Double bonds cause permanent kinks or bends in the fatty acid chain. Mono-unsaturated fats have only one double bond, while polyunsaturated fatty acids have two or more double bonds. The more double bonds, the more bends or kinks in the chain. This means the molecules cannot pack tightly together, and so space is left between molecules. This is what gives membranes their permeability. Compound lipids can also contain phosphorus and nitrogen. Phospholipids are hydrophilic (water-loving) at the phosphorus end and hydrophobic at the lipid end. Basic structures of carbohydrates and lipids Carbohydrates @@€ Lipids three monosaccharide disaccharide molecules of fatty ,, acids ' fatty acid polysaccharides 11
- 4. The Leading Edge - VCE Biology Write definitions for the following words: polymers hydrophobic unsaturated monosaccharides hydrophilic saturated disaccharides phospholipids fatty acids polysaccharides Proteins . 20 common amino acid sub-units . enzymes are catalysts (speed up the rates of reactions without being a part of the reaction itself) for cellular reactions . hormones communicate information around the body . carrier molecules such as haemoglobin . form channels in membranes . also involved in the storage and transport of other molecules within and between cells All proteins contain C, H, O and N. Some also contain phosphorus, sulfur or other elements. The protein sub-units are called amino acids. The bonds between amino acids are called peptide bonds, and proteins are also called polypeptides. There are four levels describing the structure of proteins: . Primary - Ihe actual sequence of amino acids . Seco ndary - pleating or coiling of the chain held together by hydrogen bonds between different amino acids . Tertia4T - folding into a three-dimensional shape, usually globular or fibrous . Quaternary - when two or more polypeptide chains join together to make a complex molecule. Nucleic acids o gen€tic material of all organisms . DNA - deoxyribonucleic acid, carries 'instructions' for building proteins . RNA - ribonucleic acid, involved in polypeptide synthesis. The sub-units of nucleic acids are nucleotides. There are only five different nucleotides in nucleic acids, and they are distinguished by their bases - adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), thymine (T) and uracil (U). Adenine, cytosine and guanine are found in both DNA and RNA. Thymine is found only in DNA, and uracil is found only in RNA. ln DNA, sequences of bases are called genes. Multiple genes are carried in chains called chromosomes. The nucleotides are organised into triplet codes or codons, which translate into amino acids. The sequence of these amino acids determines the protein that is synthesised. The proteins then determine all inherited characteristics of the organism. . DNA nucleotides join in chains with distinctive ends because each nucleotide has a phosphate group, a five-carbon sugar and one of the following nitrogen bases: o purines - double-ring bases o ff - adenine r G - guanine . pyrimidines - single-ring bases o | - thymine o Q - cYtosine Complementary base pairing between A-T (double hydrogen bond) and G-C (triple hydrogen bond) forms the 'rungs' of the 'twisted ladder' appearance of the double helix. An organism's genome contains all of its genes. The proteome is the entire complement of structural and functional proteins that are coded for by the genome. 12
- 5. The Leading Edge - VCE Biology Basic structure of proteins and nucleic acids Proteins Nucleic acids phosphate Q nucleotide _"__-l_ _ sugar @ I bases (four types) AI o l I A amino acid subunits e FrIl CI r F.r,l Write definitions for the following words: amino acid DNA triplet codes enzymes RNA codons catalysts nucleotides genes peptide bonds bases genome polypeptides chromosomes proteome anic molecule summa Main Type Sub-units Complex product Example elements Carbohydrate c,H,o saccharides polysaccharides sucrose fatty acids Lipid c,H,o and oils saturated fats vegetable oil Protein C,H,O,N amino acids polypeptide enzyme Nucleic acid C,H,O,N,P nucleotides often genes DNA Organelles and membranes Membranes . Possibly the most important part of a cell, the plasma membrane (also called the cell membrane) selectively regulates movement of substances into and out of a cell. Most organelles are also enveloped in membranes. . Membranes create separate compartments within the cell, keeping different functioning centres and substances apart and controlling the movement of substances between the different compartments. . Many chemical reactions occur in, on or around membranes. . Plasma membranes are involved in cell recognition and intercellular communication, both electrically and chemically . Plasma membranes consist of a bilayer (double layer) of phospholipids with their hydrophobic ends together (see diagram on page 14), as well as carbohydrates and proteins. The bilayer of phospholipids is impermeable to water-soluble or polar substances 13
