Tb12
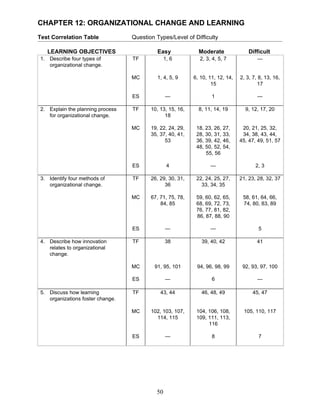
- 1. CHAPTER 12: ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE AND LEARNING Test Correlation Table Question Types/Level of Difficulty LEARNING OBJECTIVES Easy Moderate Difficult 1. Describe four types of TF 1, 6 2, 3, 4, 5, 7 — organizational change. MC 1, 4, 5, 9 6, 10, 11, 12, 14, 2, 3, 7, 8, 13, 16, 15 17 ES — 1 — 2. Explain the planning process TF 10, 13, 15, 16, 8, 11, 14, 19 9, 12, 17, 20 for organizational change. 18 MC 19, 22, 24, 29, 18, 23, 26, 27, 20, 21, 25, 32, 35, 37, 40, 41, 28, 30, 31, 33, 34, 38, 43, 44, 53 36, 39, 42, 46, 45, 47, 49, 51, 57 48, 50, 52, 54, 55, 56 ES 4 — 2, 3 3. Identify four methods of TF 26, 29, 30, 31, 22, 24, 25, 27, 21, 23, 28, 32, 37 organizational change. 36 33, 34, 35 MC 67, 71, 75, 78, 59, 60, 62, 65, 58, 61, 64, 66, 84, 85 68, 69, 72, 73, 74, 80, 83, 89 76, 77, 81, 82, 86, 87, 88, 90 ES — — 5 4. Describe how innovation TF 38 39, 40, 42 41 relates to organizational change. MC 91, 95, 101 94, 96, 98, 99 92, 93, 97, 100 ES — 6 — 5. Discuss how learning TF 43, 44 46, 48, 49 45, 47 organizations foster change. MC 102, 103, 107, 104, 106, 108, 105, 110, 117 114, 115 109, 111, 113, 116 ES — 8 7 50
- 2. CHAPTER 12: ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE AND LEARNING True/False Questions Learning Objective 1 1. Radical change occurs when organizations make major adjustments in the ways they do business. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Easy, p. 325 2. The radical change model was developed by professors at the Harvard School of Business. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 325 3. During radical change, the transitioning stage occurs between the unfreezing and the freezing stage. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 325 4. Total Quality Management (TQM) is an approach that relies heavily on radical change. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 326 5. Timing has very little to do with the magnitude or results of an organizational change. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 326 6. Reactive change can be incremental or radical. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Easy, p. 327 7. Incremental anticipatory change is future-oriented and results from constant tinkering and improvements. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 328 Learning Objective 2 8. Chaos is a symptom of a poorly managed organizational change. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 329 9. For innovation and change to occur without chaos or disorder, the nine steps that constitute the basic components of a change process must be followed in their proper sequence. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 329 51
- 3. CHAPTER 12: ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE AND LEARNING 10. A roofing company that receives a large number of water damage claims is experiencing a performance gap. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Easy, p. 330 11. Organizational diagnosis identifies both the nature and the extent of problems. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 330 12. Organizations often hire outside consultants to assist with problem diagnosis because they offer expertise that the organization lacks to conduct and properly analyze employee attitude surveys. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 330 13. Organizational diagnosis is where the need for change is articulated in describing specific measures to be used in progressing toward goals. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Easy, p. 331 14. Some resistance to change is good, with employees operating as a check-and-balance mechanism to ensure that management properly plans and implements change well. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 333 15. Education, participation, and incentives are three methods used by managers to overcome resistance of employees. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Easy, p. 333 16. Managers can effectively use fear tactics to eliminate the effects of vested interests. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Easy, p. 333 17. Managers who initiate change are wrong if they believe that anyone with the same information would make the same decision. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 333 18. Empowering workers by giving them some control over the change process is an effective way to reduce the stress they experience. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Easy, p. 333 19. One way to reduce cynicism is to make changes take place as infrequently as possible. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 334 20. The results of a change process are monitored typically at predetermined intervals. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 334 52
- 4. CHAPTER 12: ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE AND LEARNING Learning Objective 3 21. There are four methods of organizational change: technological, organization redesign, job redesign, and organizational development. Seldom can significant change be based on one of these methods alone. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Difficult, pp. 335–336 22. Structural change involves incremental changes that affect workflows, production methods, and materials. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 335 23. Sometimes the need for organizational redesign follows directly from implementing new technologies. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 336 24. Downsizing is a familiar approach to structural redesign. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 336 25. Reengineering typically means reconfiguring the organization by changing the levels of authority, responsibility, and control. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 336 26. Downsizing is a painful process but it continues to be popular because it has proven to be highly effective as a survival strategy. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Easy, pp. 336–337 27. Several researchers have found that restructuring is not guaranteed to work. Several studies indicate that restructured firms end up in worse financial shape after the restructuring than they were before. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Moderate, pp. 336–337 28. Reengineering involves redesign of an organization’s processes (e.g., logistics, distribution, and manufacturing) with the goal of designing the most effective process for making and delivering a product. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 337 29. Job enrichment involves the scientific analysis of tasks performed by employees in order to discover procedures that produce the maximum output for the minimum input. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Easy, p. 337 53
