Knee 2
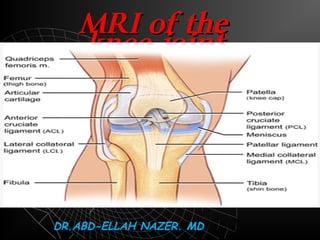
- 1. MRI OF THE KNEE JOINT. Dr/ ABD ALLAH NAZEER. MD.
- 2. Clinical Indication Acute pain secondary to trauma in the presence of an effusion without fracture on x-ray. Suspected unstable knee with history of knee locking or positive McMurray test on examination. Suspected stable meniscus tear following treatment with analgesia and physiotherapy and activity modification for at least 4 weeks in the presence of persistent joint effusion or history of locking Suspected cruciate ligament injury with a history of knee giving way and laxity of between 5 and 11mm) on examination grade II-III instability (medial laxity between 5 and 11mm on examination. Suspected multi-ligamentous or lateral collateral ligament injury when there is grade II-III instability Suspected medial collateral ligament injury with grade II-III instability despite treatment with brace and activity modification for at least 6 weeks Other knee conditions of unknown etiology when there are both symptoms and signs that suggest a significant underlying injury and when knee x-ray is non-diagnostic for the etiology of the underlying condition
- 3. Knee - AP View
- 4. Lateral View
- 6. Protocol of examination Axial T1 localizer Sagittal T1, PD, T2 Coronal gradient echo, STIR If contrast is injected [ Axial, Sagittal ,coronal T1 WIs ]
- 7. How to know the pulse sequence?! T1 T2 Gradient STIR Upper EgyptLower Egypt
- 8. Items to be evaluated Where?! Menisci (medial & lateral) Ligaments - Cruciate (ACL, PCL) - Collateral - Retinacular Tendons ( Quadriceps, Patellar) Bones Synovial effusion Sagittal PD Coronal. Sagittal,coronal and axial. Coronal Axial Sagittal PD Sagittal T1& T2 Sagittal T2
- 9. Anatomy of the meniscus.
- 10. Meniscus Medial meniscus Semilunar - shaped Posterior horn wider, longer, taller than anterior horn Posterior horn tightly attached to the capsule
- 11. Lateral meniscus C- shape Posterior and anterior horns are symmetric Anterior horn may be hypo plastic, extremely thin Discoid meniscus and meniscal cysts more common
- 12. AC B A B C
- 13. Lateral meniscus
- 14. Medial meniscus
- 15. Medial and lateral meniscus.
- 17. Medial and lateral meniscusMedial and lateral meniscus..
- 23. Proton density coronal image shows the normal medial collateral ligament as a thin, taut, well-defined, low-signal structure extending from the medial femoral epicondyle to the medial tibial metaphysis
- 24. Coronal and sagittal proton density image demonstrating the normal lateral collateral ligament in its entirety, from the femoral condyle origin to the fibular head insertion.
- 26. Simple Tear Complex Tear Type II Type I Normal
- 27. Types of Meniscal degenerationTypes of Meniscal degeneration Grade IGrade I Grade IIGrade II Meniscal frayingMeniscal fraying
- 28. Tear
- 29. Grade 1 degeneration. Grade 11 degeneration
- 30. Meniscal degeneration with free edge fraying.
- 31. Meniscal degeneration with free edge fraying
- 33. Types of Meniscal TearsTypes of Meniscal Tears SimpleSimple ComplexComplex Special typesSpecial types
- 34. Simple Meniscal TearSimple Meniscal Tear HorizontalHorizontal VerticalVertical RadialRadial
- 36. Horizontal tear
- 37. Horizontal tear
- 38. Horizontal tear
- 40. Vertical tear Occurs typically in the outer 1/3 of the posterior horn or body of the meniscus ]rare in the anterior horn[
- 41. Vertical tear
- 42. Vertical tear
- 47. Full thickness body radial tear
- 48. Marching cleft sign in discoid lateral meniscus indicates radial meniscal tear
- 49. Meniscal radial tear (arrow).
