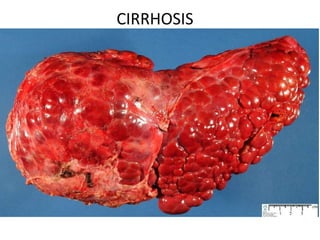
Cirrhosis
- 1. CIRRHOSIS
- 2. • Cirrhosis is a condition that is defined histopathologically. characterised by: Development of fibrosis Architectural distortion Formation of regenerative nodules • This results : Decrease in hepatocellular mass, and thus function, Alteration of blood flow.
- 4. • Patients who have cirrhosis have varying degrees liver function Stable, Compensated cirrhosis Decompensated cirrhosis. • Patients who have developed complications of their liver disease and have become decompensated should be considered for liver transplantation
- 5. Causes • • • • • • Alcoholic Cirrhosis(50%) Chronic viral Hepatitis Autoimmune hepatitis Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis Biliary cirrhosis Cardiac cirrhosis • • • • • Hemochromatosis Wilson's disease Alpha 1 Antitrypsin deficiency Cystic fibrosis Cryptogenic cirrhosis
- 6. Symptoms • Patient may present with complications of chronic liver disease: o Ascites o Edema, o Upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage o Jaundice o Encephalopathy.
- 7. Signs • The liver and spleen may be enlarged, with the liver edge being firm and nodular. • Scleral icterus, • Palmar erythema • Spider angiomas • Parotid gland enlargement, • Fetor Hepaticus. • Digital clubbing, white nails. • muscle wasting, • Edema and ascites. • Dupuytrens Contracture, Flapping tremors. • Men may have decreased body hair and gynecomastia as well as testicular atrophy, • In women with advanced alcoholic cirrhosis, menstrual irregularities usually occur. • Kayser Fleischer rings should be looked for in all young cirrhotics.
- 8. Investigations • Laboratory tests may be completely normal in patients with early compensated cirrhosis. • Decreased Serum Albumin Levels may be the only abnormality. • Bilirubin (may remain normal),aminotransferases and prothrombin time may rise with progressing disease. • ALP is elevated in patients with biliary cirrhosis. • Platelet counts are often reduced early in the disease. • Ultrasonography is the most informative and least costly imaging technique.
- 9. Model for End stage Liver Disease. MELD Score = 3.78[serum bilirubin (mg/dL)] + 11.2[Ln INR] + 9.57[serum creatinine (mg/dL)] + 6.43. 3 month Mortality • • • • • 40 or more — 71.3% mortality 30–39 — 52.6% mortality 20–29 — 19.6% mortality 10–19 — 6.0% mortality <9 — 1.9% mortality
- 10. Child Pugh Score Measure Total bilirubin, (mg/dl) 1 point 2 points 3 points (<2) (2-3) (>3) Serum albumin, g/dl >3.5 2.8-3.5 <2.8 PT INR <1.7 1.71-2.30 > 2.30 Ascites None Mild Moderate to Severe Hepatic encephalopathy None Grade I-II (or suppressed with medication) Grade III-IV (or refractory) Points 5-6 7-9 10-15 Class A B C One year survival 100% 81% 45% Two year survival 85% 57% 35%
- 11. Alcoholic Liver Disease. • Cause several different types of chronic liver disease: 1. alcoholic fatty liver, 2. alcoholic hepatitis, alcoholic 3. cirrhosis. Chronic alcohol use can produce fibrosis in the absence of accompanying inflammation and/or necrosis(80 g/day for 10 to 20 years). • A unique form of hemolytic anemia (with spur cells and acanthocytes) with hyperlipoproteinaemia called Zieve's syndrome can occur in patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis. • The underlying cause is liver delipidization, that can occur during withdrawal from prolonged alcohol abuse. • AST levels are higher than ALT levels, usually by a 2:1 ratio.
- 12. Treatment • Abstinence of alcohol is the cornerstone of therapy • In patients for Discrimination Fraction. >32, there is improved survival at 28 days with the use of glucocorticoids. The DF is calculated as the serum total bilirubin plus the difference in the patient's prothrombin time compared to control (in seconds) multiplied by 4 • Oral Pentoxifylline, which decreases the production of tumor necrosis factor (TNF-) and other proinflammatory cytokines. • Inhibitors of TNF- such as infliximab or etanercept.; however, there was no clear-cut improvement in survival. • Anabolic steroids, • Propylthiouracil, • Aantioxidants, • Colchicine, • penicillamine have all been used but do not show clear-cut benefits and are not recommended.
