Starch
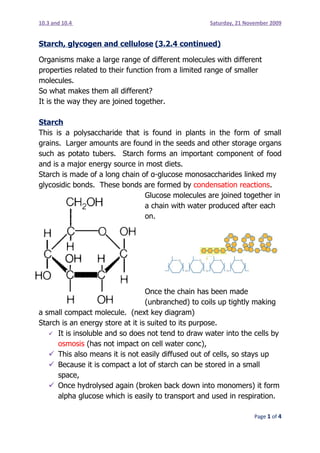
- 1. 10.3 and 10.4 Saturday, 21 November 2009 Starch, glycogen and cellulose (3.2.4 continued) Organisms make a large range of different molecules with different properties related to their function from a limited range of smaller molecules. So what makes them all different? It is the way they are joined together. Starch This is a polysaccharide that is found in plants in the form of small grains. Larger amounts are found in the seeds and other storage organs such as potato tubers. Starch forms an important component of food and is a major energy source in most diets. Starch is made of a long chain of α-glucose monosaccharides linked my glycosidic bonds. These bonds are formed by condensation reactions. Glucose molecules are joined together in a chain with water produced after each on. Once the chain has been made (unbranched) to coils up tightly making a small compact molecule. (next key diagram) Starch is an energy store at it is suited to its purpose. It is insoluble and so does not tend to draw water into the cells by osmosis (has not impact on cell water conc), This also means it is not easily diffused out of cells, so stays up Because it is compact a lot of starch can be stored in a small space, Once hydrolysed again (broken back down into monomers) it form alpha glucose which is easily to transport and used in respiration. Page 1 of 4
- 2. 10.3 and 10.4 Saturday, 21 November 2009 Animals do not make starch, however, a similar polysaccharide called glycogen is found and serves the same role. Glycogen It has a similar structure but is shorter and much more branched. As it is the major carbohydrate storage product in animals it is sometimes referred to as ‘animal starch’. Again it is stored as small grains this time in muscles and the liver. It is suited for storage for much the same reasons. The highly branches structure makes it even easier to hydrolyse and release the glucose. This is never in plants. Cellulose This is important for structure and support in plants. It is different from both starch and glycogen in one major respect: it is made of monomers of β-glucose rather than α-glucose. Whilst this might not seem a great difference it produces a fundamental difference in the structure and function of the polysaccharide. These two forms of glucose are (stereo) isomers, because they contain the same atoms, but they differ in the arrangement of their atoms in space. Alpha and beta glucose differ only in the direction that -H and -OH groups point on carbon 1. Alpha glucose has an -OH group that points "downwards", away from the ring, whereas the -OH on carbon 1 of beta glucose is in line with the ring. This means that to form the glycosidic links, each β-glucose molecule must be rotated by 180o compared to its neighbour. So the –CH2OH groups also alternates. Page 2 of 4
- 3. 10.3 and 10.4 Saturday, 21 November 2009 How does this alter the structure? Rather than forming a coiled chain like starch, cellulose has straight, unbranched chains. These run parallel to one another forming many hydrogen bonds to form cross-linkage between adjacent chains. This gives massive strength to the structure because whilst each bond is weak the sheer number of them makes a massive difference. The cellulose molecules are grouped together to form microfibrils which, in turn, are arranged in parallel groups called fibres. (see page 157). Cellulose is a major component of plant cell walls and gives them the rigidity they need. It is also important because it prevents cells from bursting as water enters it by osmosis (unlike animal cells). This happens because it gives and inward pressure that stops the cell expanding. Plant cells become turgid and push against each other. Plants need this for increased surface area for photosynthesis. 10.4 Plant cell structure Plant cells are eukaryotic cells so have a distinct nucleus and membrane- bound organelles, such as mitochondria and chloroplasts. Leaf palisade cells These are typical plant cells that carry out photosynthesis. Looking at the diagram you can see how it is adapted to suit its function. Page 3 of 4
- 4. 10.3 and 10.4 Saturday, 21 November 2009 They are long thin cells to help absorb sunlight. Numerous chloroplasts that arrange themselves in good positions to collect the maximum amount of light depending on the surroundings. Have a large vacuole that pushes the cytoplasm and chloroplasts to the edge of the cell. Chloroplasts are the organelles that carry out photosynthesis. Whilst they can and do vary in size and shape they are typically disc- shaped, between 2-10 µm long and 1µm in diameter. The chloroplast envelop is a double plasma membrane that surrounds the organelle. It is highly selective in what it allows to enter and leave the chloroplast. The grana are stacks of up to 100 disc-like structures called thylakoids. Within the thylakoids is the photosynthetic pigment called chlorophyll. Some thylakoids have tubular extensions that join up with thylakoids in adjacent grane. The grana are where the first stage of photosynthesis takes place. The stroma is a fluid-filled matrix where the second stage of photosynthesis takes place. Within the stroma are a number of other structures, such as starch grains. Page 4 of 4