- 50. Vertical radial meniscal tear in the mid-body lateral meniscus. (A) A sagittal fat-suppressed proton-density image shows a vertical tear (arrow) of the central edge of the lateral meniscus, oriented perpendicular to the curvature of the meniscus. Note the superimposed horizontal tear of the anterior horn. (B) A coronal fat-suppressed T2-weighted image shows the same tear with truncation of the central meniscal margin (arrow).
- 51. Radial tear of lateral meniscus.
- 53. Vertical tear of the free edge of the meniscus [Root tear[ Ghost meniscus
- 54. Ghost meniscus If there is no history of Meniscal surgery and the posterior horn is absent near the intercondylar notch
- 57. Special Meniscal TearsSpecial Meniscal Tears FlapFlap Bucket handleBucket handle MC separationMC separation
- 58. Flap tear:displaced horizontal or longitudinal tears
- 59. Flap tear [Oblique[ Should have tow components , horizontal and Vertical common in the medial meniscus
- 60. Flap tear.
- 61. Bucket handle tearBucket handle tear
- 62. Small sized posterior horn [ sagittal[ Medially displaced fragment[ coronal[ Double PCL sign ]sagittal[
- 64. Bucket Handel tearBucket Handel tear
- 65. Bucket Handel tearBucket Handel tear
- 66. Flipped meniscus : Double Delta Sign Bucket Handel tear , Lateral meniscus
- 67. Flipped meniscus : Double Delta Sign
- 68. Flipped meniscus : Double Delta Sign
- 69. Flipped meniscus : Double Delta Sign
- 70. Parrot beak tear (displaced radial oblique tear(.
- 72. Post-traumatic contusion of the lateral femoral and tibial condyles
- 74. Discoid meniscus Dysplastic meniscus with loss of normal semi lunar shape. 50%or more coverage of the tibial plateau. Meniscal body segment seen in 3 or more sagittal images
- 77. Meniscal cyst A Cyst extending from a meniscal tear Common sites : Anterior horn LM , Posterior horn MM
- 78. Meniscal cyst
- 79. Meniscal cyst
- 85. In closed MRI scanner,In closed MRI scanner, magic angle artifact canmagic angle artifact can be found in one locationbe found in one location:: The up-sloping of theThe up-sloping of the posterior horn lateralposterior horn lateral meniscusmeniscus.. In open, vertical field magnets, magic angle artifact will be found in two locations: 1)1(junction of anterior horn and body of meniscus and 2)2(junction of posterior horn and body of meniscus
- 86. Normal intrameniscal signal evolution in the site of surgery, with very good final result.
- 87. Normal healing sequence. Typical worsening in the first scans - intrameniscal signal after surgery is worse then before surgery. No healing disturbance.
- 88. Abnormal healing of degenerated meniscus.
- 89. Ligamentous Lesions ACL PCL Collateral Retinacular
- 92. MRI shows the normalMRI shows the normal linear low signal intensitylinear low signal intensity ACL adjacent to theACL adjacent to the lateral bony wall of thelateral bony wall of the upper intercondylar notchupper intercondylar notch (arrow). The normal ACL(arrow). The normal ACL moves away from the wallmoves away from the wall and diverges into multipleand diverges into multiple fascicles on more distalfascicles on more distal imagesimages.
- 93. Anterior cruciate ligament Posterior cruciate ligament
- 94. Primary signs [ In the ligament ] Total discontinuity Abnormal signal Abnormal configuration Abrupt angulation Wavy appearance Abnormal axis Anterior cruciate ligament injury Intercondylar roof
- 95. Anterior cruciate ligament injury
- 96. Anterior cruciate ligament injury.
- 97. Normal ACL
- 98. Normal ACL Non visualization of the ACL with a cloud of edema and hemorrhage
- 99. Secondary signs [ Outside the ligament ] • Blumensaat angle sign. • Bone contusions [Pivot- shift bruises ] • Anterior translocation of the tibia • Uncovered meniscus sign • Avulsion fracture of the tibial insertion • Segond fracture 70-100% with ACL tear • PCL buckling • PCL line sign Anterior cruciate ligament injury Hyperextension ACL tear withHyperextension ACL tear with "kissing bone bruises"kissing bone bruises."."
- 100. Negative Blumensaat angleNegative Blumensaat angle..
