Mark Davess KS3 history schemes of work (basic)
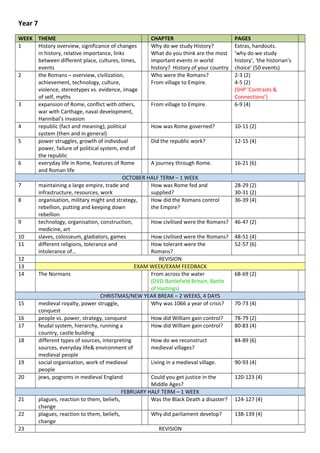
- 1. Year 7 WEEK THEME CHAPTER PAGES 1 History overview, significance of changes in history, relative importance, links between different place, cultures, times, events Why do we study History? What do you think are the most important events in world history? History of your country Extras, handouts. ‘why do we study history’, ‘the historian’s choice’ (50 events) 2 the Romans – overview, civilization, achievement, technology, culture, violence, stereotypes vs. evidence, image of self, myths Who were the Romans? From village to Empire. 2-3 (2) 4-5 (2) (SHP ‘Contrasts & Connections’) 3 expansion of Rome, conflict with others, war with Carthage, naval development, Hannibal’s invasion From village to Empire. 6-9 (4) 4 republic (fact and meaning), political system (then and in general) How was Rome governed? 10-11 (2) 5 power struggles, growth of individual power, failure of political system, end of the republic Did the republic work? 12-15 (4) 6 everyday life in Rome, features of Rome and Roman life A journey through Rome. 16-21 (6) OCTOBER HALF TERM – 1 WEEK 7 maintaining a large empire, trade and infrastructure, resources, work How was Rome fed and supplied? 28-29 (2) 30-31 (2) 8 organisation, military might and strategy, rebellion, putting and keeping down rebellion How did the Romans control the Empire? 36-39 (4) 9 technology, organisation, construction, medicine, art How civilised were the Romans? 46-47 (2) 10 slaves, colosseum, gladiators, games How civilised were the Romans? 48-51 (4) 11 different religions, tolerance and intolerance of… How tolerant were the Romans? 52-57 (6) 12 REVISION 13 EXAM WEEK/EXAM FEEDBACK 14 The Normans From across the water (DVD-Battlefield Britain, Battle of Hastings) 68-69 (2) CHRISTMAS/NEW YEAR BREAK – 2 WEEKS, 4 DAYS 15 medieval royalty, power struggle, conquest Why was 1066 a year of crisis? 70-73 (4) 16 people vs. power, strategy, conquest How did William gain control? 78-79 (2) 17 feudal system, hierarchy, running a country, castle building How did William gain control? 80-83 (4) 18 different types of sources, interpreting sources, everyday life& environment of medieval people How do we reconstruct medieval villages? 84-89 (6) 19 social organisation, work of medieval people Living in a medieval village. 90-93 (4) 20 jews, pogroms in medieval England Could you get justice in the Middle Ages? 120-123 (4) FEBRUARY HALF TERM – 1 WEEK 21 plagues, reaction to them, beliefs, change Was the Black Death a disaster? 124-127 (4) 22 plagues, reaction to them, beliefs, change Why did parliament develop? 138-139 (4) 23 REVISION
- 2. 24 EXAM WEEK/EXAM FEEDBACK 25 Medieval civilisation, culture and architecture. (DVD-How We Built Britain – The East: A New Dawn) EASTER BREAK – I WEEK, 1 DAY 26 Islamic Empire, Saudi Arabia, overview. Connecting empires. Arabia before Islam. 154-155 156-157 27 Conditions, life and culture of Arabian peninsula. Life of Muhammad, seeds of Islam. Arabia before Islam. Muhammad and Islam: the role of the individual. 158-159 160-161 28 Rise of Islam, Quran, belief and philosophy of Islam. Muhammad and Islam: the role of the individual. 162-165 29 Islam after Muhammad, organisation and legacy. Trade, international connections. How did Islam survive the death of Muhammad? How important were trade and travel? 166-167 180-181 MAY HALF TERM – 1 WEEK 30 Trade, international connections. How important were trade and travel? 182-185 31 Belief, philosophy, rules, diversity, tolerance. Were people religious in the Islamic world? 186-189 32 Medicine, scientific knowledge, organisation, civilisation. Were Muslims healthy? 190-193 33 Crusades, relations with Europe and Christianity. Crusades or invasions? 194-197 34 Crusades, relations with Europe and Christianity. Crusades or invasions? 198-201 35 REVISION 36 EXAM WEEK/EXAM FEEDBACK 37 Islamic influences in the western and further world, consequences in the Islamic world. Who benefited from the Crusades? 204-207 SCHOOL YEAR ENDS- SUMMER BREAK Year 8 WEEK THEME CHAPTER PAGES 1 History overview, significance of changes in history, relative importance, links between different place, cultures, times, events Why do we study History? What do you think are the most important events in world history? History of your country Extras, handouts. ‘why do we study history’, ‘the historian’s choice’ (50 events) 2 Overview of life and social structure in 1500s. England in the 1500s 2-7 (SHP “Societies in Change”) 3 Beliefs and culture in the early modern period. Private Lives 16-21 4 Religious belief, Catholic Church. Religious conflict and persecution, Henry VIII and his conflict with the church. Was the Catholic Church still healthy in 1500? Henry VIII: Catholic or Protestant? 26-27 28-29 5 Attack on monasteries, reformation, changes in belief. Religious struggle, persecution, punishment. Henry VIII: Catholic or Protestant? Bloody Queen Mary? 30-31 32-33 6 Changes in church practice and factors behind them. The Reformation in English villages. 34-35
