Socialstratificationandsocialmobility
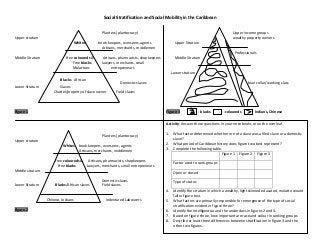
- 1. Social Stratification and Social Mobility in the Caribbean Planters (plantocracy) Upper income groups wealthy property owners Upper stratum Whites book-keepers, overseers, agents Artisans, merchants, middlemen Upper Stratum Professionals Middle Stratum Free coloureds & Free blacks Mulattoes Artisans, pharmacists, shopkeepers lawyers, merchants, small entrepreneurs Middle Stratum Lower stratum Lower Stratum Blacks African Slaves Domestic slaves Chattel/property of slave owner blue collar/working class Field slaves Figure 1 Figure 3 - blacks -coloureds Indians, Chinese Activity: Answer these questions in your note books or on the overleaf. Planters (plantocracy) Upper stratum Whites book-keepers, overseers, agents Artisans, merchants, middlemen Free coloureds & Free blacks 1. 2. 3. Artisans, pharmacists, shopkeepers lawyers, merchants, small entrepreneurs Factor used to rank groups Middle stratum Lower Stratum Open or closed Blacks/African slaves Domestic slaves Field slaves Type of status 4. Chinese, Indians Figure 2 What factor determined whether or not a slave was a filed slave or a domestic slave? What period of Caribbean history does figure two best represent? Complete the following table. Figure 1 Figure 2 Figure 3 Indentured Labourers 5. 6. 7. 8. Identify the stratum in which a wealthy, light skinned educated, mulatto would fall in figure two. What factors are primarily responsible for emergence of the type of social stratification evident in figure three? Identify the intelligentsia and the underclass in figures 2 and 3. Based on figure three, how important are race and colour in ranking groups. Describe at least three differences between stratification in figure 3 and the other two figures.