Food chains and food webs final
- 1. Food Chains and Food Webs Next
- 2. Objectives Students will be able to define a food chain and food web Students will construct a food chain and food web by placing producers primary consumers, secondary consumers, and top predators in the correct order. Identify and define the role of organisms within a food chain. Students will explore how humans disrupt natural food chains. Previous slide Next
- 3. Discussion Questions: • What is a food chain? •What is a food web? •How are humans apart of the food chain? •How do humans damage food chains and food webs? Previous slide Next
- 4. Table of Contents: Section 1: Energy Section 2: Consumers Living things need food Herbivores How do we get energy? How do animals get Carnivores energy? How do animals get Omnivores energy? Summary of Where do plants get their Section 2 energy? Summary of section 1 Review quiz: 2 Review Quiz: 1 Section 3: Food Chains and Food Webs What did we learn today? Food Chains Food Webs Final Quiz Human Interference Summary of section 3 Review Quiz: 3 Previous slide Next
- 5. Why do living things need food? •People, plants, and animals are all living things. • All living things need air, water, sunlight, and food to stay alive. Previous slide Next
- 6. How do we get this energy? •Food contains nutrients that give living things energy. Living things need energy to grow, move, and stay healthy. • Not all living things get their food the same way. Each living thing finds food in its habitat, the environment in which it lives. Previous slide Next
- 7. Where do animals get their energy? • Animals and people cannot make their own food. They are consumers, because they must consume, or eat, other living things to energy. • Consumers are divided into more groups, such as herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores. Consumers: Carnivores Omnivores Herbivores Previous slide Next
- 8. Where do plants get their energy? • Plants get their energy from the sun. Plants are producers. A plant produces its own food through photosynthesis. Photosynthesis: •During photosynthesis, sunlight is used to combine (mix) water (H2o) and carbon dioxide (CO2)to make food. •The food that plants make is called glucose. Glucose is a type of sugar. Interesting Fact: Plants do not use all the food; they store some of it away. Previous slide Next
- 9. Summary of Section 1: •In section one we learned that all living things need food and energy to survive. People get energy from nutrients in foods. Animals (consumers) get their food by eating other living things. Plants (producers) get their food by photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is when sunlight combines with water and carbon dioxide to make glucose (sugar). You will now take a short review quiz on section 1. Previous slide Next
- 10. Section 1 Review Quiz: 1) A plant is a ___________ a)Producer b) Consumer Previous slide Next
- 11. 2) A plant produces its own food through _____________ a) Photosynthesis b) Food Web Next
- 12. 3) Animals are ________. a) Producers b) consumers Next
- 13. Herbivores : • Herbivores are animals that eat plants. •Many animals eat grass, flowering plants, and other parts of trees, such as fruit, roots, and bark. •There are two types of herbivores: Grazers: Animals that eat grass and small plants near the ground. (can either be a grazer or a browser) Browsers: Animals that eat leaves, shoots, and twigs. Previous slide Next
- 14. Carnivores: •are animals that eat other animals. •Carnivores are predators. Predators hunt other animals for food. The animals they hunt for are called prey. When predators eat herbivores, they are secondary consumers. •When they eat other carnivores, they are tertiary consumers. Large Carnivores Medium Carnivores Small Carnivores Previous slide Next
- 15. Omnivores: Omnivores eat both plants and other animals. Most omnivores have no trouble finding food, because they are not picky eaters. Interesting Fact: People are also omnivores. We eat different foods to get all the nutrients that our bodies need. ‘ Previous slide Next