- 101. Positive Blumensaat anglePositive Blumensaat angle..
- 102. ACL Graft with negative Blumensaat angleACL Graft with negative Blumensaat angle..
- 103. The probability of anThe probability of an ACL tear is very highACL tear is very high if both such boneif both such bone bruises are present,bruises are present, only slightly lower ifonly slightly lower if the tibial bone bruisethe tibial bone bruise is present in isolation,is present in isolation, and still slightlyand still slightly lower with anlower with an isolated femoral boneisolated femoral bone bruise of thisbruise of this appearance.appearance.
- 105. Anterior tibial translocation with” uncovered meniscus sign”
- 106. Segond fractureSegond fracture.. An elliptical verticallyAn elliptical vertically 3x10mm bone3x10mm bone fragment parallel to thefragment parallel to the lateral tibial cortex,lateral tibial cortex, about 4mm distal toabout 4mm distal to the plateau. Best seenthe plateau. Best seen on AP or tunnelon AP or tunnel radiographic viewsradiographic views 75-100%association with ACL tear
- 107. Segond fracture inSegond fracture in patient with ACLpatient with ACL tear. T1- weightedtear. T1- weighted coronal MRI shows acoronal MRI shows a small, low-signalsmall, low-signal elongated fractureelongated fracture fragment that isfragment that is parallel to the lateralparallel to the lateral tibia. The associationtibia. The association of Segond fracturesof Segond fractures with ACL tearswith ACL tears approaches 100%.approaches 100%.
- 108. ACL injury
- 109. +ve PCL LINE SIGN
- 110. PCL redundancy as a secondary sign of ACL tear. This is a relativelyPCL redundancy as a secondary sign of ACL tear. This is a relatively unreliable secondary sign of ACL tear.unreliable secondary sign of ACL tear.
- 111. Partial ACL tearPartial ACL tear Common about 10-43% of ACL tearsCommon about 10-43% of ACL tears Suboptimal accuracy of MRISuboptimal accuracy of MRI Subtle 1ry and 2ry signsSubtle 1ry and 2ry signs Focal angulationsFocal angulations Focal increase T2 signalFocal increase T2 signal [[non specificnon specific ]] Single bundle signSingle bundle sign Sagittal MRI shows an abruptlySagittal MRI shows an abruptly angulated mid-ACL (arrow) .A wavy orangulated mid-ACL (arrow) .A wavy or sharply angulated appearance issharply angulated appearance is abnormal.abnormal.
- 112. T1-weighted sagittalT1-weighted sagittal MRI shows a normal-MRI shows a normal- appearing ACL.appearing ACL. Partial ACL tear T1-weighted sagittal MRI imageT1-weighted sagittal MRI image immediately adjacent to theimmediately adjacent to the previous image shows a partiallyprevious image shows a partially disrupted ACLdisrupted ACL
- 113. Partial ACL tear
- 114. Partial ACL tear with thickening, angulations and abnormal brightPartial ACL tear with thickening, angulations and abnormal bright signal inside. The tibial and femoral attachment is preservedsignal inside. The tibial and femoral attachment is preserved..
- 115. Partial ACL tear with thickening and abnormal bright signal insidePartial ACL tear with thickening and abnormal bright signal inside..
- 116. Partial ACL tear with diffuse thickening and abnormal signal insidePartial ACL tear with diffuse thickening and abnormal signal inside..
- 117. Chronic ACL TearChronic ACL Tear Fragmented ACL [ common finding ]Fragmented ACL [ common finding ] Absent bone edema and contusionsAbsent bone edema and contusions Empty notch signEmpty notch sign ACL attached to PCLACL attached to PCL
- 118. ACL tear on axial image showing non-visualization of the anteriorACL tear on axial image showing non-visualization of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) in the upper inter-condylar notchcruciate ligament (ACL) in the upper inter-condylar notch A large knee effusion and a Baker cyst are noted incidentally.A large knee effusion and a Baker cyst are noted incidentally. Empty notch sign
- 119. Chronic ACL tear, empty notch sign. T1-weighted coronal MRI shows fat in theChronic ACL tear, empty notch sign. T1-weighted coronal MRI shows fat in the lateral intercondylar notch, ACL is absent. This is a frequent MRI appearance of alateral intercondylar notch, ACL is absent. This is a frequent MRI appearance of a chronic ACL tear after resolution of acute edema and hemorrhage.chronic ACL tear after resolution of acute edema and hemorrhage.