- 5. CHAPTER 12: ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE AND LEARNING 30. Changing job specifications to broaden and add challenge to required tasks in order to increase productivity is called job enrichment. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Easy, p. 338 31. The downside to job enrichment is that it leads to low employee commitment and high turnover. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Easy, p. 337 32. Organizational development is a broad term that refers to several different methods for creating organizational change. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 338 33. Focus groups need to operate in an open, nonthreatening environment where there is no designated leader that can dominate and make people feel inhibited. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 338 34. When employee surveys are designed to address issues of strategic importance, they can be used to enhance the organization’s competitive advantage. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 339 35. Team building is more important in tall organizations with narrow spans of control. ANSWER: F, Application, Moderate, p. 339 36. E-engineering is a reengineering initiative that uses Web-based technology. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Easy, p. 340 37. Installing ERP software is considered an incremental change. ANSWER: F, Application, Difficult, p. 340 Learning Objective 4 38. Innovation is just another name for change. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Easy, p. 341 39. Innovation and change are more important environmental elements for new organizations than for established organizations. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 341 40. Three basic types of innovation are technical, process, and administrative. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 341 41. Convergence and implementation are basic types of innovation. 54
- 6. CHAPTER 12: ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE AND LEARNING ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 341 42. Offering telecommuting to employees is an example of an administrative innovation. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 342 Learning Objective 5 43. A learning organization is one that sees changes and innovations as a part of a daily routine. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Easy, p. 343 44. Learning organizations have the distinction of being customer-focused. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Easy, p. 344 45. As a result of providing a culture of innovation within the organization, Continental Airlines created and was the first to use electronic ticketing in airline travel. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 345 46. The flat, team-based structure found in learning organizations facilitates learning more than a vertical organization. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 346 47. Knight-Ridder’s long-term perspective led it to successfully enter broadcast journalism. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 346 48. Xerox hired an anthropologist to study the ways the firm’s workers went about their jobs. ANSWER: T, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 347 49. Scanning the environment includes the observation of tacit knowledge or gossip. ANSWER: F, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 347 55
- 7. CHAPTER 12: ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE AND LEARNING Multiple Choice Questions Preview 1. When Bill Zollars started his survival campaign to make the necessary changes at Yellow Freight, all of the following had recently happened except __________. a. deregulation of the trucking industry b. company losses of $30 million c. two rounds of layoffs d. a major strike by the teamsters union ANSWER: A, Knowledge, Easy, p. 324 2. Yellow Freight employees now have adequate __________ to enable them to solve problems and assess the performance of their company. a. motivation b. information c. incentives d. all of the above ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 324 Learning Objective 1 Types of Organizational Change 3. All of the following are considered types of organizational change except __________. a. fast-paced accrual change b. incremental anticipatory change c. incremental reactive change d. radical reactive change ANSWER: A, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 327 4. __________ change refers to any transformation in the design or functioning of an organization. a. Restructuring b. Redesigning c. Organizational d. Incremental ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Easy, p. 324 5. A(n) _______ change occurs when organizations make major adjustments in the ways they do business. a. organizational b. incremental c. radical d. redesigning ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Easy, p. 325 56
- 8. CHAPTER 12: ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE AND LEARNING 6. All of the following are true concerning radical change except __________. a. it occurs relatively infrequently b. adopting a new organizational structure is an example c. it generally takes a short time to implement d. it can be stimulated by changes in the environment ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 325 7. All of the following correctly describe the common framework for radical organizational change except __________. a. the framework was developed by social scientist Kurt Lewin b. the model divides the change process into four stages c. stage 1 is referred to as “unfreezing” d. the change is solidified in the “refreezing” stage ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 325 8. Monitoring the intended outcomes and providing support for new behaviors are completed in what stage of radical organizational change? a. freezing b. refreezing c. transitioning d. none of the above ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 325 9. __________ change is an ongoing process of evolution over time, during which small changes occur routinely. a. Incremental b. Radical c. Transitory d. Anticipatory ANSWER: A, Knowledge, Easy, pp. 325–326 10. TQM (total qualify management) relies heavily on what type of organizational change? a. radical b. incremental c. anticipatory d. none of the above ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 326 11. The degree and ________ of change combine to form different types of change. a. severity b. depth c. timing d. consequence ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 326 57
