Punic Wars
- 1. PUNIC WARS
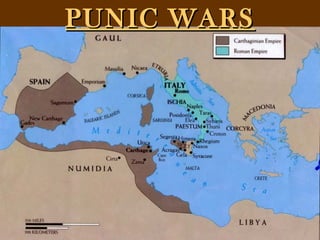
- 2. The greatest naval power of the Mediterranean in the third century BCE was the North African independent city of Carthage. The Carthaginians were originally Phoenicians and Carthage was a colony founded by the Phoenician capital city of Tyre in the ninth century BCE Carthage was powerful in the western Mediterranean, had a powerful navy and trading connections and territories in Spain, north Africa, Sardinia, Corsica
- 3. Carthage was a formidable power; it controlled almost all the commercial trade in the Mediterranean, had subjected vast numbers of people all whom sent soldiers and supplies, and amassed tremendous wealth from gold and silver mines in Spain. The Romans had had some contact with Carthage. They were perfectly aware of the Carthaginian heritage: they called them by their old name, Phoenicians. In Latin, the word is Poeni, which gives us the name for the wars between the two states, the Punic Wars.
- 4. Rivalryand tension led to three lengthy conflicts called the Punic Wars, named after puniqus, Latin for Phoenician
- 5. Punic Wars: Three Punic Wars (Rome vs. Carthage)
- 6. Why was a war with Carthage inevitable?
- 7. Roman republic’s first territorial interest outside of Italy was Africa. Target was the Phoenician city of Carthage, great naval power with outposts on Mediterranean islands of Sicily and Sardinia. Rome desired Carthage because: 1. Carthage controlled much of Sicily (island rich in wheat). 2. Navy posed a threat to west
- 8. The Romans greatly feared the Carthaginians and wanted build as large a buffer zone as soon as possible between them and the Carthaginians. By gaining Sicily, the Romans had expelled the Carthaginians from their back yard; they now wanted them out of their front yard, that is, the islands of Corsica and Sardinia west of the Italian peninsula.
- 9. The First Punic War ( 264 BC - 241 BC E) Fought partly on land in Sicily and Africa , but was primarily a naval war. Carthage underestimated Rome and allowed a large part of its force to be withdrawn to another campaign in Africa The struggle was costly to both powers, but Rome was victorious — it conquered the island of Sicily. The effect of the war destabilized Carthage so much that Rome was able to seize Sardinia and Corsica a few years later.
- 11. Rome developed a navy in a short time and proved to be tactically superior Rome improved naval technology by designing a hook that attaches to enemy boats so troops could fight along the deck. Carthaginians agreed to pay Rome 3300 talents of silver and surrender Sicily. Romans took many slaves in Carthage, meaning their free men were able to fight abroad while slaves worked the land
- 12. Following its defeat in the First Punic War, Carthage rebuilt its strength by expanding its empire in Spain. Growing increasingly anxious, the Romans had imposed a treaty on Carthage not to expand their empire past the Ebro river in Spain. However, when a small city in Spain, Saguntum, approached Rome asking for Roman friendship and alliance, the Romans couldn't resist having a friendly ally right in the heart of the Carthaginian Iberian empire.
- 14. 221 BC, Hannibal assumed command over Carthaginian Spain (at age 25) At first, Hannibal gave the Saguntines wide berth for he wished to avoid coming into conflict with Rome. But the Saguntines were flush with confidence in their new alliance and began playing politics with other Spanish cities. Hannibal, despite direct threats from Rome, attacked Saguntum and
- 15. Romans attempted diplomacy Demanded that Carthage dismiss Hannibal and send him to Rome - Carthage refused. Carthage was still a powerful opponent - had created a powerful empire in Spain with a large army. Hannibal marched out of Spain and across Europe and, in September of 218 BCE, he crossed the Alps with his army and entered Italy on a war of invasion.
- 16. 2 nd Punic War 218 BCE – 202 BCE Romans became suspicious of Carthage’s growing influence in western Mediterranean Hamilcar Barca (Carthaginian general in First Punic War), conquered parts of
- 17. Hannibal takes ambitious journey from Spain with 40 000 troops , 8000 cavalry, and 60 elephants over Alps; During the crossing of the Alps, he lost half his infantry, 2000 cavalry and
- 18. Although his army was tired from the journey, he literally smashed the Roman armies he encountered in northern Italy. Within two months, he had conquered the whole of northern Italy, with the exception of two cities. A horde of 50 000 Gauls from the north to help him Hannibal’s victory over Rome, would be guaranteed if he could convince Roman allies and subject cities to join Carthage.
