A. measure of central tendency
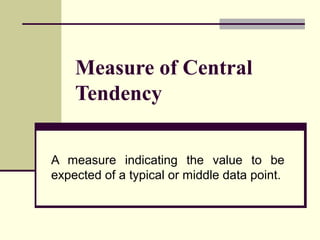
- 1. Measure of Central Tendency A measure indicating the value to be expected of a typical or middle data point.
- 2. The Arithmetic Mean A central tendency measure representing the arithmetic average of a set of observations. The Population Arithmetic Mean, µ, = Σx N The Sample Arithmetic Mean, x = Σx n
- 3. The Arithmetic Mean Calculating the Mean from Grouped Data: x = Σfx n Calculating the Mean of Grouped Data Using Codes: x = x0 + w * Σ(u*f) n
- 4. The Arithmetic Mean Advantages: Its concept is familiar to most of people Every data set has one & only one mean It is useful for comparison Disadvantages: It is affected by the extreme values in the data set It is tedious to calculate for large data It cannot be calculated for grouped data with open- ended classes
- 5. The Weighted Mean Weighted Mean xw = Σ(w *x) Σw Where, xw = symbol for the weighted mean w = weight assigned to each observation Σ(w *x) = sum of the weight of each element times that element Σw = sum of all the weights
- 6. Geometric Mean For quantities that change over a period of time, if we need to know an average rate of change, the arithmetic mean is inappropriate. Geometric mean offers useful measure in such a case. GM = (product of all x values)1/n Where n is number of x values
- 7. The Median The median is a single value that measures the central item in the data set. Half the items lie above the median, half below it. If the data set contains an odd number of items, the middle item of the array is the median. For an even number of items, the median is the average Median = (n + 1)th item in a data array 2 Where n = number of items in the array
- 8. The Median Calculating Median of grouped data = m = [ (n + 1)/2 – (F + 1)]*w + Lm. fm Where, m = median, n = total number of items, F = the sum of all the class frequencies up to, but not including, the median class, fm = frequency of observations of the median class w = the class-interval width Lm = lower limit of the median class interval
- 9. The Median Advantages: Extreme values do not affect the median. It is easy to understand and can be calculated from any kind of data, even for grouped data with open-ended classes, unless the median falls in an open-ended class. Can be calculated for qualitative data.
- 10. The Median Disadvantages: Certain statistical procedures that use the median are more complex than those that use the mean. To find median value, data first need to be arranged in ascending order. For large set of data this could be time consuming.
- 11. The Mode The mode is that value most often repeated in the data set. The mode of grouped data, M o = LM + [ d1 ]*w (d1 + d2) LM= lower limit of mode class d1 = frequency of the modal class minus the frequency of the class directly below it d2 = frequency of the modal class minus the frequency of the class directly above it w = width of the modal class interval
- 12. Dispersion The spread or variability in a set of data. Measures of Dispersion: • Range • Interfractile Range: Quartiles, Deciles, percentiles • Variance • Standard Deviation
- 13. Range The range is the difference between the highest and the lowest values in a frequency distribution The interquartile range measures approximately how far from the median we must go on either side before we can include one-half the values of the data set. Interquartile Range = Q3 – Q1.
- 14. Variance & Standard Deviation of Population Variance is a measure of the average squared distance between the mean and each item in the data set. σ2 = Σ(x - µ)2 = Σ x2 - µ2 N N The standard deviation is the positive square root of the variance. It is expressed in the same units as the data. σ = √σ2
- 15. Variance & Standard Deviation of Population For calculating variance of grouped data σ2 = Σf*(x - µ)2 = Σf x2 - µ2 N N Where, f represents the frequency of the class and x represents the midpoint.
- 16. Variance & Standard Deviation of Sample S2 = Σ(x - x)2 = Σ x2 – n*x2 n–1 n–1 n–1 Notice the change in formula, instead of N, n – I has come as divisor. If we divide by n, the result will have some bias as an estimator. Using a divisor of n – 1 gives us an unbiased estimation.
- 17. Uses of Standard Deviation It helps determining, where the values of a frequency distribution are located in relation to mean. (Standard Normal Curve) It is also useful in describing how far individual items in a distribution depart from the mean of the distribution.