- 9. CHAPTER 12: ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE AND LEARNING 12. What type of change occurs when an organization is forced to change in response to some event in the external or internal environment? a. anticipatory b. large-scale c. evolutionary d. reactive ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 326 13. General Electric managers are encouraged to make __________ through Work-Out sessions. a. reactive change b. anticipatory change c. incremental change d. both a and c ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 327 14. Reactive change can be incremental or radical. What company’s share price fell 50 percent in 6 months after the CEO attempted to make a radical reactive change instead of radical incremental change? a. Prudential b. Citibank c. AT&T d. P&G ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 327 15. What type of change occurs when managers make organizational changes in advance of upcoming events or early in the cycle of a new trend? a. anticipatory b. reactive c. radical d. incremental ANSWER: A, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 328 16. Davis Owen has just administered questionnaires (like the one in your textbook) to each of his employees concerning how they respond to innovation and change. Over 80% of his employees received a score more than 9. What can Davis conclude from this new information? a. His employees would be most comfortable in a traditional environment. b. They will enjoy working in an organization that offers cutting-edge products or services. c. They are unlikely to create changes in the organization. d. They do not see how change can improve performance. ANSWER: B, Application, Difficult, pp. 328–329 58
- 10. CHAPTER 12: ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE AND LEARNING 17. Ramona Chavez has just completed the self-management competency questionnaire and has determined from her score that she would work well in an organization that makes changes fast. Despite her overall high score however, her supervisor is concerned about a response she gave on one of the questions. Which question and response indicates she may prefer an organization that makes changes more slowly? a. She seldom follows rules that she think are silly or ineffective b. She will have a new job in five years that she can’t even imagine yet c. She believes she would prefer a job that she can master and become a real expert at doing d. She enjoys trying news foods, even if she isn’t sure of the ingredients ANSWER: C, Application, Difficult, pp. 328–329 Learning Objective 2 Planning for Organizational Change 18. The process of planned organizational change comprises a series of steps. The first step is to __________. a. follow-up the change b. assess the environment c. diagnose organizational problems d. identify sources of resistance ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 329 19. All of the following are components of organizational change except for __________. a. assessing the environment b. reducing the resistance c. diagnosing organizational problems d. All of the above are components of organizational change. ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Easy, p. 329 20. Of the environmental factors listed, which is the least responsible for stimulating organizational change? a. customers b. technology c. unions d. workforce ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 330 21. Of the environmental factors listed, which is the most responsible for stimulating organizational change? a. globalization b. technological advances c. actions of important stakeholders d. competitors ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 330 59
- 11. CHAPTER 12: ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE AND LEARNING 22. Marriott Hotels and Bank of America use __________ and other forms of market research to assess customers’ preferences. a. customer satisfaction surveys b. “whack-o-meter” sessions c. performance appraisals d. diagnostic methods ANSWER: A, Knowledge, Easy, p. 330 23. Ed Zander, president of Microsystems, Inc., used __________ to assess the competitive marketplace. a. performance appraisals b. customer satisfaction surveys c. “whack-o-meter” sessions d. diagnostic methods ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 330 24. The __________ is the difference between what the organization wants to do and what it actually does. a. conversion system b. codifying values c. performance gap d. behavioral displacement ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Easy, p. 330 25. Whalen Industries is going through a planned process for organizational change. They have already analyzed the environment and they should now ___________. a. get feedback from the environment b. determine the difference between what the organization aspires to do to take advantage of its opportunities and what it actually does c. determine all new technical breakthroughs d. none of the above ANSWER: B, Application, Difficult, p. 330 26. The aim of the __________ step in the planning process for organizational change is to identify the nature and extent of problems before taking action. a. communication b. refreezing c. assessment d. organizational diagnosis ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 330 60
- 12. CHAPTER 12: ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE AND LEARNING 27. The HR director at Food Ingredient Specialties used __________ to encourage employees to creatively analyze company problems. a. motivational speakers b. videos c. music d. all of the above ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 330 28. The fourth step in planning for organizational change is: a. diagnosis of organizational problems. b. articulating and communicating a vision. c. anticipate resistance. d. There are no steps to organizational change. ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 329 29. Bill Zollar communicated his vision for Yellow Freight Systems by: a. announcing the vision in memos. b. publishing the vision in employee newspapers. c. taking an 18-month road trip. d. taking out a display ad in the Wall Street Journal. ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Easy, p. 331 30. The fifth step in planning for organizational change is: a. develop and implement an action plan. b. determine the performance gap. c. assess the environment. d. diagnose organizational problems. ANSWER: A, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 329 31. An action plan provides all of the following except __________. a. articulation of the goals for change b. describes the specific measures to be used to monitor progress c. describes specific measures to be used to evaluate progress toward those goals d. An action plan provides all of the above. ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 331 32. The text mentioned all of the following alternatives to layoffs except __________. a. reducing hours b. reducing pay c. encouraging leaves of absence d. getting rid of part-time workers ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 331 61