- 6. VCE Biologlt .( Plasma membrane carbohydrates cell adhesion pump protein - protein glycoProtein - active transport recognition phospholiPid bilayer m;il lofcell I p.,t,u" diffusion cholesterol and osmosis Most of the different types of molecules within a bilayer can move around to a varying extent. The fluid-mosaic model explains this movement. Gholesterol is between the layers of phospholipids, making the structure more stable by preventing the molecules from moving around too much. Cholesterol prevents the membrane from breaking down and decreases permeability to polar molecules. Only found in animal cells. of a cell Permeable structure providing support to cell; only in plants (cellulose), some Cellwall protists, prokaryotes (murein) and fungi (chitin). Organelle Function Centrioles Microtubules involved in separating chromosomes during cell division. Chloroplast Contains chlorophyll and is the site of photosynthesis. Cytoplasm Contents of the cell apart from the nucleus. Cytosol Fluid component of the cytoplasm. Endoplasmic Membrane network linked with plasma membrane and other membrane-bound reticulum organelles. Produces, packages, stores and transports materials within the cell. (ER) cqn be rough (associated with ribosomes, RER)or smooth (without ribosomes, SER). Abundant in cells that actively synthesise and secrete enzymes. Golgi Linked to endoplasmic reticulum. synthesises and packages proteins into apparatus vesicles. Lysosomes Vesicles containing strong enzymes that break down cell debris and foreign matter. Mitochondria Site of cellular respiration to release energy for the cell to use. Nucleus Double-membrane bound organelle with pores allowing movement between the nucleus and cytoplasm. Contains genetic material (DNA). Plasma Bilayer of phospholipids controlling movement of substances into and out of the membrane cell. Also responsible for recognition, adhesion and chemical communication between cells. Ribosomes Synthesise proteins; often associated with endoplasmic reticulum. Vacuole membrane in plants. Regulates movement of substances into and out of Tonoplast vacuole. Membrane-bound fluid spaces, varying in size and number depending on cell Vacuoles type. Provide turgidity (support) in plants, or involved with digestion and water balance. Vesicles Membrane-bou nd organelles involved in transportation of substances. I4
- 7. The Leading Edge - VCE Biolog Write definitions for the following words: phospholipid bilayer cholesterol fluid-mosaic model organelle Synthesis of biomolecules . The largest organelle in the cell is usually the nucleus, and most cells only have one. Some cells, such as red blood cells, lose their nucleus after maturity. The nucleus has a double-layered nuclear envelope containing many nuclear pores through which many substances can pass. . The nucleolus is the only visible structure within the nucleus in a non-dividing cell. Nucleoli are rich in RNA and proteins and are the site of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) synthesis. There can be more than one nucleolus in the nucleus. . The instructions for building enzymes and other proteins are in the DNA. This means all cell maintenance and functions are regulated and controlled by the DNA in the nucleus. Messenger RNA (mRNA)and rRNA, produced in the nucleus, pass out through the nuclear pores into the cytoplasm. . mRNA and rRNA bind with ribosomes and start protein synthesis. Amino acids are added one at a time in the sequence outlined by the mRNA translation of the DNA. Enzymes produced by free ribosomes usually function within the cytoplasm. Ribosomes bound to endoplasmic reticulum, RER, usually produce proteins that are used in membranes or are packaged into vesicles for export from the cell. Packaging and transport of biomolecules . Fats, phospholipids and steroids are synthesised by SER. SER is abundant in the cells of steroid-secreting organs such as the testes and adrenal gland. . The Golgi apparatus also packages polysaccharides and creates lysosomes, which are membrane-bound vesicles budded off the Golgi apparatus. They contain enzymes that are used to break down debris in the cell. Reusable material diffuses back into the cytoplasm from the lysosomes, while unwanted material is expelled by exocytosis. Gonstruction, packaging ER is composed of interconnecting cisternae (membrane sacs) and branching tubes that are attached to the nuclear membrane. The internal cavity, the lumen, contains enzymes and proteins that metabolise, synthesise and process other molecules. They ensure that proteins have the correct 3-D shape and regulate the calcium concentration in the cytoplism. 2 As the proteins are synthesised, they pass into the lumen and then on to the Golgi apparatus. Here they are further modified; carbohydrates and proteins are added to form glycoproteins. 3 The proteins are then packaged into vesicles, which fuse with the plasma membrane and release their contents into the intercellular space by exocytosis. 15