Carbohydrate 2
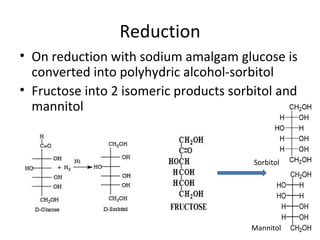
- 1. Reduction • On reduction with sodium amalgam glucose is converted into polyhydric alcohol-sorbitol • Fructose into 2 isomeric products sorbitol and mannitol Sorbitol Mannitol
- 2. Reaction of glucose with weak alkali In the presence of weak alkali glucose in converted into fructose and vice versa
- 3. Reaction of carbonyl group Glucose and fructose condense with hydroxyl amine and phenyl hydrazine to produce oximes and osazones
- 5. Reaction with non-reducing agents • Pentoses on heating with HCl/H2SO4 produce furfural-aldehyde of furan, whereas hexoses produce hydroxy methyl furfural • This provides the basis of tests such as Molisch’s test, Anthrone test, Salivonoff test etc.
- 6. Cont’d
- 7. Reaction with calcium hydroxide On reacting with calcium hydroxide, glucose produces calcium glucosate + Ca (OH)2
- 8. Fermentation Both glucose and fructose are attacked by enzymes of yeast to produce ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide C6H12O6 → 2C2H5OH + 2CO2
- 9. Reaction with acetone 2 acetone -2 H2O
- 10. Methylation On methylation glucose produces glucosides or glycosides
- 11. Configuration of monosaccharides • Due to presence of asymmetric carbon monosaccharides rotate the plane polarized light either toward right or left • Those rotating towards right are dextrorotatory (d or +) and those towards left are levorotatory (l, -) • (d and l) isomers are mirror image of each other when substituents are arranged in space
- 12. • D and L are used in place of + and – with reference to glyceraldehyde- the farthest asymmetric or penultimate carbon • Aldoses with at least three carbons and ketoses with at least four carbons contain chiral centres
- 13. Cyclic Structures and Anomeric Forms • Although Fischer projections are useful for presenting the structures of particular monosaccharides and their stereoisomers , they ignore one of the most interesting facts of sugar structure —the ability to form cyclic structures with formation of an additional asymmetric centre
- 14. • Alcohols react readily with aldehydes to form hemiacetals – A British Chemist Sir Norman Haworth showed that the linear form of glucose and other aldohexoses could undergo a similar intramolecular reaction to form a cyclic hemiacetal – The resulting six- membered, oxygen-containing ring is similar to pyran and is designated as pyranose- glucopyranose. The reaction is catalysed by acid or base and is readily reversible Pyran
- 16. • An analogous intramolecular reaction of a ketose sugar such as fructose yields a cyclic hemiketal • The five-membered ring thus formed is reminiscent of furan and is referred to as a furanose • The cyclic pyranose and furanose forms are the preferred structures for monosaccharides in aqueous solution • At equilibrium, the linear aldehyde or ketone structure is only a minor component of the mixture (generally much less than 1%)
- 18. • When hemiacetals and hemiketals are formed, the carbon atom that carried the carbonyl function becomes an asymmetric carbon atom – Isomers of monosaccharides that differ only in their configuration about that carbon atom are called anomers, designated as α or β • When the hydroxyl group at the anomeric carbon is on the same side of a Fischer projection as the oxygen atom at the highest numbered carbon, the configuration at the anomeric carbon is α, as in α-D-glucopyranose
- 19. • When the anomeric hydroxyl is on the opposite side of oxygen in the Fischer projection, the configuration is β, as in β-D- glucopyranose
- 20. Muta rotation • The addition of this asymmetric centre upon hemiacetal and hemiketal formation alters the optical rotation properties of monosaccharides Early carbohydrate chemists frequently observed that the optical rotation of glucose (and other sugar) solutions could change with the time, a process called muta rotation. This indicated that a structural change was occurring
- 21. Muta rotation • A freshly prepared D-glucose solution shows specific rotation of +111.5o which changes to +52.5o and becomes constant • It was eventually found that α-D-glucose has a specific optical rotation, +111.5°, and that β -D-glucose has a specific optical rotation of +19.2°. When both of these are mixed in 38: 62, specific rotation of +52.5 is obtained