- 13. CHAPTER 12: ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE AND LEARNING 33. What is the best way to assure that a plan for organizational change will be implemented? a. involve employees early in the process b. correctly diagnose the problem c. empower a task force to implement the change d. prioritize short-term goals over long-term goals. ANSWER: A, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 331 34. As one of the world’s largest companies with 101,000 employees and $128 billion in annual revenues, size could not protect Royal Dutch/Shell from __________. a. the World Trade Organization b. European hypermarkets c. price shocks in the oil markets d. environmental threats ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 332 35. Royal Dutch/Shell needed a more fundamental change than downsizing. One of the major challenges that were identified was __________. a. making its prices more competitive b. achieving consistent brand recognition internationally c. boosting retail outlet sales d. inefficient use of its refinery capabilities ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Easy, p. 332 36. Steve Miller, managing director of Royal Dutch/Shell, is convinced that creating change is __________. a. a top-down task b. a bottom-up task c. the most essential activity d. an unending cycle ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 332 37. For change to be effective, __________ should be set before the change effort is started. a. reasons b. rewards c. guarantees d. goals ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Easy, p. 332 62
- 14. CHAPTER 12: ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE AND LEARNING 38. Phillip French is setting goals for his organization. For change to be effective, goals should incorporate all of the following except __________. a. be based on realistic objectives b. be stated in clear and measurable terms c. be consistent with the organization’s policies d. all of the above ANSWER: D, Application, Difficult, p. 332 39. Step six in the process of organizational change is: a. assess the environment. b. determine the performance gap. c. develop a strategic plan. d. anticipate and reduce resistance. ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 329 40. Experienced managers are aware of all the following forms of resistance to change mentioned in the chapter except __________. a. sabotage b. silence c. lawsuit d. defiance ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Easy, p. 333 41. Jimmie Compton is a manager of a computer software company and is interested in implementing changes within the organization. What forms of resistance is Compton likely to encounter? a. silence b. sabotage c. in-your-face defiance d. All of the above are forms of resistance. ANSWER: D, Application, Easy, p. 333 42. Lakisha Bullock is hoping to select the correct method of overcoming employee resistance to change. Her choices include all of the following except __________. a. education b. participation c. fear d. all are the above ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 333 43. In general, people—and sometimes even entire organizations—tend to resist change for certain reasons. Which of the following is not a typical reason to resist change? a. fear b. vested interests c. interactivity d. misunderstandings ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 333 63
- 15. CHAPTER 12: ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE AND LEARNING 44. Shirley Mason, manager of Falcon Fabrication, has tried to computerize her billing department. Most employees in that department have been working for the firm for many years and don’t feel comfortable with the prospect of having to deal with computers. Mason is likely to encounter resistance to her plans because of __________. a. fear of the unknown b. vested interests c. interorganizational agreements d. limited resources ANSWER: A, Application, Difficult, p. 333 45. Mercedes-Benz Credit Corporation set out to restructure its operations in the United States by instituting all of the following except: a. offered the security of a new job to anyone bold enough to eliminate his or her current position. b. reminded employees that fear was a normal and essential element of change. c. eliminated four layers of management as a result of employee recommendations. d. used financial incentives to convince employees that even cutting their own jobs wouldn’t hurt them. ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 333 46. Howard Chamberlain has been resisting change within his organization because he feels that he is unable to develop the new skills and behaviors required of him. Howard is experiencing __________. a. fear of the unknown b. cynicism c. competition d. vested interests ANSWER: A, Application, Moderate, p. 333 47. Fear often goes hand in hand with __________. a. misunderstandings b. cynicism c. vested interests d. technological change ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 333 48. Individuals within organizations may become resistant to change if they believe that it conflicts with their own self-interests. This resistance is usually based on _________. a. fear of the unknown b. vested interests c. misunderstandings d. cynicism ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 333 64
- 16. CHAPTER 12: ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE AND LEARNING 49. Prudential communicated the implications of its change policies through the use of a board game similar to Monopoly in order to alleviate negative effects that might be caused by __________. a. misunderstandings b. fear c. vested interests d. cynicism ANSWER: A, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 334 50. Katie Schroeder is very resistant toward any change. Her manager knows that getting employees to discuss their problems openly is crucial to overcoming resistance to change. What is Schroeder’s manager trying to resolve? a. fear of the unknown b. vested interest c. misunderstanding d. interorganizational disagreement ANSWER: C, Application, Moderate, p. 334 51. Kasey McLaughlin’s subordinates are resisting his “Quality is #1” campaign because they think it is just another management fad. In order to succeed with the program, Kasey will need to eliminate __________. a. the leader of resistance b. fear of the unknown c. cynicism d. misunderstandings ANSWER: C, Application, Difficult, p. 334 52. Mark Morgan’s plan to implement organizational change was met with rumblings from his employees that he was trying to get promoted to administrative vice president. Morgan’s changes may not succeed because of his employees’ __________. a. misunderstanding b. cynicism c. fear d. impatience ANSWER: B, Application, Moderate, p. 334 53. In the __________ step, managers monitor the results of the change process. a. initial b. search c. final d. identification ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Easy, p. 334 65