- 120. ACL DegenerationACL Degeneration Intra ligamentous cystIntra ligamentous cyst May be mistaken for a tearMay be mistaken for a tear Arthroscopic decompressionArthroscopic decompression
- 121. Intercondylar notch cystIntercondylar notch cyst 1% of knee MRIs1% of knee MRIs Usually an incidental findingUsually an incidental finding Painful if erodes the bonePainful if erodes the bone Post-traumatic chronic partialPost-traumatic chronic partial cruciate ligament tear with internalcruciate ligament tear with internal degenerationdegeneration More common in the ACLMore common in the ACL Oval , rounded may be multilocularOval , rounded may be multilocular Rim enhancement if inflamedRim enhancement if inflamed Arthroscopic drainageArthroscopic drainage Cruciate ligament cyst
- 123. A 3-D cutaway at the intercondylar notch in the sagittal plane reveals normal positioning for a patellar tendon ACL autograft. The tibial tunnel should lie posterior to the line drawn parallel to the intercondylar notch (red) and the femoral attachment should lie posterior to a line drawn parallel to the cortex of the distal femoral diaphysis (blue(.
- 124. Femoral tunnel is normally positioned at the junction of the physeal scar and posterior intercondylar roof (asterisk(. Abnormal placement of the femoral tunnel (asterisk), which lies significantly anterior to a line drawn along the posterior cortex of the femoral diaphysis with graft degeneration.
- 125. Tibial tunnel cyst after ACL graft reconstruction.
- 126. Cyclops lesion (arrowheads) attached to the ACL (arrow) with a head-like appearance, showing a focal area of discoloration resembling an eye (curved arrow(
- 127. Hypointense to isointense nodule (arrowhead) attached to the anterior surface of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) graft (arrow). Sagittal T1W MRI image (C) shows a hypointense nodule (arrowhead) in the anterior intercondylar notch, related to Cyclops.
- 128. ACL reconstruction are provided. Diffuse abnormal fluid signal intensity is seen along the course of the graft (arrows) on the sagittal image, compatible with extensive graft ganglion formation.
- 129. ACL Surgery Failure with stem cells injection.
- 130. Posterior cruciate ligament.Posterior cruciate ligament. The major stabilizer of the kneeThe major stabilizer of the knee Uniform low signal , no striationsUniform low signal , no striations Twice strong as the ACLTwice strong as the ACL The menisco-femoral ligaments are intimately related to PCL.The menisco-femoral ligaments are intimately related to PCL. They connect the posterior horn of the lateral meniscus to theThey connect the posterior horn of the lateral meniscus to the medial femoral condylemedial femoral condyle Ligament of Humphrey anterior to PCLLigament of Humphrey anterior to PCL Ligament of Weisberg posterior to PCLLigament of Weisberg posterior to PCL
- 131. Proton-dense sagittal image demonstrates the normal tibial insertion of the PCL. The insertion site is a vertically inclined posterior to the articular surface.
- 132. PCL injuries represent about 12% of knee injuriesPCL injuries represent about 12% of knee injuries Combined PCL injuries represent 97%Combined PCL injuries represent 97% With ACL 65%With ACL 65% With MCL 50%With MCL 50% With MM 30%With MM 30% Posterior cruciate ligamentPosterior cruciate ligament TYPES OF PCL INJURES Complete tear 40% Partial tear 55% Avulsion tear 7%
- 133. NORMAL PCL TORN PCL MR FINDINGS Increased signal due to hemorrhage and edema Diffuse enlargement of PCL
- 134. COMPLETE PCL TEAR
- 135. An enlarged, intermediate signal (obviously torn) PCL.
