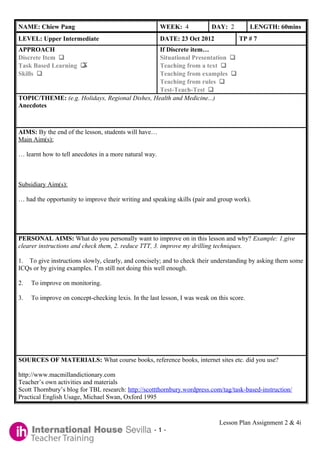
Example of a CELTA lesson plan
- 1. NAME: Chiew Pang WEEK: 4 DAY: 2 LENGTH: 60mins LEVEL: Upper Intermediate DATE: 23 Oct 2012 TP # 7 APPROACH If Discrete item… Discrete Item Situational Presentation X Task Based Learning Teaching from a text Skills Teaching from examples Teaching from rules Test-Teach-Test TOPIC/THEME: (e.g. Holidays, Regional Dishes, Health and Medicine...) Anecdotes AIMS: By the end of the lesson, students will have… Main Aim(s): … learnt how to tell anecdotes in a more natural way. Subsidiary Aim(s): … had the opportunity to improve their writing and speaking skills (pair and group work). PERSONAL AIMS: What do you personally want to improve on in this lesson and why? Example: 1.give clearer instructions and check them, 2. reduce TTT, 3. improve my drilling techniques. 1. To give instructions slowly, clearly, and concisely; and to check their understanding by asking them some ICQs or by giving examples. I’m still not doing this well enough. 2. To improve on monitoring. 3. To improve on concept-checking lexis. In the last lesson, I was weak on this score. SOURCES OF MATERIALS: What course books, reference books, internet sites etc. did you use? http://www.macmillandictionary.com Teacher’s own activities and materials Scott Thornbury’s blog for TBL research: http://scottthornbury.wordpress.com/tag/task-based-instruction/ Practical English Usage, Michael Swan, Oxford 1995 Lesson Plan Assignment 2 & 4i -1-
- 2. The LANGUAGE ANALYSIS that you need to do in the following section relates to your LINGUISTIC AIM(S) i.e. the LANGUAGE COMPONENT of your lesson. As a rough guide: • In a discrete-item lesson, you need to analyse the M,F,P,A of the discrete item i.e. the language point • In a TBL lesson, you need to analyse M,F,P,A of any topic-related lexis you intend to teach (Pre-task stage) and ‘useful language/expressions’ (Planning stage). • For ALL of the above, and skills lessons, you need to analyse any lexis that you intend to teach or that might cause problems of M, F, P, A during your lesson. The idea is that this analysis will help you to predict problems the students may have and to plan solutions to these BEFORE the lesson in the next section of the lesson plan. Assignment 2: LANGUAGE ANALYSIS MEANING/USE State what the language component of your lesson is (see above) AND what it means/how it is used. Give an example(s). For LEXIS/USEFUL PHRASES, list the words/phrases you intend to teach and the key points of their meaning. See example. FORM: State what the FORM of your language component is, showing a breakdown of the structure/phrase. Include negatives, question forms, contractions etc if necessary. Include parts of speech in your list of LEXIS. See example. PRONUNCIATION: Indicate the key pronunciation features of your language component (word/sentence stress, weak forms, silent letters, key intonation patterns etc.). See example. APPROPRIACY: indicate whether anything in your language component is colloquial, formal, informal, slang etc. See example. EXAMPLE: DISCRETE ITEM: have to vs don’t have to Meaning: I have to get up early every day. (it’s necessary/it’s an obligation for me.) I don’t have to wear a suit. (it’s not necessary; it’s optional) Form: Positive: subject + have to + infinitive Negative: subject + don’t have to + infinitive Question: Do you have to wear a suit? Short answer: Yes, I do./No, I don’t. Pronunciation /hæftə/ before infinitives beginning with a consonant sound /hæftu:/ before infinitives beginning with a vowel sound LEXIS/EXPRESSIONS to manage to do sth. Meaning to succeed in doing something, especially something that needs a lot of effort or skill Form: manage to do sth = manage (v.reg) +’to’ infinitive Pronunciation /-ɪdʒ/ a suit Meaning: a set of clothes made from the same cloth, usually a jacket with trousers or a skirt Form: noun (in this context) Pronunciation: /su:t/ WRITTEN RECORD: What written record will students get of key features of M,F,P,A of the language you are teaching? Students get a written record of the exercises used in the lesson, along with the answers. Lesson Plan Assignment 2 & 4i -2-