- 17. CHAPTER 12: ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE AND LEARNING 54. The final stage of planned organizational change is __________. a. diagnosis of organizational problems b. identification of sources of resistance c. plan the next cycle of change d. monitor change ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 334 55. Jeanine Yates has initiated and implemented many changes in her workplace. Some have been successful, and others have not. Yates must understand that the ability to sustain and make change work depends primarily on ___________. a. the ability to terminate poor workers after change has been made b. the skill of the change initiator c. how well the organization monitors reactions and improvements after the change effort d. the skills and abilities of the employees involved in the change ANSWER: C, Application, Moderate, p. 334 56. Carol Bernick believed the best way to change Alberto-Culver’s performance was to __________. a. change its marketing b. change its culture c. change its pricing structure d. change the top management team ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 335 57. Alberto-Culver created growth development leaders to take part in all of the following except __________. a. performance reviews b. one-on-one mentoring c. communicating the family friendly benefits d. meeting and communicating with the CEO ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 335 Learning Objective 3 Implementing Change 58. Sabrina Neely has been very involved with incorporating planned organizational change. In fact, she has already assessed the environment, determined the performance gap, diagnosed organizational problems, identified sources of resistance, reduced those sources of resistance, and developed a method to monitor organizational change. Sabrina must next __________. a. follow-up on the goals b. search for approaches to change c. implement the change d. reassess the environment ANSWER: B, Application, Difficult, p. 335 59. There are four methods of organizational change that include all of the following except 66
- 18. CHAPTER 12: ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE AND LEARNING __________. a. job redesign b. organization redesign c. environmental change d. technological change ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 336 60. __________ comprises complex networks of computer, telecommunications systems, and remote-controlled devices. a. Information technology b. Inventory management c. Network design d. Infrastructure management ANSWER: A, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 335 61. Deluxe Electronics can link its manufacturing and inventory functions so that as soon as the system runs low on a part, a central computer automatically executes an electronic purchase order signaling the supplier to ship new parts. Deluxe is effectively utilizing __________. a. a warehouse control system b. information technology c. just-in-time technology d. interval schedules ANSWER: B, Application, Difficult, p. 335 62. At Wal-Mart, the electronic cash register monitors the goods sold, their prices, and the amounts remaining on hand. If the inventory of an item is low, the system sends the message to the appropriate distribution center and a reorder is placed. What approach to implementing change is Wal-Mart using? a. technological change b. organization Redesign c. organization development d. none of the above ANSWER: A, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 335 63. Kristina Falk has noticed that her plant needs improvement when it comes to workflows and production methods. The change that Kristina should initiate is a __________. a. conceptual framework strategy b. organization redesign c. organization development d. technological change ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 335 67
- 19. CHAPTER 12: ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE AND LEARNING 64. Regardless of the type of redesign selected, the intent is usually to clarify what gives the organization its __________. a. technological superiority b. leadership position with customers c. maximum efficiency d. best possible profitability ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 336 65. As Mellon Bank’s customers became more comfortable using ATMs, the bank found that it needed 30 percent fewer branches. The remaining branches were changed by what method? a. organization redesign b. technological change c. job redesign d. a combination of the above ANSWER: A, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 336 66. Which of the following statements is true concerning the organization redesign method? a. One basic approach to organizational design is changing the organization’s processes. b. The intent of redesigning organizations is to clarify what gives the organization its leadership position with its customers. c. Design changes should capitalize on the capabilities that differentiate the organization from its competitors. d. All of the above are true. ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 336 67. Managers are being bombarded by ideas on how to redesign their organizations to improve customer satisfaction. These recommendations include all of the following except __________. a. redesigning b. downsizing c. reengineering d. reformation ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Easy, pp. 336–337 68. __________ typically means reconfiguring the distribution of authority, responsibility, and control in an organization. a. Streamlining b. Standardization c. Restructuring d. Re-aligning ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 336 68
- 20. CHAPTER 12: ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE AND LEARNING 69. In 1994, Sears, Roebuck, & Company sold off interests in insurance, real estate, and finance to focus on its core competency of merchandising. Sears was thereby __________. a. simplifying b. restructuring c. re-shuffling d. resisting change ANSWER: B, Application, Moderate, p. 336 70. What approach to structural redesign is known to be used as a response to poor organizational performance, is seldom effective in the long run, and presents a painful experience to those who endure the process? a. reengineering b. downsizing c. job simplification d. job creation ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Moderate, pp. 336–337 71. __________ has to do with changing the processes by which work is carried out. a. Feedback control b. Reengineering c. Ingenuity d. Standardization ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Easy, p. 337 72. Donovan Feldman has been involved in reengineering his organization. He is redesigning the organization’s processes to ensure __________. a. lower costs b. better quality c. increased speed d. All of the above may result from reengineering. ANSWER: D, Application, Moderate, p. 337 73. When organizations want to improve their efficiency and the quality of their products and services, they often examine their __________. a. internal production processes b. focus group results c. acquisition of resources d. all of the above ANSWER: A, Knowledge, Moderate, 337 69