- 22. Muta rotation • Hence, naturally occurring glucose contains 38% α and 62% β isomer • Therefore, Muta rotation involves inter-conversion of α into β forms of the monosaccharide with intermediate formation of the linear aldehyde or ketone
- 23. Derivatives of Monosaccharides • Sugar Acids Sugars with free anomeric carbon atoms are reasonably good reducing agents and reduce hydrogen peroxide, ferricyanide , certain metals (Cu2+ and Ag+), and other oxidizing agents. Such reactions convert the sugar to a sugar acid
- 24. • Sugar Alcohols – Prepared by the mild reduction of the carbonyl groups of aldoses and ketoses. Sugar alcohols are linear molecules that cannot cyclize in the manner of aldoses – Alditols are characteristically sweet tasting, and are widely used as sweetening agents – Sorbitol build-up in the eyes of diabetics is implicated in cataract formation
- 26. Amino Sugars • D-glucosamine and D-galactosamine contain an amino group (instead of a hydroxyl group) at the C-2 position. They are found in many oligo- and polysaccharides, including chitin, a polysaccharide in the exoskeletons of insects
- 27. Storage Polysaccharides • Storage polysaccharides are important carbohydrate forms in plants and animals • It seems likely that organisms store carbohydrates in the form of polysaccharides rather than as monosaccharaides to lower the osmotic pressure of the sugar reserves • Because, osmotic pressure depends only on numbers of molecules – Hence, the osmotic pressure is greatly reduced by formation of a few polysaccharide molecules out of thousands (or even millions) of monosaccharide units
- 28. Starch • The most common storage polysaccharide in plants is starch, which has two components: – α-amylose – amylopectin • Most forms of the starch in nature contain 10-30% α- amylose and 70-90% amylopectin • α -Amylose is composed of linear chains of D-glucose in α(1-4) linkages. The chains are of varying lengths, having molecular weights from several thousand to half a million
- 29. • The chain has a reducing end and a non- reducing end • Although poorly soluble in water, α -amylose forms micelles in which the polysaccharide chain adopts a helical conformation. Iodine reacts with α-amylose to give a characteristic blue colour, which arises from the insertion of iodine into the middle of the hydrophobic amylose helix
- 30. CH2OH 6CH OH CH2OH CH2OH CH2OH 2 O 5 O H O H O H H O H H H H H H H H H H H OH H 1 4 OH H 1 OH H OH H OH H O O O O OH OH 2 3 H OH H OH H OH H OH H OH amylose Non-Reducing end Reducing end
- 31. • In contrast to α-amylose, amylopectin, the other component of typical starches, is a highly branched chain of glucose units • Branches occur in these chains every 12 to 30 residues • The average branch length is between 24 and 30 residues, and molecular weights of amylopectin molecules can range up to 100 million • The linear linkages in amylopectin are α(1-4), whereas the branch linkages are α(1-6) • As is the case for α-amylose , amylopectin forms micellar suspensions in water. Iodine reacts with such suspensions to produce a red-violet colour
- 32. Starch CH2OH 6CH OH CH2OH CH2OH CH2OH 2 O 5 O H O H O H H O H H H H H H H H H H H OH H 1 4 OH H 1 OH H OH H OH H O O O O OH OH 2 3 H OH H OH H OH H OH H OH amylose
- 33. Glycogen • The major form of storage polysaccharide in animals is glycogen • Glycogen is found mainly in the liver (where it may amount to as much as 10% of the liver mass) and skeletal muscle (where it accounts form 1-2% of the muscle mass) • Liver glycogen consists of granules containing highly branched molecules, with α(1-4) linkage in linear structure and α(1-6) linkage at branching, which occurrs every 8-12 glucose units
- 34. • Like amylopectin, glycogen yields a red-violet colour with iodine • Glycogen can be hydrolyzed by α-amylase, yielding glucose • It can also be hydrolyzed by glycogen phosphorylase, an enzyme present in liver and muscle tissue, to release glucose-1-phosphate
- 36. Structural polysaccharides • Cellulose • Chitin • Alginates • Agarose • Glycosaminoglycans