- 13. Cirrhosis Due to Chronic Viral Hepatitis B or C • Several clinical trials demonstrated that patients with decompensated liver disease can become compensated with the use of antiviral therapy directed against hepatitis B • Interferon should not be used in cirrhotics. • Treatment of patients with cirrhosis due to hepatitis C is a little more difficult because the side effects of pegylated interferon and ribavirin therapy are oftentimes difficult to manage. • If patients can tolerate treatment, and if it is successful, the benefit is great and disease progression is reduced.
- 14. Autoimmine hepatitis • Many patients with autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) present with cirrhosis that is already established. • Patients will not benefit from immunosuppressive therapy with because the AIH is "burned out.“ • Diagnosis is supported by (ANA) or anti-smooth-muscle antibody (ASMA). • When patients with AIH present with cirrhosis and active inflammation accompanied by elevated liver enzymes, there can be benefit from the use of immunosuppressive therapy.[ Glucocorticoids and Azathioprine]
- 15. Biliary Cirrhosis. • Biliary cirrhosis has pathologic features that are different from other forms of cirrhosis. o o o o Cholate stasis; Copper deposition; Xanthomatous transformation of hepatocytes; Irregular, so-called biliary fibrosis • Due to Abnormal bile retention: intrahepatic and extrahepatic.
- 16. The major causes of chronic cholestatic syndromes are • Primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC), • Autoimmune cholangitis (AIC), • Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC), • Idiopathic adulthood ductopenia
- 17. Primary Biliary Cirrhosis • Strong female preponderance • The cause is unknown • A median age of around 50 years at the time of diagnosis. • Portal inflammation and necrosis of cholangiocytes in small- and medium-sized bile ducts. • Antimitochondrial antibodies (AMA) are present in about 90% of patients with PBC
- 18. • Most patients are actually asymptomatic • Fatigue out of proportion to the severity of the liver disease • Pruritus is seen 50% of patients and it can be debilitating…usually is most bothersome in the evening. • Hyperpigmentation, xanthelasma, and xanthomata, which are related to the altered cholesterol metabolism seen in this disease. • There is an increased incidence of osteopenia and osteoporosis in patients with cholestatic liver disease, and bone density testing should be performed
- 19. • UDCA (15 mg/kg/day)has been shown to slow the rate of progression of PBC, but it does not reverse or cure the disease. • Pruritus is treated with antihistamines, naltrexone, and rifampin. • Plasmapheresis has been used rarely in patients with severe intractable pruritus. • Bisphosphonate should be instituted when bone disease is identified.
- 20. Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Characterized by diffuse inflammation and fibrosis involving the entire biliary tree. Fatigue, pruritus, steatorrhea, deficiencies of fat-soluble vitamins. As in PBC, the fatigue is profound and nonspecific. Metabolic bone disease is also seen. • • • (p-ANCA), is positive in about 65% of patients with PSC Over 50% of patients with PSC also have ulcerative colitis The definitive diagnosis of PSC requires cholangiographic imaging. is the first choice] [MRCP There is no specific proven treatment for PSC, although studies are currently ongoing using high-dose (20 mg/kg per day) UDCA to determine its benefit. Endoscopic dilatation of dominant strictures can be helpful. Cholangiocarcinoma can develop, which is a contraindication to Liver transplantation.