- 3. Gunpowder plot Were the Catholics framed? 36-37 OCTOBER HALF TERM – 1 WEEK 7 England leading up to civil war: King & Parliament, money & taxes, religion, Scotland, Ireland, etc., etc. Why did civil war break out in 1642? 42-45 8 England leading up to civil war: King & Parliament, money & taxes, religion, Scotland, Ireland, etc., etc. Why did civil war break out in 1642? 46-49 9 Combat and consequences, daily lives, beliefs, perceptions and prejudices. What was life during the Civil War? 52-55 10 Battle, strategy, circumstance. Why did the Royalists lose at Marson Moor? 56-57 11 Assessment of King, judicial process and politics behind it, execution Why did the English execute their King? 58-61 12 Deeper assessment of King and his role/situation/perception of him Charles the martyr or Charles the traitor? 62-63 13 REVISION 14 EXAM WEEK/EXAM FEEDBACK 15 (DVD-Battlefield Britain: Battle of Naseby) CHRISTMAS/NEW YEAR BREAK – 2 WEEKS, 4 DAYS 16 Rise of Cromwell, battle of Drogheda, Rump Parliament. What kind of man was Oliver Cromwell? 64-65 17 Protectorate, government What kind of man was Oliver Cromwell? 66-67 18 Civil and social upheaval, new political movements The world turned upside down. 68-69 19 Restoration of monarchy, new political structure. James II – the same old story? 70-71 20 Scientific discovery, changes in perception Science & superstition. 78-79 21 Growth, life, conditions in London, plague, Great Fire How did London change? 84-87 FEBRUARY HALF TERM – 1 WEEK 22 Louis XVI and Marie Antoinette, regime in France, estates system Was France well-governed before the revolution? 100-103 23 Complex relations and influences of various estates What was life like before the Revolution? 104-109 24 REVISION 25 EXAM WEEK/EXAM FEEDBACK 26 (DVD-Battlefield Britain, Battle of Culloden) EASTER BREAK – I WEEK, 1 DAY 27 1787-89: triggers and events, power shifts between estates, organisation, revolts, Declaration of the Rights of Man and Citizen Why did revolution erupt in 1789? 114-117 28 Changes in organisation, government, church, sharing of power, rights, women’s situation Did the Revolution make France a fairer country? 118-121 29 Assessment of King and his role, judicial process, execution, comparison with Charles I Why did the French execute their King? 128-131 30 Consolidation and enforcing of revolution, mass executions, effect on people Was the Terror necessary? 132-137 MAY HALF TERM – 1 WEEK
- 4. 31 Attitudes and reactions to the revolution Did French people support the revolution? 140-143 32 Robespierre: life, character, assessment of and reaction to actions Robespierre: hero or villain? 144-145 33 1799: Napoleon’s coup Coup d’etat! 146-149 34 Comparison of regimes, situation under Napoleon Did Napoleon betray the Revolution? 150-153 35 Napoleon’s wars, Europe Why was Napoleon defeated? 156-159 36 Napoleon’s wars, Europe, Russia, downfall Why was Napoleon defeated? 160-163 37 EXAM WEEK/EXAM FEEDBACK 38 Consequences and remnants of ideas and practices from time of the French Revolution The legacy of the French Revolution (+video/dvd?) 166-167 SCHOOL YEAR ENDS- SUMMER BREAK Year 9 WEEK THEME CHAPTER PAGES 1 History overview, significance of changes in history, relative importance, links between different place, cultures, times, events Why do we study History? What do you think are the most important events in world history? History of your country Extras, handouts. ‘why do we study history’, ‘the historian’s choice’ (50 events) 2 General overview of changes in culture, work, transport, population and health and medicine. Britain 1750-1900: What changed? 2-7 (SHP “Peace & War”) 3 Business: production, sales, markets, infrastructure, investment. Why did businesses grow? 8,9 4 Iron industry, development of a business (strategy) The Darbys of Coalbrookdale. 10-11 5 Factory conditions, child labour Children in the mills 16-19 6 Improving conditions for workers, trade unionism, early socialist ideas Robert Owen: a better way to run a factory 20,21 7 Combination of invention and enterprise: starting, developing and running a factory business; appearance of factory machinery Boulton & Watt: who was more important? 22-25 OCTOBER HALF TERM – 1 WEEK 8 Changes in agricultural practice How did farmers produce more food? 26-29 9 Raw materials: requirements and delivery. Transport and trade. Did Britain have the raw materials it needed? Changing transport. 30,31 40,41 10 International empire, goods and trade, slave trade overview. Empire and trade. 42-45 11 Work, systems of production, life of workers. Was there an industrial revolution? A tale of two families. 48,49 50,51 12 Changes in work and life due to development of iron industry. How did Merthyr Tydfil change? 56-58 13 REVISION 14 EXAM WEEK/EXAM FEEDBACK 15 (DVD-How We Built Britain – The North: Full Steam Ahead) CHRISTMAS/NEW YEAR BREAK – 2 WEEKS, 4 DAYS