- 21. CHAPTER 12: ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE AND LEARNING 74. By __________ its insurance claims processes, National Grange Mutual was able to reduce its response time by 55 percent. a. redesigning b. restructuring c. reengineering d. streamlining ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 337 75. __________ involves the scientific analysis of tasks performed by employees in order to discover procedures that produce the maximum output for the minimum input. a. Job enrichment b. Job simplification c. Job redesign d. Job empowerment ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Easy, p. 337 76. The oldest task approach to change is __________. a. job enrichment b. job simplification c. job empowerment d. job deployment ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 337 77. Fast-food restaurants most likely use __________. They use this design because their employees can learn tasks rapidly, they have short work cycles, and low-skilled and low- paid employees can be trained easily. a. team-based structures b. tangible outputs c. situation analysis leadership d. job simplification ANSWER: D, Application, Easy, p. 337 78. At “Toys for Tots,” specific jobs were changed with the intent of broadening and adding to the challenge of the tasks required. Productivity improved due to the company’s __________ approach to change. a. trend line b. job rotation c. job enrichment d. job engineering ANSWER: C, Application, Easy, p. 338 70
- 22. CHAPTER 12: ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE AND LEARNING 79. Beth Hayden has been attempting to increase productivity through job enrichment. Job enrichment encompasses all of the following unique aspects except: a. employees are likely to develop attitudes that support the new job-related behaviors. b. job enrichment can humanize an organization. c. employees become more involved and more satisfied. d. All of the above are aspects of job enrichment. ANSWER: D, Application, Moderate, p. 338 80. All of the following are true regarding job enrichment except: a. it changes the basic relationship between employees and their work. b. it changes employee behaviors in ways that gradually lead to more positive attitudes about the organization. c. it offers opportunities for initiating other types of organizational change. d. promotes social loafing within the organization. ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 338 81. Amelia Rash is studying various approaches to organizational change. She should use a(n) __________ approach if she needs a long-range strategy for developing her workforce and improving their effectiveness. a. organization development b. organization redesign c. reactive d. radical ANSWER: A, Application, Moderate, p. 338 82. __________ is a planned, long-range behavioral science strategy for understanding, changing, and developing an organization’s work force in order to improve its effectiveness. a. Survey feedback b. Organization development c. Team building d. Behavior modification ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 338 83. Organization development (OD) has three most commonly used methods for achieving organizational change. All of the following are included except __________. a. focus groups b. information systems c. team building d. survey feedback ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 338 71
- 23. CHAPTER 12: ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE AND LEARNING 84. __________ is an organization development (OD) method that allows managers and employees to report their thoughts and feelings about the organization and to learn about how others think and feel about their own behaviors. a. Survey feedback b. Semantics training c. Team building d. Reorientation ANSWER: A, Knowledge, Easy, p. 338 85. Survey feedback is obtained by means of a __________. a. questionnaire b. portfolio c. PERT chart d. GANTT chart ANSWER: A, Knowledge, Easy, p. 338 86. Intel conducted a survey of its 85,000 employees using a(n) __________ method. a. Web-based b. ERP c. pen and paper d. both a and c ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 339 87. Lonnie Hadley is a human resources manager for the credit card division of First USA. He has decided to initiate some team building activities which might include all of the following except __________. a. emphasis upon a trust-based environment b. outdoor adventures c. competitive games d. creativity exercises ANSWER: C, Application, Moderate, 339 88. ___________ is a description of reengineering initiatives that use Web-based technology as the primary method for managing business-to-business processes. a. E-engineering b. E-commerce c. E-generation d. E-digitalizing ANSWER: A, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 340 72
- 24. CHAPTER 12: ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE AND LEARNING 89. The installation of ERP software at Fairchild Semiconductor was a radical change that created all of the following results except: a. it replaced all the business processes throughout the company. b. it allowed significant workforce reductions. c. it created “plain vanilla” processes that fit the generic software system. d. employees became more knowledgeable and excited about their roles in the company. ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Difficult, pp. 340–341 90. Fairchild Semiconductor implemented an ERP application from Peoplesoft. A key step was to educate users on how their own work was related to the overall process so that the workers might __________. a. save training time b. make the purchase decision appear worthwhile c. be committed to fully using the new system d. not request pay raises for the extra work ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Moderate, pp. 340–341 Learning Objective 4 Role of Innovation in Organizational Change 91. __________ is the process of creating and implementing a new idea. a. Change b. Strategy c. Innovation d. none of the above ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Easy, p. 341 92. Kodak’s lack of innovation caused all of the following except __________. a. profits plummeted b. 34,000 workers were laid off c. the CEO was fired d. all of the above ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 341 93. Which of the following is not considered a basic type of innovation? a. technical innovation b. process innovation c. behavioral innovation d. All of the above are types of innovation ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 341 73