- 22. • Portal hypertension • • • • • Gastroesophageal varices Portal hypertensive gastropathy Splenomegaly, hypersplenism Ascites Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis • Hepatorenal syndrome • • • • • • Type 1 Type 2 Hepatic encephalopathy Hepatopulmonary syndrome Portopulmonary hypertension Malnutrition
- 23. • Coagulopathy • • • Factor deficiency Fibrinolysis Thrombocytopenia • Bone disease • • • Osteopenia Osteoporosis Osteomalacia • Hematologic abnormalities • • • • Anemia Hemolysis Thrombocytopenia Neutropenia
- 24. Portal Hypertension • Portal hypertension is defined as the elevation of the hepatic venous pressure gradient (HVPG) to >5 mmHg. It is a result of: • (1) increased intrahepatic resistance to the passage of blood flow through the liver due to cirrhosis and regenerative nodules • (2) increased splanchnic blood flow secondary to vasodilation within the splanchnic vascular bed • The three primary complications of portal hypertension are 1. Gastroesophageal varices with hemorrhage, 2. Ascites, and 3. Hypersplenism
- 25. Esophageal varices • Approximately one-third of patients with histologically confirmed cirrhosis have varices. • The majority of patients with cirrhosis will develop varices over their lifetimes. • One-third of patients with varices will develop bleeding. • TREATMENT: • (1) Primary prophylaxis • (2) Prevention of re-bleeding once there has been an initial variceal hemorrhage.
- 26. • Primary prophylaxis requires routine screening by endoscopy of all patients with cirrhosis. • Once varices that are at increased risk for bleeding are identified, primary prophylaxis can be achieved 1. Through nonselective beta blockade or 2. variceal band ligation
- 27. Variceal haemorrage. • Treatment of Acute bleeding requires both fluid and blood-product replacement as well as prevention of subsequent bleeding with EVL. • The use of vasoconstricting agents, usually somatostatin or Octreotide. • Balloon tamponade can be used in patients who cannot get endoscopic therapy immediately or who need stabilization prior to endoscopic therapy • Endoscopic intervention is employed as first-line treatment to control bleeding acutely. • When bleeding continues from gastric varices, consideration for transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) should be made. • Encephalopathy can occur in as many as 20% of patients after TIPS
- 28. Prevention of rebleed • This usually requires repeated variceal band ligation until varices are obliterated. • Despite successful variceal obliteration, many patients will still have portal hypertensive gastropathy from which bleeding can occur. • Nonselective beta blockade may be helpful to prevent further bleeding from portal hypertensive gastropathy once varices have been obliterated.
- 29. Splenomegaly and Hypersplenism. • Congestive splenomegaly is common in patients with portal hypertension. • Splenomegaly itself usually requires no specific treatment. • Hypersplenism with the development of thrombocytopenia is a common feature of patients with cirrhosis . • It is usually the first indication of portal hypertension.
- 30. Ascites .
- 31. • Patients usually have at least 1–2 L of fluid in the abdomen before they are aware that there is an increase. • When patients present with ascites for the first time, it is recommended that a diagnostic paracentesis be performed to characterize the fluid. • In patients with cirrhosis, the protein concentration of the ascitic fluid is quite low, with the majority of patients having an ascitic fluid protein concentration <1 g/dL • When the gradient between the serum albumin level and the ascitic fluid albumin level is >1.1 g/dL, the cause of the ascites is most likely due to portal hypertension
- 32. Treatment. • Sodium Restriction : ingest <2 g of sodium per day, which is the recommended amount. • Traditionally, spironolactone at 100–200 mg/d as a single dose is started, and furosemide may be added at 40–80 mg/d. • spironolactone can be increased to 400–600 mg/d and furosemide increased to 120–160 mg/d. • If ascites is still present with these dosages of diuretics in patients who are compliant with a low-sodium diet, then they are defined as having refractory ascites.
- 33. Managing refractory ascitis. o Repeated large-volume paracentesis,+ Albumin Infusion. o TIPS procedure should be done . It does not improve survival in these patientsbe considered . Unfortunately, TIPS is often associated with an increased frequency of hepatic encephalopathy. • The prognosis for patients with cirrhosis with ascites is poor, and some studies have shown that <50% of patients survive 2 years after the onset of ascites.
- 34. Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis • Spontaneous infection of the ascitic fluid without an intraabdominal source. • Bacterial translocation is the presumed mechanism. • SBP can occur in up to 30% of individuals and can have a 25% in-hospital mortality rate. • The most common organisms are Escherichia coli and other gut bacteria; however, gram-positive bacteria, including Streptococcus viridans, Staphylococcus aureus, and Enterococcus sp., can also be found.
