Chapter28
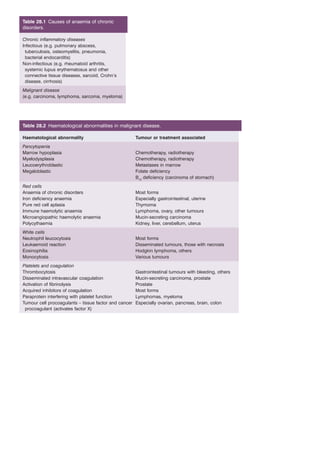
- 1. Table 28.1 Causes of anaemia of chronic disorders. Chronic inflammatory diseases Infectious (e.g. pulmonary abscess, tuberculosis, osteomyelitis, pneumonia, bacterial endocarditis) Non-infectious (e.g. rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus and other connective tissue diseases, sarcoid, Crohn’s disease, cirrhosis) Malignant disease (e.g. carcinoma, lymphoma, sarcoma, myeloma) Table 28.2 Haematological abnormalities in malignant disease. Haematological abnormality Tumour or treatment associated Pancytopenia Marrow hypoplasia Chemotherapy, radiotherapy Myelodysplasia Chemotherapy, radiotherapy Leucoerythroblastic Metastases in marrow Megaloblastic Folate deficiency B12 deficiency (carcinoma of stomach) Red cells Anaemia of chronic disorders Most forms Iron deficiency anaemia Especially gastrointestinal, uterine Pure red cell aplasia Thymoma Immune haemolytic anaemia Lymphoma, ovary, other tumours Microangiopathic haemolytic anaemia Mucin-secreting carcinoma Polycythaemia Kidney, liver, cerebellum, uterus White cells Neutrophil leucocytosis Most forms Leukaemoid reaction Disseminated tumours, those with necrosis Eosinophilia Hodgkin lymphoma, others Monocytosis Various tumours Platelets and coagulation Thrombocytosis Gastrointestinal tumours with bleeding, others Disseminated intravascular coagulation Mucin-secreting carcinoma, prostate Activation of fibrinolysis Prostate Acquired inhibitors of coagulation Most forms Paraprotein interfering with platelet function Lymphomas, myeloma Tumour cell procoagulants – tissue factor and cancer Especially ovarian, pancreas, brain, colon procoagulant (activates factor X)
- 2. Table 28.3 Haematological abnormalities in renal failure. Anaemia Reduced erythropoietin production Aluminium excess in dialysis patients Anaemia of chronic disorders Iron deficiency blood loss (e.g. dialysis, venesection, defective platelet function) Folate deficiency chronic haemodialysis without replacement therapy Abnormal platelet function Thrombocytopenia Immune complex-mediated (e.g. systemic lupus erythematosus, polyarteritis nodosa) Some cases of acute nephritis and following allograft Haemolytic uraemic syndrome and thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura Thrombosis Some cases of the nephrotic syndrome Polycythaemia In renal allograft recipients Rarely in renal cell carcinoma, cysts, arterial disease Table 28.4 Haematological abnormalities in liver disease. Liver failure ± obstructive jaundice ± portal hypertension Refractory anaemia– usually mildly macrocytic, often with target cells; may be associated with: Blood loss and iron deficiency Alcohol (± ring sideroblastic change) Folate deficiency Haemolysis (e.g. Zieve’s syndrome, Wilson’s disease, immune hypersplenism from portal hypertension) Bleeding tendency Deficiency of vitamin K-dependent factors; also of factor V and fibrinogen Thrombocytopenia hypersplenism, immune platelet function defects Functional abnormalities of fibrinogen Increased fibrinolysis Portal hypertension – haemorrhage from varices Viral hepatitis Aplastic anaemia Tumours Polycythaemia Neutrophil leucocytosis and leukaemoid reactions
- 3. Table 28.5 Blood abnormalities associated with infections. Haematological abnormality Infection associated Anaemia Anaemia of chronic disorders Chronic infections especially tuberculosis Aplastic anaemia Viral hepatitis Transient red cell aplasia Human parvovirus Marrow fibrosis Tuberculosis Immune haemolytic anaemia Infectious mononucleosis, Mycoplasma pneumoniae Direct red cell damage or microangiopathic Bacterial septicaemia (associated DIC), Clostridium perfringens, malaria, bartonellosis Viruses – haemolytic uraemic syndrome and TTP Hypersplenism Chronic malaria, tropical splenomegaly syndrome, leishmaniasis, schistosomiasis White cell changes Neutrophil leucocytosis Acute bacterial infections Leukaemoid reactions Severe bacterial infections particularly in infants Tuberculosis Eosinophilia Parasitic diseases (e.g. hookworm, filariasis, schistosomiasis, trichinosis) Recovery from acute infections Monocytosis Chronic bacterial infections: tuberculosis, brucellosis, bacterial endocarditis, typhoid Neutropenia Viral infections – HIV, hepatitis, influenza Fulminant bacterial infections (e.g. typhoid, miliary tuberculosis) Lymphocytosis Infectious mononucleosis, toxoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus, rubella, viral hepatitis, pertussis, tuberculosis, brucellosis Lymphopenia HIV infection Legionella pneumophila Thrombocytopenia Megakaryocytic depression, immune complex-mediated and direct interaction with platelets Acute viral infections particularly in children (e.g. measles, varicella, rubella, malaria, severe bacterial infection) Prothrombotic state All with prolonged inflammation DIC, disseminated intravascular coagulation; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; TTP, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura.
- 4. Table 28.6 Advantages and disadvantages of the tests used to monitor the acute phase response. Advantages Disadvantages CRP* Specific test of acute phase protein More than one protein required to measure acute (CRP) and chronic inflammation Fast response (6 hours) to change in disease activity Costly when assayed in small numbers High sensitivity – owing to large incremental change Sophisticated equipment and antisera required Can be measured on stored serum Small sample volumes Automated analysis ESR and plasma viscosity Useful in chronic disease Not sensitive to acute changes (<24 hours) ESR inexpensive, easy, no electrical power required Not specific for acute phase response Plasma viscosity – result obtained quickly (15 min) Slow to change with alteration in disease activity and insensitive to small changes in activity Plasma viscosity not affected by anaemia Fresh samples (<2 hours) required for ESR ESR, erythrocyte sedimentation rate. * C-reactive protein (CRP) is normally present in low concentrations (<5 mg/L). Levels are not influenced by anaemia, pregnancy or heart failure. During severe acute infection the plasma concentration may rise 100-fold.