- 136. NORMAL PCL AVULSION TEAR • Involves the tibial insertion • Retracted bone fragment • Bone marrow edema at avulsion site • The actual PCL may be normal
- 137. AVULSION PCL TEAR
- 138. AVULSION PCL TEAR
- 139. PARTIAL PCL TEAR
- 140. PD sagittal image shows partial tear of the mid-substance of the PCL. The normal ligament of Humphrey (small arrow) is visualized better because it is adjacent to the high signal intensity edema of the torn PCL. PARTIAL PCL TEAR
- 141. Collateral ligaments. MCL is about 8-11 cm LCL is about 5-7 cm Isolated injuries are rare, usually with ACL and MM
- 142. Collateral ligaments Grade I : microscopic tear Grade II :partial tear Grade III : complete tear GRADING SYSTEM Grade I,II and isolated grade III are treated conservatively, while grade III tears associated with ACL tears are treated by repairing ACL only
- 143. Proton density coronal image shows the normal medial collateral ligament as a thin, taut, well-defined, low-signal structure extending from the medial femoral epicondyle to the medial tibial metaphysis
- 144. Coronal and sagittal proton density image demonstrating the normal lateral collateral ligament in its entirety, from the femoral condyle origin to the fibular head insertion.
- 145. Grade I medial collateral ligament tear with surrounding edema (straight arrows) on a T2WI. Note the normal thickness and signal of the medial collateral ligament and continued close apposition to the femoral and tibial cortices.
- 146. Grade 1 sprain of the medial collateral ligamentGrade 1 sprain of the medial collateral ligament..
- 147. Grade 11 sprain of the medial collateral ligamentGrade 11 sprain of the medial collateral ligament..
- 148. Grade II medial collateral ligament tear seen on a coronal proton density image shows slight thickening of the medial collateral ligament and separation from the underlying cortices. Bone marrow edema of the lateral tibial plateau is seen due to valgus stress 7months after conservative treatment
- 149. Grade II medial collateral ligament tear seen on a coronal T1 and STIR images showing slight thickening of the medial collateral ligament and separation from the underlying cortices.
- 150. Grade 111 tear of the MCLGrade 111 tear of the MCL..
- 151. Grade III medial collateral ligament tear on a coronal fast spin-echo T2- weighted image demonstrates a disrupted ligament that is thickened and retracted with surrounding edema (black arrow).
- 152. Acute grade III tear with a folded ligament (arrow) and surrounding edema on a coronal proton density image.
- 153. Acute tear of the proximal portion of the lateral collateral ligament is seen on this coronal proton density image (white arrow). Note the associated grade II medial collateral ligament tear.
- 154. Grade III MCL tear with retraction
- 155. Grade III MCL tear with abnormal signal and edema
- 156. Grade 111 tear of the LCLGrade 111 tear of the LCL..
- 157. Ilio-tibial band syndrome. Distal tendon of IT fascia and insert at gerdy,sIlio-tibial band syndrome. Distal tendon of IT fascia and insert at gerdy,s tubercle of the tibia. It occur in runner, cyclists, football players and weight liftertubercle of the tibia. It occur in runner, cyclists, football players and weight lifter..
- 158. Pre-patellar bursitis.(housemaid bursitisPre-patellar bursitis.(housemaid bursitis((
- 160. Backer and Pes anserine cystBacker and Pes anserine cyst..
- 161. Patellar and quadriceps tendons
- 164. Patellar tendons
- 165. Complete tear of the patellar tendon with ACL teaComplete tear of the patellar tendon with ACL tearr
- 166. Complete tear of the patellar tendon with ACL tear
- 167. Partial tear of the patellar tendon
- 168. Lateral pressure syndrome Thickening of the lateral retinaculum Lateral knee pain Obese, athletic patients May be associated with chondromalacia
- 169. Patella alta Sequlae of patellofemoral dysplasia Lengthening of the infrapatellar tendon May be associated with chondromalacia Length of patellar tendon/ length of patella > 1.3
- 170. Patella Baja Poliomyelitis Achondroplasia JRA
- 171. Hyaline cartilage
- 172. Hyaline cartilage
- 174. Articular cartilage
- 175. MT STIR
- 176. Chondromalacia patellae Degeneration of the hyaline cartilage Anterior knee pain in young adults Four stages Signal abnormalities Ulceration [ fraying , partial or full thickness defects ] Reactive bone changes [ edema , cyst formation , sclerosis ] Osteoartheritic changes
- 180. Loose bodies • Read with plain films • Low signal fragments Synovial osteochondromatosis.