- 35. • The diagnosis of SBP is made when the fluid sample has an absolute neutrophil count >250/μL. • If more than two organisms are identified, secondary bacterial peritonitis due to a perforated viscus should be considered. • Treatment is with a second-generation cephalosporin, with cefotaxime being the most commonly used antibiotic • In patients with variceal hemorrhage, the frequency of SBP is significantly increased, and prophylaxis against SBP is recommended. • Furthermore, in patients who have had an episode(s) of SBP and recovered, once-weekly administration of antibiotics is used as prophylaxis for recurrent SBP.
- 36. Hepatoernal Syndrome. • Form of functional renal failure without renal pathology that occurs in about 10% of patients with advanced cirrhosis or acute liver failure. • There is marked disturbance in the arterial renal circulation in patients with HRS. • There is reduction in systemic vascular resistance • The reason for renal vasoconstriction is most likely multifactorial • HRS is often seen in patients with refractory ascites and requires exclusion of other causes of acute renal failure
- 37. • Type 1 HRS is characterized by a progressive impairment in renal function and a significant reduction in creatinine clearance within 1–2 weeks of presentation. • Type 2 HRS is characterized by a reduction in glomerular filtration rate with an elevation of serum creatinine level, but it is fairly stable and is associated with a better outcome than that of Type 1 HRS. • Patients are treated with midodrine, an -agonist, along with octreotide and intravenous albumin. • The prognosis is poor unless transplant can be achieved within a short period of time.
- 38. Hepatic Encephalopathy. • Broadly defined as an alteration in mental status and cognitive function occurring in the presence of liver failure. • Gut-derived neurotoxins that are not removed by the liver because of vascular shunting and decreased hepatic mass get to the brain and cause the symptoms . • The correlation between severity of liver disease and height of ammonia levels is often poor. • Other compounds that may contribute to the development of encephalopathy include certain false neurotransmitters and mercaptans.
- 39. Precipitating events : • Hypokalemia, • Infection, an • Increased dietary protein load, • Electrolyte disturbances. • If patients have ascites, this should be tapped to rule out infection. • In patients presenting with encephalopathy, asterixis is often present
- 40. • Hydration and correction of electrolyte imbalance. • Restrtiction of dietary protien is discouraged. • There may be some benefit to replacing animal-based protein with vegetable-based protein. • The mainstay of treatment, is to use lactulose, a nonabsorbable disaccharide, which results in colonic acidification, contributing to the elimination of nitrogenous products in the gut that are responsible for the development of encephalopathy. The goal of lactulose therapy is to promote 2–3 soft stools per day. • Poorly absorbed antibiotics are often used as adjunctive therapies . • Rifaximin at 550 mg twice daily has been very effective without the known side effects of neomycin (oto, nephrotoxicity) or metronidazole(peripheral neuropathy). • Zinc supplementation is sometimes helpful
- 41. Malnutrition in Cirrhosis • Poor dietary intake, • Alterations in gut nutrient absorption, • Alterations in protein metabolism. • Dietary supplementation for patients with cirrhosis is helpful in preventing patients from becoming catabolic.
- 42. Abnormalities in coagulation. • There is decreased synthesis of clotting factors and impaired clearance of anticoagulants. • Patients may have thrombocytopenia from hypersplenism due to portal hypertension. • Platelet function is often abnormal in patients with chronic liver disease, in addition to decreases in platelet levels due to hypersplenism.
- 43. Bone disease in Cirrhosis • Osteoporosis is common in patients with chronic cholestatic liver disease because of malabsorption of vitamin D and decreased calcium ingestion. • Dual x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) is a useful method for determining osteoporosis or osteopenia. • Treatment should be administered with bisphosphonates that are effective at inhibiting resorption of bone
- 44. Hematological Abnormalities. ANEMIA from a variety of causes including o hypersplenism, o hemolysis, o iron deficiency o folate deficiency from malnutrition. • Macrocytosis is a common abnormality. • Neutropenia may result as a result of hypersplenism.
- 45. Hepatopulmonary syndrome • Hepatopulmonary syndrome is a syndrome of shortness of breath and hypoxemia) caused by vasodilation in the lungs of patients with liver disease. • Platypnoea is a peculiar feature. • Results from the formation of microscopic intrapulmonary arteriovenous dilatations in patients with both chronic and acute liver failure. • Increased hepatic production or decreased hepatic clearance of vasodilators, possibly involving nitric oxide.
- 46. Thank You.