- 3. Assignment 2: LANGUAGE ANALYSIS Topic-related lexis (pre-task stage) basin Meaning: an open container used for holding liquids (as used in context) Form: noun, countable Pronunciation: | ˈbeɪsn̩ | embarrassed Meaning: ashamed of something and worried about what other people will think of you Form: adjective Pronunciation: | ɪmˈbærəst | chore Meaning: an ordinary job that must be done regularly Form: noun, countable Pronunciation: | tʃɔː | circuit breaker Meaning: a piece of equipment designed to stop an electric current automatically if it becomes too strong or dangerous Form: noun, countable Pronunciation: | ˈsɜːkɪt ˈbreɪkə | cape Meaning: in this context, it’s the piece of cloth matadors use to attract the bulls Form: noun, countable Pronunciation: | keɪp | Lesson Plan Assignment 2 & 4i -3-
- 4. Assignment 2: LANGUAGE ANALYSIS (Cont.) Useful language chunks (planning stage) Have I ever told you…? Meaning: a useful expression to begin a story Form: Interrogative using present perfect Pronunciation: | həv aɪ ˈevə təʊld ju | I was doing the washing-up when the lights went out. Meaning: to speak about an event that interrupted another which was in progress Form: Past continuous and past simple Pronunciation: weak form of was | wəz | suss out Meaning: to understand a situation or the reason why someone does something Form: verb, transitive Pronunciation: | sʌst aʊt | Appropriacy: Only in informal usage Note: I could easily have used “realised” instead of “sussed out”, but with Underhill and Scrivener’s Demand- high ELT in mind, I decided to keep the more informal “sussed out”. gosh Meaning: used to express surprise or annoyance Form: interjection Pronunciation: | ɡɒʃ | Appropriacy: Informal. Although it’s deemed to be old-fashioned, I think it is still used a lot, along with other interjections such as Cor! or Crikey! Thank goodness! Meaning: used for saying that you are happy that something unpleasant has stopped or has not happened Form: interjection Pronunciation: | θæŋk ˈɡʊdnəs | Appropriacy: Fairly informal. “Goodness” can be replaced by “God” or heaven(s)”. In the end Meaning: useful phrase to end an anecdote or story Form: mainly spoken Pronunciation: | ɪn ði end | Lesson Plan Assignment 2 & 4i -4-
- 5. Assignment 2: PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS What problems of M,F,P,A might students have with the previously analysed language? List and explain these problems and include details of a solution immediately after each (please label them Problem 1, Solution 1 etc.) MEANING: Please include full details of how you will convey meaning and check understanding in your solutions, including timelines, concept questions etc, as necessary. Alternatively, refer to the exercise/worksheet which does this. Example: Problem 1: Ss may think that ‘don’t have to’ means ‘obligation not to do sth’. Solution 1: In worksheet 1 Ex.1 Ss choose the correct meanings from several options. Problem 2: Ss may not know the meaning of a. To manage to do sth, b. To refuse to do sth, etc. Solution 2: Ss match these words to their definitions on Worksheet 1, Ex.2. Problem 1: Although this is an upper intermediate group, they still may have some difficulty understanding some words such as basin (not mentioned, but a translation of “palangana”, which was mentioned), embarrassed (false friend of “embarazada”), chore and cape. Solution 1: The use of images in the PowerPoint should clarify any doubts fairly easily. Some CCQs may have to be employed: CCQ embarrassed: What happens to most of us when we feel embarrassed? Our face go red. Do we feel ashamed or do we feel proud when we’re embarrassed? Ashamed. CCQ chore: Is ironing a chore? Yes. Is making the bed a chore? Yes. Is listening to music a chore? No. Problem 2: Most likely, they wouldn’t have heard of “suss out” before. This word doesn’t form part of the blocking lexis, so they may not enquire on this. Solution 2: Explain that we use this to express that we have understood something, usually not immediately but after a time. CCQ: Can we use “realised” instead of “sussed out”? Yes. When we sussed something out, do we realise it immediately or after a period of time? After a period of time. FORM: Example: Problem 1: Ss may think the negative of ‘have to’ is ‘haven’t to’. Solution: ask Ss to find examples of negatives in text. Problem 2: Ss may not know ‘suit’ is both n + v. Solution: Give examples. Because the level is upper intermediate, I don’t envisage problems with neither the present perfect nor the past continuous, but it is possible that some of them may still not have understood its use perfectly. Problem 1: “Have I ever told you I’m living in Las Palmas?” Solution 1: CCQ: The verb “told” – does it refer to a period of time in the past or a definite time? Do we mention the time? No. Can I say “Have I told you yesterday I’m living in Las Palmas?” No. Problem 2: “I was doing the washing-up when the lights went off”. Solution 2: Draw a time line: Lesson Plan Assignment 2 & 4i -5-