- 25. CHAPTER 12: ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE AND LEARNING 94. Susan Tillery’s organization Silk Flowers, Inc., has created and adopted a substantially new method of producing silk flowers. This is an example of what type of innovation? a. process b. organizational c. administrative d. technical ANSWER: A, Application, Moderate, p. 342 95. The shift to wireless communications systems represents what type of innovation? a. process b. administrative c. technical d. production ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Easy, pp. 341–342 96. The introduction of do-it-yourself online stock trading represents what type of innovation? a. environmental b. technical c. production d. process ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 342 97. At Toyota, oobeya was a process innovation that enabled the company to __________. a. produce more futuristic automobile designs b. maintain the perfect inventory levels at dealers c. build cars with almost no workers d. dramatically lower production costs ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 342 98. All of the following are examples of administrative innovation except __________. a. flexible work schedules b. telecommuting c. e-commerce d. virtual organizations ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 342 99. Champion International was a traditional __________ company that followed technical innovations and moved higher in Fortune’s listings for six consecutive years. a. spark plug manufacturing b. chemical c. food service d. paper manufacturing ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 343 74
- 26. CHAPTER 12: ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE AND LEARNING 100. Champion International made all of the following changes as a result of technical innovations except __________. a. major investments in technical skills training b. in-house manufacturing of its state-of-the-art equipment c. restructured 10 of its 11 mills d. changed management structure from hierarchical to team-based ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 343 101. An architecture for innovation builds an infrastructure that encourages innovation and change. All of the following are key features of that architecture except __________. a. developing a learning environment b. fostering workforce resilience c. providing a support system for innovation d. all of the above ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Easy, p. 343 Learning Objective 5 Learning Organizations 102. A(n) __________ organization has both the drive and the capabilities to improve its performance continuously. a. progressive b. redesigned c. innovative d. learning ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Easy, p. 343 103. Which of the following are learning organizations least likely to learn from? a. past experiences b. textbooks c. other companies d. customers ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Easy, p. 343 104. All of the following are considered distinctive features of learning organizations except __________. a. shared leadership b. intensive use of information c. hierarchical chain of command d. organic organization design ANSWER: C, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 344 75
- 27. CHAPTER 12: ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE AND LEARNING 105. Management of Nantucket Nectars encourages employees to learn by allowing them to make mistakes. Managers believe this will result in __________. a. lower worker turnover b. better quality beverages c. better financial performance in the long run d. another product breakthrough ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 344 106. Which company first implemented an employee’s innovative idea of electronic plane tickets? a. Southwest Airlines b. Continental c. People Express d. British Airways ANSWER: A, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 345 107. When people feel they are part of a community, they are more willing to __________. a. share solutions to problems with their coworkers b. find problems c. make extra effort d. all of the above ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Easy, p. 345 108. Learning organizations encourage individual learning in which of the following ways? a. delegation b. empowerment c. “oobeya” d. all of the above ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 346 109. What organizational structure facilitates learning? a. flat structure b. team-based structure c. hierarchical structure d. both a and b are correct ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 346 76
- 28. CHAPTER 12: ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE AND LEARNING 110. Which of the following is true concerning Knight-Ridder’s purchase of Dialog Information Services? a. The purchase price was attractive so Knight-Ridder decided to make the short-term investment. b. The new service reaches a newspaper readership audience of primarily 25 to 43 year olds. c. The acquisition of Dialog transformed the traditional newspaper company to a leader in online business information. d. The company’s acceptance of the need for a short-term perspective was crucial for a learning organization. ANSWER: C, Application, Difficult, p. 346 111. The design of learning organizations emphasizes the use of all of the following except __________. a. teams b. strategic alliances c. boundaryless networks d. All of the above are emphasized in learning organizations. ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 346 112. In addition to experimenting on their own, many learning organizations use strategic alliances with suppliers, customers, and even competitors as a method of learning. What alliance has Amgen, a Japanese biotech company, made with Kirin Brewery? a. Alcohol intake studies helping cancer research. b. Amgen learns about the fermentation processes, which are crucial for producing synthetic blood clotting protein. c. Kirin learns about amino-acid/protein combinations that can act as catalysts to speed up the brewing process. d. both b and c describe the “alliance” ANSWER: D, Application, Difficult, pp. 346–347 113. A design option for learning organizations is to become a network of cooperating units connected by a sense of community among a larger pool of people who share their diverse knowledge and expertise. What is this network design called? a. strategic alliance b. team-based c. measurement-oriented d. boundaryless ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 347 77
