Denunciar
Compartir
Recomendados
Recomendados
Más contenido relacionado
La actualidad más candente
La actualidad más candente (19)
Wk 5 p1 wk 6-p2_12.1-12.2_thermal properties of materials

Wk 5 p1 wk 6-p2_12.1-12.2_thermal properties of materials
Destacado
Destacado (20)
Chemical Vaour Deposition & Physical Vapour Deposition techniques.

Chemical Vaour Deposition & Physical Vapour Deposition techniques.
Configuration Management with AWS OpsWorks - November 2016 Webinar Series

Configuration Management with AWS OpsWorks - November 2016 Webinar Series
Similar a Thermo#1
Similar a Thermo#1 (20)
20- Explain the difference between temperature and heat- Also- state w.docx

20- Explain the difference between temperature and heat- Also- state w.docx
Diploma_I_Applied science(chemistry)U-V Thermodynamics 

Diploma_I_Applied science(chemistry)U-V Thermodynamics
Más de gbsliebs2002
Más de gbsliebs2002 (20)
Thermo#1
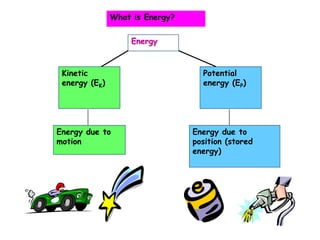
- 1. Energy Kinetic energy (EK) Potential energy (EP) Energy due to motion Energy due to position (stored energy) What is Energy?
- 2. Total Energy = Kinetic Energy + Potential Energy E = EK + EP Kinetic energy & potential energy are interchangeable Ball thrown upwards slows & loses kinetic energy but gains potential energy The reverse happens as it falls back to the ground
- 3. Law of Conservation of Energy: the total energy of the universe is constant and can neither be created nor destroyed; it can only be transformed. The internal energy, U, of a sample is the sum of all the kinetic and potential energies of all the atoms and molecules in a sample i.e. it is the total energy of all the atoms and molecules in a sample
- 4. State Functions A property of a system that changes independently of its pathway Energy changes this way
- 5. Temperature vs. Heat Temperature (T) is a measure of the kinetic energy of particles’ random motion (°C, °F or K) Heat (q) is a measure of the total amount of energy transferred from an object of high temperature to one of low temperature (J or cal)
- 7. The Ultimate Formula (not really) The heat energy needed to raise a substance to a certain temperature is related to the mass of the substance and the temperature change (ΔT) q = mass x specific heat x temperature change q = m CpΔT