- 19. The Romans were divided as to whether they could beat Hannibal in open warfare and they knew that he and his army were alone and far from any supplies. Despite Hannibal's certainty that Roman allies would join him, the allies remained faithful to Rome. So on the eve of his invasion of Rome, Hannibal steered south. The Romans, desperate because of their losses, asked Quintus Fabius Maximus to become absolute dictator of Rome. Fabius determined to avoid open warfare at any cost and simply shadowed and harassed the Carthaginian army until they were weak
- 20. Fabius, Roman military leader at the time, believed Hannibal lacked the equipment for a prolonged siege on Rome and that a delay in battle would seriously reduce the Carthaginian food
- 21. His instinct was to wait out Hannibal; he was hated for this policy—the Romans called him "The Delayer" and eventually removed him from power. But when Hannibal marched into Cannae in southern Italy and started decimating the countryside in 216 BC, the two inexperienced consuls who had replaced Fabius as generals of the army sent an army of eighty thousand soldiers against him. This army, vastly outnumbering the Carthaginian
- 22. 216 BCE Roman army marched against Hannibal at Cannae and lost. Hannibal positioned his infantry in a crescent-shaped formation that bulged out in the centre towards Romans. On the wings, he placed his cavalry. As Romans pushed forward, they pushed Hannibal’s infantry back in
- 24. The battle had proven that Fabius was right all along to avoid direct battles, so the Romans went back to his strategy of waiting out Hannibal. Roman allies in the south of Italy literally ran to Hannibal's side; the whole of Sicily allied itself with the Carthaginians. In addition, the king of Macedon, Philip V, who controlled most of the mainland
- 25. The situation looked bad for the Romans; however, none of the central Italian allies had gone over to Hannibal's side after Cannae. The Romans had been chastened by their defeat and absolutely refused to go against Hannibal, whose army moved around the Italian countryside absolutely unopposed. Hannibal, however, was weak in numbers and in equipment. He didn't have enough soldiers to lay seige to cities such as Rome, and he didn't have either the men or equipment to storm those cities by force. All he could do
- 26. Devastating defeat: 25 000 men were killed. Southern Italian towns surrendered to Hannibal out of fear! As Hannibal marched south to regroup and get food, Roman army recovered from their losses.
- 27. In211, he marched right up the walls of Rome, but he never laid siege to it. So confident were the Romans, that on the day that Hannibal marched around the walls of Rome with his cavalry, the land on which he had camped was sold at an auction in
- 29. The Romans, however, very shrewdly decided to fight the war through the back door. They knew that Hannibal was dependent on Spain for future supplies and men, so they appointed a young, strategically brilliant man as proconsul and handed him the imperium over Spain. This move was unconstitutional, for this young man had never served as consul. His name: Publius Cornelius Scipio (237-183 BC). Scipio, who would later be called Scipio Africanus for his victory over Carthage (in Africa), by 206 BCE had conquered all of Spain, which was converted into two Roman
- 30. Scipio then crossed into Africa in 204 BC and took the war to the walls of Carthage itself. This forced the Carthaginians to sue for peace with Rome; part of the treaty demanded that Hannibal leave the Italian peninsula. Hannibal was one of the great strategic generals in history; all during his war with Rome he never once lost a major battle, although he had lost a couple small skirmishes. Now, however, he was forced to retreat; he had, despite winning every battle, lost the war. When he returned to Carthage, the Carthaginians took heart and rose up against Rome in one last gambit in 202
- 31. At Zama in northern Africa, Hannibal, fighting against Scipio and his army, met his first defeat. Rome reduced Carthage to a dependent state; Rome now controlled the whole of the western Mediterranean including northern Africa.
- 32. The Second Punic War turned Rome from a regional power into an international empire: it had gained much of northern Africa, Spain, and the major islands in the western Mediterranean. Because Philip V of Macedon had allied himself with Hannibal and started his own war of conquest, the second Punic War forced Rome to turn east in wars of conquest against first Philip and then other Hellenistic kingdoms. The end result of the second Punic War, in
- 33. This was the defining historical experience of the Romans. They had faced certain defeat with toughness and determination and had won against overwhelming odds. Their system of alliances had held firm; while Hannibal had depended on the allies running to his side, only the most remote Roman allies, those in the south and Sicily, left the Roman alliance. For the rest of Roman history, the character of being Roman would be distilled in the histories of this
- 34. The Second Punic War ( 218 BC - 202 BC) Carthaginian general Hannibal departs from Spain, crosses the Alps to invade Italy from the north Hannibal is successful in several battles, but never manages to effect a political break between Rome and her allies in the Italian cities Hispania, Sicily and Greece were also key theatres, Rome emerging victorious in all three. Eventually, the war was taken to North Africa, under the control of the brilliant Roman stragegist, the general Scipio Carthage was annihilated at the Battle of Zama, its territories everywhere outside of Africa were now under Roman control and they had to pay an
- 35. Inthe years intervening, Rome undertook the conquest of the Hellenistic empires to the east. In the west, Rome brutally subjugated the Iberian people who had been so vital to Roman success in the second Punic War. However, they were especially angry at the Carthaginians who had almost destroyed them. The great statesman of Rome, Cato, is reported by the historians as ending all his speeches, no matter what their subject, with the statement, "I also think that
- 36. The Third Punic War involved an extended siege of Carthage between 149 BC and the spring of 146 BC, ending in the city's destruction and the enslavement of many of its people. The resurgence of the struggle can be explained by growing anti-Roman agitations in Hispania and Greece, and the visible improvement of
- 37. 3 rd Punic 149 War BCE – 146 BCE. 50 years after Hannibal’s defeat, Carthage was ready for more and violates peace treaty by building up military.
- 38. Carthage had, through the first half of the second century BC, recovered much of its prosperity through its commercial activities, although it had not gained back much power. The Romans, deeply suspicious of a reviving Carthage, demanded that the Carthaginians abandon their city and move inland into North Africa. The Carthaginians, who were a commercial people that depended on sea trade, refused. The Roman Senate declared war, and Rome attacked the city itself.
- 39. After a siege, the Romans stormed the town and the army went from house to house slaughtering the inhabitants in what is perhaps the greatest systematic execution of non-combatants before World War II. Carthaginians who weren't killed were sold into slavery. The harbor and the city was demolished, and all the surrounding countryside was sown with salt in order to render it uninhabitable.
- 40. Rome invades Carthage and burns it to the ground, steals many wealthy and luxurious objects, salts the ground so nothing will grow! Anyone not killed was sold into slavery.
- 41. North Africa became province of Rome. Rome became unrivaled power and began conquering Corsica, Sicily, Sardinia, Spain, Greece, Egypt, Asia Minor, Macedonia, Gaul, Syria, Crete, and Bythynia.