- 29. CHAPTER 12: ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE AND LEARNING 114. Information is the lifeblood of learning organizations. To be effective they must undertake all of the following except __________. a. extensive scanning b. be measurement oriented c. share problems d. all of the above ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Easy, p. 347 115. Learning organizations are measurement oriented in their efforts to improve performance. In learning organizations, what information do employees have access to? a. customer satisfaction surveys b. market share c. competitors’ strategies d. All of the above should be available to employees in learning organizations. ANSWER: D, Knowledge, Easy, p. 347 116. Pharmaceutical companies are described in the text as good examples of learning organizations. They do all of the following except __________. a. develop new products and bring them to the market b. rely on hierarchical structures to maintain control of the drug development process c. track the expertise of their scientists and engineers d. predict in advance the new products to be introduced ANSWER: B, Knowledge, Moderate, p. 347 117. Xerox identified which of the following as one of its key strategic challenges? a. increasing the amount and effectiveness of soft information b. increasing the amount and effectiveness of audit data c. consolidating the international accounting network with national standards d. using e-mail more effectively ANSWER: A, Knowledge, Difficult, p. 347 Essay Questions Learning Objective 1 1. Describe four types of organizational change. Organizational changes vary in both degree and timing. In terms of degree, change can be radical or incremental. In terms of timing, change can be reactive or anticipatory. Combinations of these possibilities create four basic types of change: radical reactive change, radical anticipatory change, incremental reactive change, and incremental anticipatory change. Moderate, pp. 325–328 78
- 30. CHAPTER 12: ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE AND LEARNING Learning Objective 2 2. Explain the planning process for organizational change. Although change often involves a bit of chaos, organizations can usually reduce its amount and impact by carefully planning for major change. Through planning, the organization begins to unfreeze and prepares for the change. The key planning activities are (1) assessing the environment; (2) determining whether a performance gap exists, and if so, its nature and magnitude; (3) diagnosing organizational problems; (4) articulating and communicating a vision for the future; (5) developing an action plan for the change; (6) anticipating and making plans to reduce resistance; and (7) developing a way to monitor change and following up after the main initiatives have been implemented. Difficult, pp. 329–334 3. What are some ways to cut costs that will avoid the long-term negative effects of laying off workers? a. reduce working hours for all employees rather than eliminating individuals b. encourage employees to take temporary leaves of absence c. not renewing contracts for temporary and part-time workers d. job sharing e. reduction of executive salaries and bonuses Difficult, p. 331 4. What are four of the reasons for the resistance to change? a. fear b. vested interests c. misunderstandings d. cynicism Easy, pp. 333–334 79
- 31. CHAPTER 12: ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE AND LEARNING Learning Objective 3 5. Identify four methods of organizational change. Many approaches to implementing change are possible. Four general methods are technological change, organization redesign, job redesign, and organization development. Technological change often involves changing the way work is done by adopting new information technologies. The organization redesign method may involve changing the organizational structure and/or organizational processes. Organization redesign normally affects large portions of an organization. Downsizing and reengineering are examples of this method. Job redesign involves changing employees’ jobs, either simplifying or enriching them. Organization development can be used to change employee attitudes and behaviors. Focus groups and survey feedback permits managers and employees to provide information about a range of topics, including job satisfaction, organizational commitment, and perceptions of supervisory and managerial behaviors. Team building is used to improve the functioning of people who must work together to achieve assigned tasks. Change efforts often involve a combination of these methods. Difficult, pp. 335–340 Learning Objective 4 6. Explain the relationship between innovation and organizational change. Innovation is the process of creating and implementing a new idea. Three basic types of innovation are technical, process, and administrative. Organizational change refers to any transformation in the design or functioning of an organization. Generally, innovations require organizational change. Innovation and change are important to both new and established organizations, owing to the dynamic nature of the external environments of most organizations. Moderate, pp. 341–343 Learning Objective 5 7. Discuss how learning organizations foster change. Organizations are redesigning themselves to become learning organizations capable of quickly adapting their practices to satisfy the needs of their customers. The basic features of such organizations are leadership that is shared, a culture that supports innovation, a strategy focused on customers, an organic organization design, and an intensive use of information. In a learning organization, change is not a special event; it’s a natural part of the organization’s continuous attempts to satisfy customers. Difficult, pp. 343–347 80
- 32. CHAPTER 12: ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE AND LEARNING 8. Describe how information is effectively used in the learning organization. Learning organizations aggressively scan both the internal and external environments for information. They do not want to miss an important trend or change. Information is essential to judgements relating to the creation of new products and services. Systematic measurement is used to make these improvements possible. This includes data pertaining to profits, customer satisfaction, and competitors’ strategies. The learning organization gathers data and disseminates it internally. In addition to numerical data is “soft” information that may be gathered through anecdotal evidence. This can speed up the process of organizational learning. Moderate, p. 347 81