Hybrid kernel
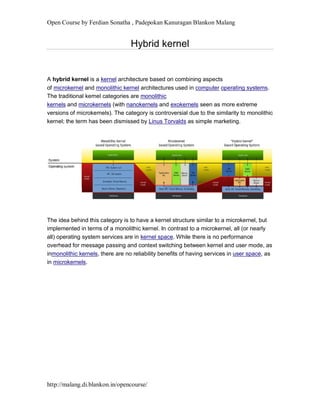
- 1. Open Course by Ferdian Sonatha , Padepokan Kanuragan Blankon Malang http://malang.di.blankon.in/opencourse/ Hybrid kernel A hybrid kernel is a kernel architecture based on combining aspects of microkernel and monolithic kernel architectures used in computer operating systems. The traditional kernel categories are monolithic kernels and microkernels (with nanokernels and exokernels seen as more extreme versions of microkernels). The category is controversial due to the similarity to monolithic kernel; the term has been dismissed by Linus Torvalds as simple marketing. The idea behind this category is to have a kernel structure similar to a microkernel, but implemented in terms of a monolithic kernel. In contrast to a microkernel, all (or nearly all) operating system services are in kernel space. While there is no performance overhead for message passing and context switching between kernel and user mode, as inmonolithic kernels, there are no reliability benefits of having services in user space, as in microkernels.
- 2. Open Course by Ferdian Sonatha , Padepokan Kanuragan Blankon Malang http://malang.di.blankon.in/opencourse/ NT kernel The Windows NT operating system family's architecture consists of two layers (user mode andkernel mode), with many different modules within both of these layers. The best known example of a hybrid kernel is the Microsoft NT kernel that powers all operating systems in the Windows NTfamily, up to and including Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012, and powers Windows Phone 8. NT-based Windows is classified as a hybrid kernel (or a macrokernel[2] ) rather than a monolithic kernel because the emulation subsystems run in user-mode server processes, rather than in kernel mode as on a monolithic kernel, and further because of the large number of design goals which resemble design goals of Mach (in particular the separation of OS personalities from a general kernel design). Conversely, the reason NT is not a microkernel system is because most of the system components run in the same address space as the kernel, as would be the case with a monolithic design (in a traditional monolithic design, there would not be a microkernel per se, but the kernel would implement broadly similar functionality to NT's microkernel and kernel-mode subsystems). Description The Windows NT design included many of the same objectives as Mach, the archetypal microkernel system, one of the most important being its structure as a collection of modules that communicate via well-known interfaces, with a small microkernel limited to core functions such as first-level interrupt handling, thread scheduling and
- 3. Open Course by Ferdian Sonatha , Padepokan Kanuragan Blankon Malang http://malang.di.blankon.in/opencourse/ synchronization primitives. This allows for the possibility of using either direct procedure calls or interprocess communication (IPC) to communicate between modules, and hence for the potential location of modules in different address spaces (for example in either kernel space or server processes). Other design goals shared with Mach included support for diverse architectures, a kernel with abstractions general enough to allow multiple operating system personalities to be implemented on top of it and an object- oriented organisation. The reason NT is not a micro-kernel system is that nearly all of the subsystems providing system services, including the entire Executive, run in kernel mode (in the same address space as the microkernel itself), rather than in user-mode server processes, as would be the case with a microkernel design. This is an attribute NT shares with early versions of Mach, as well as all commercial systems based on Mach, and stems from the superior performance offered by using direct procedure calls in a single memory space, rather than IPC, for communication amongst subsystems. In describing NT, the list of subsystems that do not run in kernel mode is far shorter than the list of those that do. The user-mode subsystems on NT include one or more emulation subsystems, each of which provides an operating system personality to applications, the Session Manager Subsystem (smss.exe), which starts the emulation subsystems during system startup and the Local Security Authority Subsystem Service (lsass.exe), which enforces security on the system. The subsystems are not written to a particular OS personality, but rather to the native NT API (or Native API). The primary operating system personality on Windows is the Windows API, which is always present. The emulation subsystem which implements the Windows personality is called the Client/Server Runtime Subsystem (csrss.exe). On versions of NT prior to 4.0, this subsystem process also contained the window manager, graphics device interface and graphics device drivers. For performance reasons, however, in version 4.0 and later, these modules (which are often implemented in user mode even on monolithic systems, especially those designed without internal graphics support) run as a kernel-mode subsystem. As of 2007, one other operating system personality, UNIX, is offered as an optionally installed system component on certain versions of Windows Vista and Windows Server 2003 R2. The associated subsystem process is the Subsystem for UNIX-Based Applications (psxss.exe), which was formerly part of a Windows add-on called Windows Services for UNIX. An OS/2 subsystem (os2ss.exe) was supported in older versions of Windows NT, as was a very limited POSIX subsystem (psxss.exe). The POSIX subsystem was supplanted by the UNIX subsystem, hence the identical executable name.[4]
