PNEUMATIC
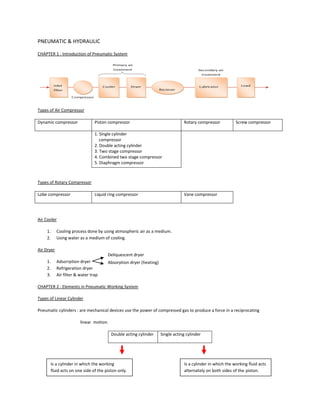
- 1. PNEUMATIC & HYDRAULIC CHAPTER 1 : Introduction of Pneumatic System Types of Air Compressor Dynamic compressor Piston compressor Rotary compressor Screw compressor 1. Single cylinder compressor 2. Double acting cylinder 3. Two stage compressor 4. Combined two stage compressor 5. Diaphragm compressor Types of Rotary Compressor Lobe compressor Liquid ring compressor Vane compressor Air Cooler 1. Cooling process done by using atmospheric air as a medium. 2. Using water as a medium of cooling. Air Dryer Deliquescent dryer 1. Adsorrption dryer Absorption dryer (heating) 2. Refrigeration dryer 3. Air filter & water trap CHAPTER 2 : Elements in Pneumatic Working System Types of Linear Cylinder Pneumatic cylinders : are mechanical devices use the power of compressed gas to produce a force in a reciprocating linear motion. Double acting cylinder Single acting cylinder Is a cylinder in which the working Is a cylinder in which the working fluid acts fluid acts on one side of the piston only. alternately on both sides of the piston.
- 2. Cushioning in Pneumatic System To decelerate a cylinder's piston before it strikes the end cap. Reducing the piston velocity and reduces vibration transmitted to the machine structure. Mounting Cylinder Standard cylinders are not designed to absorb the load from the piston side. The cylinder must be fitted with care and precision to ensure that the load movement parallel and balanced with the center line of the cylinder. Type of mounting cylinder. Mounting directly (Direct) • Cylinder mounted directly to the front surface of the rod Mounting Threads (Threaded Neck) • Cylinder fitted with lock nuts that are on the front of the cylinder. Mounting Legged (Foot Mount) • Cylinder mounted horizontally by installing two feet in front and behind the cylinder. Suspension Mounting Rear (Rear Flange) • Cylinder mounted on the back of the keyboard. Front Suspension Mounting (Front Flange) • Cylinder mounted on the front of the keyboard. Oscillation Mounting Rear (Rear Clevis) • Cylinder mounted on the front of the joints that can swing. Trunnion Mounting • Mounting hinge mounted on the center of the cylinder to allow it swing
- 3. Valve Methods of how the valve is moved Figure Symbol Human Moved by the operator by means of pressing the button provided. Mechanical Valve is actuated by a mechanical mechanism such as wheeled switch and the cylinder rod. Pneumatic Valve is actuated by the compressed air that act to move the position of wind channel. Electrical Valve is actuated by a solenoid powered by electricity. CHAPTER 3 : Pneumatic Circuit Design CYLINDER NUMEROUS CONTROL For operating multi-cylinder sequence control circuit below, there are two action pneumatic cylinder rod is moved or controlled will take turns using the aid of pneumatic components.
- 4. TIME MOTION DIAGRAM Figure movement time (RGM) or "Time Motion Chart", can describe a sequence of two or more cylinders are moved automatically. BUIDING CIRCUIT WITH CASCADE METHOD To build a counter circuit step, you need a step counter module consists of valve 3/2 and valve AND. It has 6 points of connection as pictured below. WARNING! You must draw a counter module form in step 3.9 diagram below so as not to confuse the counter circuit construction step.
- 5. CHAPTER 4 : Hydraulic Component
- 7. CHAPTER 5 : Basic Hydraulic Circuit To perform a useful task a hydraulic simple circuit consists of a group of parts such as pumps, actuators (motors and cylinders), control valves and conductors (pipe and hoses).Hydraulic simple circuit is categorized into 2 types: open center and closed center. The type of circuit is usually designated by directional control valves. The basic design of an open circuit Simple design with a fixed displacement pump, fixed displacement motor and cylinder block. Direction of stroke and output are on one side. A direction control valve (10) and bi-directional motor (3) was included in the system. By direction control valve the movement of the actuators could be changed. The basic design of a close circuit This type of hydraulic system comprises a variable displacement pump and motor with interconnecting hydraulic lines. The flow rate and direction of flow is controlled by the pump swivel angle. The motor may swivel on one side of centre and is also adjustable. Two relief valves were added in hydraulic system. Their function ensures maximum pressure and also protecting the system against overload.
- 8. CHAPTER 6 : Hydraulic Circuit Design Bleed-off speed control Bleed-off circuits do not work with a running-away load. When using a bleed-off circuit with a running-away load, use the counterbalance circuit. Notice that a bypass check valve forces fluid through an adjustable orifice just before it enters the actuator. With a meter-in circuit, fluid enters the actuator at a controlled rate. The action of meter-out flow controls is smooth and steady in hydraulic circuits. meter-out flow controls are controlling the load on a down-acting vertical cylinder.
- 9. Diaphragm type Accumulators Diaphragm type Accumulators Operations Bladder type Accumulators
- 10. Operations Bladder Type Accumulators