- 5. 16 Overview of 19th century culture What are Victorian values? 64-66 17 Slavery, slave trade, imperialism, treatment of other races. Were the British racist? 70,71 18 Slavery, slave trade, imperialism, treatment of other races. Were the British racist? 72-75 19 Various campaigns against slavery and the people behind them. Factors behind abolition. Why was slavery abolished? 82-85 20 Electoral systems and features of them, changes over the last 2 centuries. Trying to get the vote 86-89 21 Motives behind attitudes to electoral reform, aspects of the system and pros and cons, fighting for change. Trying to get the vote 88-91 FEBRUARY HALF TERM – 1 WEEK 22 Campaigning for electoral reform, context, motives, protests, conflicts. Were the Chartists revolutionaries? 92-95 23 Victorian working conditions, workers organisation and striking for their rights. Women lead the way 98-99 24 REVISION 25 EXAM WEEK/EXAM FEEDBACK 26 (Video-The Story of Wales – Episode 4: Furnace of change) EASTER BREAK – I WEEK, 1 DAY 27 20th century overview, evaluating significance, pre war tension and build-up to and triggers of the Great War Introduction: Now that’s what I call important. 1.2 Why did the Great War happen? 2-4 (“The Twentieth Century” by Christopher Culpin) 10-11 28 War conditions and casualties 1.3 What happened on the battlefields? 29 Recruitment, propaganda, public attitudes, situation of women 1.4 What happened on the home front? 16,17,20-23 30 Build-up to WWII 1.5 From war to war. 24-30 MAY HALF TERM – 1 WEEK 31 WWII: overview of combat 2.2 A ‘World War’? 42-45 32 Pacific war with Japan, Hiroshima & Nagasaki bombings 2.4 Why did the Americans drop the first atomic bomb? 46-51 33 Nazi genocide 2.5 Why did the Holocaust happen? 52-57 34 Post-war recovery and changes 2.6 How did the Second World War change the world? 58-62 35 Cold War overview 3.2 What was the Cold War? 66-71 36 Cuban Missile Crisis 3.3 Thirteen days of dread. 72-77 37 EXAM WEEK/EXAM FEEDBACK 38 Reform/collapse of Soviet Union 3.5 Mikhail Gorbachev: success or failure. Conclusion 84-85 88-89 SCHOOL YEAR ENDS - SUMMER BREAK
- 6. 16 Overview of 19th century culture What are Victorian values? 64-66 17 Slavery, slave trade, imperialism, treatment of other races. Were the British racist? 70,71 18 Slavery, slave trade, imperialism, treatment of other races. Were the British racist? 72-75 19 Various campaigns against slavery and the people behind them. Factors behind abolition. Why was slavery abolished? 82-85 20 Electoral systems and features of them, changes over the last 2 centuries. Trying to get the vote 86-89 21 Motives behind attitudes to electoral reform, aspects of the system and pros and cons, fighting for change. Trying to get the vote 88-91 FEBRUARY HALF TERM – 1 WEEK 22 Campaigning for electoral reform, context, motives, protests, conflicts. Were the Chartists revolutionaries? 92-95 23 Victorian working conditions, workers organisation and striking for their rights. Women lead the way 98-99 24 REVISION 25 EXAM WEEK/EXAM FEEDBACK 26 (Video-The Story of Wales – Episode 4: Furnace of change) EASTER BREAK – I WEEK, 1 DAY 27 20th century overview, evaluating significance, pre war tension and build-up to and triggers of the Great War Introduction: Now that’s what I call important. 1.2 Why did the Great War happen? 2-4 (“The Twentieth Century” by Christopher Culpin) 10-11 28 War conditions and casualties 1.3 What happened on the battlefields? 29 Recruitment, propaganda, public attitudes, situation of women 1.4 What happened on the home front? 16,17,20-23 30 Build-up to WWII 1.5 From war to war. 24-30 MAY HALF TERM – 1 WEEK 31 WWII: overview of combat 2.2 A ‘World War’? 42-45 32 Pacific war with Japan, Hiroshima & Nagasaki bombings 2.4 Why did the Americans drop the first atomic bomb? 46-51 33 Nazi genocide 2.5 Why did the Holocaust happen? 52-57 34 Post-war recovery and changes 2.6 How did the Second World War change the world? 58-62 35 Cold War overview 3.2 What was the Cold War? 66-71 36 Cuban Missile Crisis 3.3 Thirteen days of dread. 72-77 37 EXAM WEEK/EXAM FEEDBACK 38 Reform/collapse of Soviet Union 3.5 Mikhail Gorbachev: success or failure. Conclusion 84-85 88-89 SCHOOL YEAR ENDS - SUMMER BREAK