- 4. Open Course by Ferdian Sonatha , Padepokan Kanuragan Blankon Malang http://malang.di.blankon.in/opencourse/ Applications that run on NT are written to one of the OS personalities (usually the Windows API), and not to the native NT API for which documentation is not publicly available (with the exception of routines used in device driver development). An OS personality is implemented via a set of user-mode DLLs (see Dynamic-link library), which are mapped into application processes' address spaces as required, together with an emulation subsystem server process (as described previously). Applications access system services by calling into the OS personality DLLs mapped into their address spaces, which in turn call into the NT run-time library (ntdll.dll), also mapped into the process address space. The NT run-time library services these requests by trapping into kernel mode to either call kernel-mode Executive routines or make Local Procedure Calls (LPCs) to the appropriate user-mode subsystem server processes, which in turn use the NT API to communicate with application processes, the kernel-mode subsystems and each other. XNU kernel Main article: XNU XNU is the kernel that Apple Inc. acquired and developed for use in the OS X and iOS operating systems and released as free and open source software as part of the Darwin operating system. XNU is an acronym for X is Not Unix.[5] Originally developed by NeXT for the NeXTSTEP operating system, XNU was a hybrid kernel combining version 2.5 of the Mach kernel developed at Carnegie Mellon Universitywith components from 4.3BSD and an object-oriented API for writing drivers called Driver Kit. After Apple acquired NeXT, the Mach component was upgraded to 3.0, the BSD components were upgraded with code from the FreeBSD project and the Driver Kit was replaced with a C++ API for writing drivers called I/O Kit. Description Like some other modern kernels, XNU is a hybrid, containing features of both monolithic and microkernels, attempting to make the best use of both technologies, such as themessage passing capability of microkernels enabling greater modularity and larger portions of the OS to benefit from protected memory,[citation needed] as well as retaining the speed of monolithic kernels for certain critical tasks. Currently, XNU runs on ARM,[6] IA-32, and x86-64 based processors, both single processor and SMP models. Implementations BeOS kernel
- 5. Open Course by Ferdian Sonatha , Padepokan Kanuragan Blankon Malang http://malang.di.blankon.in/opencourse/ Haiku kernel Syllable BSD-based DragonFly BSD (first non-Mach BSD OS to use a hybrid kernel) XNU kernel (core of Darwin, used in OS X and iOS) NetWare kernel[7] Inferno kernel NT kernel (used in Windows NT 3.1, Windows NT 3.5, Windows NT 4.0, Windows 2000, Windows Server 2003, Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008,Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows 8, and Windows Server 2012) ReactOS kernel See also Microkernel Exokernel Nanokernel Monolithic kernel Single address space operating system Notes As to the whole "hybrid kernel" thing - it's just marketing. It's "oh, those microkernels had good PR, how can we try to get good PR for our working kernel? Oh, I know, let's use a cool name and try to imply that it has all the PR advantages that that other system has—Linus Torvalds, http://www.realworldtech.com/forums/index.cfm?action=detail&id=66630&threadid=66595&roomid=11 "MS Windows NT Kernel-mode User and GDI White Paper". Microsoft Corporation. 2007. Retrieved 2007-03-01. Silberschatz, Abraham; Peter Baer Galvin and Greg Gagne (2005). Operating System Concepts; 7th Edition. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons Inc.ISBN 978-0-471- 69466-3. Probert, Dave (2005). "Overview of Windows Architecture". Using Projects Based on Internal NT APIs to Teach OS Principles. Microsoft Research/Asia - Beijing. Retrieved 2007- 03-01.
- 6. Open Course by Ferdian Sonatha , Padepokan Kanuragan Blankon Malang http://malang.di.blankon.in/opencourse/ "Porting UNIX/Linux Applications to Mac OS X: Glossary". Apple Computer. 2005. Retrieved 2009-03-27. iPhone processor found: 620MHz ARM CPU (1 July 2007 . Retrieved 2008-01-06. An Overview of the NetWare Operating System(2007-02-07)