- 37. Cellulose • The most abundant natural polymer found in the world • Found in the cell walls of nearly all plants • One of the principal components providing physical structural and strength • Cotton is almost pure cellulose • Cellulose is a linear homopolymer of D-glucose units, just as in α-amylose. • The structural difference, which completely alters the properties of the polymer, is that in cellulose the glucose units are linked by β(1-4)-glycosidic bonds, whereas in α - amylose the linkage is α(1-4)
- 38. CH2OH 6CH OH CH2OH CH2OH CH2OH 2 O 5 O O H O H O OH H H H H H H H H OH H 1 O 4 OH H 1 O OH H O OH H O OH H OH H H H H 2 H 3 H OH H OH H OH H OH H OH cellulose β-linkages promote intra-chain and inter-chain H-bonds and van der Waals interactions, that cause cellulose chains to be straight & rigid, and pack with a Schematic arrangement of crystalline arrangement in thick cellulose chains in a microfibril. bundles - microfibrils
- 39. Glycosaminoglycans • Previously called mucopolysaccharides •Linear polymers of repeating disaccharides –The constituent monosaccharides tend to be modified, with acidic groups, amino groups, sulfated hydroxyl and amino groups, etc. •Such compounds tend to be negatively charged, because of the prevalence of acidic groups
- 40. Hyaluronate (Hyaluronic acid) •Hyaluronate is a glycosaminoglycan with a repeating disaccharide consisting of 2 glucose derivatives, D-glucuronic acid & N-acetyl-D- glucosamine •These monosaccharides are linked through β(1→3) linkages •Disaccharides are linked through β(1→4).
- 41. CH2OH D-glucuronate 6 − H 5 O 6COO H 4 1 O O H H 5 H OH H 4 H 1 3 2 OH H H NHCOCH3 3 2 O H OH N-acetyl-D-glucosamine hyaluronate
- 42. Proteoglycans • These are also glycosaminoglycans that are covalently linked to serine residues of specific core proteins •The glycosaminoglycan chain is synthesized by sequential addition of sugar residues to the core protein
- 43. Heparan sulfate is initially synthesized on a membrane- embedded core protein as a polymer of alternating N- acetylglucosamine and glucuronate residues. Later, in segments of the polymer, glucuronate residues may be converted to the sulfated sugar iduronate 2-sulfate, while N-acetylglucosamine residues may be sulfated- N-sulfo-glucosamine-6- sulfate iduronate-2-sulfate N-sulfo-glucosamine-6-sulfate H CH2OSO3− H O H O H − COO H OH H O OH H H O H OSO3− H NHSO3− heparin or heparan sulfate - examples of residues
- 44. Heparin, a soluble glycosaminoglycan found in granules of mast cells, has a structure similar to that of heparan sulfates, but is more highly sulfated When released into the blood, it inhibits clot formation by interacting with the protein antithrombin. Heparin has an extended helical conformation Charge repulsion by the many negatively charged groups may contribute to this conformation
- 45. Some proteoglycans of the extracellular matrix bind non-covalently to hyaluronate via protein domains called link modules. E.g. • Multiple copies of the aggrecan proteoglycan associate with hyaluronate in cartilage to form large complexes • Versican, another proteoglycan, binds hyaluronate in the extracellular matrix of loose connective tissues. CH2OH D-glucuronate 6 − H 5 O 6COO H 4 1 O O H H 5 H OH H 4 H 1 3 2 OH H H NHCOCH3 3 2 O H OH N-acetyl-D-glucosamine hyaluronate
- 46. Chitin • A polysaccharide that is similar to cellulose, both in its biological function and its primary, secondary, and tertiary structure • The structure of chitin is identical to cellulose, except that the -OH group on each C-2 is replaced by -NHCOCH3, so that the repeating units are N-acetyl-D-glucosamines in β-(1-4) linkage
- 47. • An other, significant difference between cellulose and chitin is that the chains are arranged in parallel (all the reducing ends together at one end of a packed bundle and all the non-reducing ends together at the other end) or antiparallel (each sheet of chains having the chains arranged oppositely from the sheets above and below)
- 48. • Natural cellulose seems to occur only in parallel arrangements. Chitin, however, can occur in three forms, sometimes all in the same organism – alpha-Chitin is an all-parallel arrangement of the chains – β-chitin is an antiparallel arrangement – d-chitin, the structure is thought to involve pairs of parallel sheets separated by single antiparallel sheets.