- 6. CCQ: Which is the longer action? Washing up. Which is the shorter action? Lights went off. Which action interrupted and which action was interrupted? The lights going off interrupted the washing up. Do we use the past simple for the shorter or longer action? Shorter. Do we use the past continuous to describe the shorter or the longer action? The longer. PRONUNCIATION: Consider individual sounds, silent letters, unpronounced syllables, syllable stress, sentence stress and intonation patterns. Example: Problem 1: (a) Ss may pronounce the ‘v’ in ‘have’ as /v/ not /f/ (b) may mispronounce ‘suit’. Solution 1: drilling and phonemic script for (a) and (b). Problem 1: Some may still pronounce “embarrassed” with the additional syllable |ɪd|. Solution 1: CCQs: How do we pronounce “wanted” (writing it on the board)? | ˈwɒntɪd | How do we pronounce “depended”? | dɪˈpendɪd | Do we pronounce “kissed” | kɪsɪd |? No. What’s the ending of the sound of “want”? |t| “Depend”? |d| “Kiss”? |s| So, we only add |ɪd| when the final sound of the verb in the base form is |d| or |t| - is that right? Yes. Problem 2: Strong form of “was” is used in “I was doing the washing up…” Solution 2: Only if time: drill. Problem 3: Students may have difficulty pronouncing “sussed out” Solution 3: Tell them that the sounds are linked such that the |t| is pronounced along with the second syllable: | sʌs taʊt |. Drill. APPROPRIACY: Example: Problem 1: Ss probably won’t know that ‘loads of’ in the text is an informal way to say ‘a lot of’. Solution 1: I have included this in a short glossary under the text. Problem 1: Students may not realise that “suss out” and “gosh” are fairly informal. Solution 1: CCQ: Can we use these words when we write a formal letter, for example? No. Can we use them when we’re telling anecdotes to friends? Yes. Lesson Plan Assignment 2 & 4i -6-
- 7. SKILLS ISSUES: Is there anything related to skills that you are worried about. Example: Problem 1: The listening recording is quite long and some speakers have strong accents. Solution 1: let students listen to the recording twice if necessary. Problem 1: They may not understand me. Solution 1: I must try to speak slower and clearer. Use images to reinforce understanding. Use comprehension questions to test understanding. OTHER ISSUES: Is there anything non-language related that you are worried about, for example with tasks or activities? Example: Problem 1: The tape in the book is badly organized. Solution 1: reorganize & read myself. Problem 2: the role play requires an even no. of Ss. Solution 2: Put Javier (weaker S) in group of 3. Problem 1: Technology fails. Solution 1: Images are used to create interest and help understanding, so the effect will be dramatically reduced. It’s a waste of paper and money to create flash cards, so I’ll have to rely on strategies such as miming and asking CCQs. Lesson Plan Assignment 2 & 4i -7-
- 8. Assignment 4: POST-LESSON EVALUATION AIMS: Did you achieve your aims (fully/partially/not at all) and what evidence do you have? Main Aim(s): (fully / partially / not at all) How successful were you at meeting your main aims? Subsidiary Aim(s): (fully / partially / not at all) How successful were you at meeting your subsidiary aims? ANTICIPATED PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS: How accurate were your anticipated problems of MFPA and other problems? How successful were your solutions? What other problems did students have in these areas that you didn’t anticipate? SUMMARY: If you were to teach the same lesson again, what would you change? Lesson Plan Assignment 2 & 4i -8-
- 9. PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT: What did you learn from teaching this lesson? PERSONAL AIMS: Did you improve/work on the personal aims you set before the lesson? AREAS FOR FUTURE WORK: What areas do you think you need to work on in the future? TUTOR’S COMMENTS: ASSIGNMENT 2 (BEFORE THE LESSON) ASSIGNMENT 4 (AFTER THE LESSON) Tutor: ________________________ Tutor: ____________________________ TO STANDARD RESUBMIT TO STANDARD RESUBMIT NOT TO STANDARD NOT TO STANDARD Lesson Plan Assignment 2 & 4i -9-
