OSI Network model ppt
•Download as PPT, PDF•
14 likes•12,766 views
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Recommended
In this presentation, we will discuss in details about the TCP/ IP framework, the backbone of every ebusiness.
To know more about Welingkar School’s Distance Learning Program and courses offered, visit:
http://www.welingkaronline.org/distance-learning/online-mba.html
TCP/IP – Transmission Control Protocol/ Internet Protocol

TCP/IP – Transmission Control Protocol/ Internet ProtocolWe Learn - A Continuous Learning Forum from Welingkar's Distance Learning Program.
More Related Content
What's hot
In this presentation, we will discuss in details about the TCP/ IP framework, the backbone of every ebusiness.
To know more about Welingkar School’s Distance Learning Program and courses offered, visit:
http://www.welingkaronline.org/distance-learning/online-mba.html
TCP/IP – Transmission Control Protocol/ Internet Protocol

TCP/IP – Transmission Control Protocol/ Internet ProtocolWe Learn - A Continuous Learning Forum from Welingkar's Distance Learning Program.
What's hot (20)
TCP/IP – Transmission Control Protocol/ Internet Protocol

TCP/IP – Transmission Control Protocol/ Internet Protocol
Viewers also liked
Viewers also liked (20)
Comparison and Contrast between OSI and TCP/IP Model

Comparison and Contrast between OSI and TCP/IP Model
Similar to OSI Network model ppt
Similar to OSI Network model ppt (20)
Recently uploaded
Recently uploaded (20)
Jual Obat Aborsi Hongkong ( Asli No.1 ) 085657271886 Obat Penggugur Kandungan...

Jual Obat Aborsi Hongkong ( Asli No.1 ) 085657271886 Obat Penggugur Kandungan...
ICT Role in 21st Century Education & its Challenges.pptx

ICT Role in 21st Century Education & its Challenges.pptx
Kodo Millet PPT made by Ghanshyam bairwa college of Agriculture kumher bhara...

Kodo Millet PPT made by Ghanshyam bairwa college of Agriculture kumher bhara...
This PowerPoint helps students to consider the concept of infinity.

This PowerPoint helps students to consider the concept of infinity.
UGC NET Paper 1 Mathematical Reasoning & Aptitude.pdf

UGC NET Paper 1 Mathematical Reasoning & Aptitude.pdf
Food safety_Challenges food safety laboratories_.pdf

Food safety_Challenges food safety laboratories_.pdf
ICT role in 21st century education and it's challenges.

ICT role in 21st century education and it's challenges.
On National Teacher Day, meet the 2024-25 Kenan Fellows

On National Teacher Day, meet the 2024-25 Kenan Fellows
OSI Network model ppt
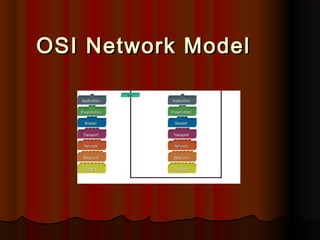
- 2. OSI Network Model The Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model began as a reference model, but has since been implemented. It was created by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) to provide a logical framework for how data communication processes should interact across networks.
- 4. There are 7 layers in the OSI model. Each layer is responsible for a particular aspect of data communication. For example, one layer may be responsible for establishing connections between devices, while another layer may be responsible for error checking during transfer. The layers of the OSI model are divided into two groups: the upper layer and lower layer . The upper layers focus on user applications and how files are represented on the computers prior to transport. For the most part, network engineers are more concerned with the lower layers. It's the lower layers that concentrate on how the communication across a network actually occurs.
- 8. Application Layer The Application layer provides network services directly to the user's application such as a web browser, email software and Windows Explorer. This layer is said to be "closest to the user". o Protocols that operate on this layer include: TELNET, HTTP, FTP, TFTP, SMTP, NTP, SNMP, EDI. o
- 9. Presentation Layer This layer 'represents' the data in a particular format to the Application layer. It defines encryption, compression, conversion and other coding functions. o Specifications defined at this layer include: GIF, TIFF, JPEG, MPEG, MIME, and ASCII. o
- 10. Session Layer The session layer is responsible for dialog control and synchronization o This layer requests for a logical connection to be established on an enduser’s request. o Any necessary log-on or password validation is also handled by this layer. o Session layer is also responsible for terminating the connection. o
- 11. This layer provides services like dialogue discipline which can be full duplex or half duplex. o Session layer can also provide checkpointing mechanism such that if a failure of some sort occurs between checkpoints, all data can be retransmitted from the last checkpoint. o
- 12. Transport Layer o Purpose of this layer is to provide a reliable mechanism for the exchange of data between two processes in different computers. o Ensures that the data units are delivered error free. o Ensures that sequence. o Ensures that there is no loss or duplication of data units. o Provides connectionless or connection oriented service. o Provides for the connection management. o Multiplex channel. data units are delivered in multiple connection over a single
- 13. Network Layer Implements routing of frames (packets) through the network. o Defines the most optimum path the packet should take from the source to the destination o Defines logical addressing so that any endpoint can be identified. o
- 14. Handles congestion in the network. o Facilitates interconnection between heterogeneous networks (Internetworking). o The network layer also defines how to fragment a packet into smaller packets to accommodate different media. o
- 15. Data Link Layer o o o o Data link layer attempts to provide reliable communication over the physical layer interface. Breaks the outgoing data into frames and reassemble the received frames. Create and detect frame boundaries. Handle errors by implementing an acknowledgement and retransmission scheme.
- 16. Implement flow control. o Supports points-to-point as well as broadcast communication. o Supports simplex, half-duplex or fullduplex communication. o
- 17. Physical Layer o Provides physical interface for transmission of information. o Defines rules by which bits are passed from one system to another on a physical communication medium. o Covers all - mechanical, electrical, functional and procedural aspects for physical communication. o Such characteristics as voltage levels, timing of voltage changes, physical data rates, maximum transmission distances, physical connectors, and other similar attributes are defined by physical layer specifications.