- 181. Loose bodies
- 182. Synovial osteochondromatosisSynovial osteochondromatosis Metaplasia of subsynovial soft tissues cartilage formation Affects any joint [ knee , hip , elbow[ Age incidence 40 years M : F = 2 : 1 FINDINGSFINDINGS Widening of the joint space Bone erosions Intra articular loose bodies Secondary osteoarthritic changes
- 185. Lipoma arborescenceLipoma arborescence RareRare IdiopathicIdiopathic Fatty synovial infiltrations formingFatty synovial infiltrations forming variable sized villous projectionsvariable sized villous projections withinwithin the joint capsule commonly in thethe joint capsule commonly in the supra- patellar pouchsupra- patellar pouch Associated with joint effusionAssociated with joint effusion Painless swellingPainless swelling Treatment by synovectomyTreatment by synovectomy
- 187. Pigmented villo-nodular synovitisPigmented villo-nodular synovitis IdiopathicIdiopathic Monoarticular disease 1% incidenceMonoarticular disease 1% incidence Hypertrophic synovial masses with hemosiderinHypertrophic synovial masses with hemosiderin laden macrophages bone erosionsladen macrophages bone erosions Intermediate signal in T1 andIntermediate signal in T1 and low signal in T2low signal in T2 withwith enhancement after contrast injectionenhancement after contrast injection Typical location posterior to HoffaTypical location posterior to Hoffa’’s fat pads fat pad Painless swelling , pain with progressive diseasePainless swelling , pain with progressive disease Treatment by synovectomyTreatment by synovectomy
- 190. PIGMENTED VILLONODULAR SYNOVITIS VERSUS LIPOMA ARBORESCENS
- 192. POPLITEAL CYST Fluid in the bursa which is usually communicating with the joint space Other names Baker’s cyst Gastrocnemius/semimembranosus bursa
- 193. Medial plica syndromeMedial plica syndrome Inflamed synovial plica causing pain , crepitusInflamed synovial plica causing pain , crepitus and pseudolockingand pseudolocking Often in adolescents and athleticsOften in adolescents and athletics No measurement for plica thicknessNo measurement for plica thickness Four types of plicaFour types of plica Suprapatellar 90%Suprapatellar 90% Medial 15 -30%Medial 15 -30% InfrapatellarInfrapatellar Lateral [ rare]Lateral [ rare]
- 194. PLICA SYNDROME
- 195. Medial plica
- 196. Osteochondritis dissecansOsteochondritis dissecans Osteochondral fragmentOsteochondral fragment in a typical locationin a typical location Young maleYoung male Lateral aspect of the medial femoral condoyleLateral aspect of the medial femoral condoyle Variable sized fragment attached or detachedVariable sized fragment attached or detached Criteria of unstable fragmentCriteria of unstable fragment Large size more than 1cmLarge size more than 1cm Fluid between the fragment and donor boneFluid between the fragment and donor bone Cystic changes at the donor siteCystic changes at the donor site Enhancement of the separation lineEnhancement of the separation line
- 198. Osteochondritis Dissecans along the medial femoral condyleOsteochondritis Dissecans along the medial femoral condyle
- 200. Red marrow recon version / marrowRed marrow recon version / marrow lesionlesion
- 203. Bone infarctsBone infarcts Serpigenous lesions in the bone marrowSerpigenous lesions in the bone marrow Variable in size [ Chinese figures ]Variable in size [ Chinese figures ] Double line sign is diagnostic [peripheralDouble line sign is diagnostic [peripheral hyperintense with hypointense inner border on T2hyperintense with hypointense inner border on T2 CAUSESCAUSES POSTTRAUMATICPOSTTRAUMATIC STEROIDSSTEROIDS COLLAGEN DISEASESCOLLAGEN DISEASES ALCOHOLISMALCOHOLISM PANCREATITISPANCREATITIS SPONTANEOUSSPONTANEOUS
- 204. BONE INFARCTS.
- 205. BONE INFARCTS
- 206. BONE INFARCTS
- 208. Thank You.