- 16. Summary of Section 2: In section two we learned that consumers are divided into three groups: Herbivores: are animals that eat plants. • 2types of herbivores Grazers: Animals that eat grass and small plants near the ground. Browsers: Animals that eat leaves, shoots, and twigs. Carnivores (predators): hunt other animals for food Two types of Carnivores: Secondary Consumers: predators who eat herbivores Tertiary consumers: predators who eat other animals Omnivores: eat both plants and other animals. • Humans are also omnivores. You will now take a short review quiz for section2 Previous slide Next
- 17. Section 2 Review Quiz 1) Is this animal a herbivore, carnivore, or omnivore? a) Herbivore b) Omnivore c)Carnivore Previous slide Next
- 18. 2) Which animal is a herbivore? a) Cow b) Lion Next
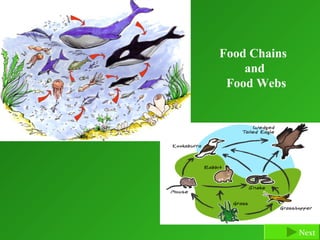
- 19. Food Chains: A food chain shows how living things rely on each other for food. It also shows how energy is moved from one living thing to another. Each food chain starts with the sun. The sun gives energy to plants. 5) Tertiary Consumers: Fox Large carnivores (Lion, Tigers, crocodiles) 4) Secondary consumers: Owl (animals that get their energy from plant eating animals.) 3) Primary Consumers: Grass Hopper Herbivores (first living thing that must eat to get energy) 2) Food chain starts with Grass plants being the producers. Sun 1)Energy: The sun gives Previous slide plants energy Next
- 20. Food Webs: A food web is a group of connected chains. When an animal from one chain is eaten by an animal from another food chain, those animals are part of a food web. Previous slide Next
- 21. Human Food Web: People are the top predators of a food chain. When we eat different foods we become part of a food web. Previous slide Next
- 22. Human Interference: •The population of people on Earth increases every year. We forget that both people and animals need to eat. •People damage food chains and webs when they change nature by: Cutting down forests to build farms or homes - destroys the homes and food supplies of animals Using chemicals called pesticides on their lawns or on farms. -They kill bees butterflies, and insects that plants need to grow. Hunting Carnivores - Killing carnivores throws food chains and webs off balance. This will increase the population of other animals. Previous slide Next
- 23. Summary of section 3 Food Chain: 1.Food chain starts with plants being the producers 2.Primary Consumers: Herbivores (first living thing that must eat to get energy 3. Secondary consumers: Carnivores (animals that get their energy from plant eating animals.) 4. Tertiary Consumers: Large carnivores (Lion, Tigers, crocodiles) Human Food Web: •When humans eat different foods they become part of a food web. •People damage food chains and webs when they change nature by: Cutting down forests to build farms or homes Using chemicals called pesticides on their lawns or on farms. Hunting Carnivores Previous slide Next
- 24. Section 3 Review Quiz 1) What is the correct food chain order for these living things? c) Tertiary a) Primary Consumer b) Producer e) Secondary Consumer consumer a)d , c, a, b , e d) Energy b)d, b, a, e, c Previous slide Next
- 25. 2) What is the correct food chain order for these living things? 1 2 3 4 a) 4,2,3,1 b)4,1,3,2 Next
- 26. 2) What is the correct order of the food chain? 1)Primary Consumers 2) Energy 2) Tertiary consumers 3)producers 4) Secondary Consumers a)2,4,3,1, 2 b) 2,3, 1,4,2 Next
- 27. What did we learn? Vocabulary List: •Photosynthesis: -During photosynthesis, sunlight is used to combine (mix) water (H2o) and carbon dioxide (CO2) to make food. •Herbivores: are animals that eat plants. Two types of herbivores: -Grazers: Animals that eat grass and small plants near the ground. -Browsers: Animals that eat leaves, shoots, and twigs. •Carnivores: are animals that eat other animals. •Omnivores: eat both plants and other animals. •Food Chain: A food chain shows how energy is moved from one living thing to another. •Food Web: A food web is a group of connected chains. Food Chain Order: • 1)producers 2)Primary Consumers 3)Secondary Consumers 4)Tertiary Consumers (plants) ( Herbivores ) (Carnivores) (Large Carnivores) Previous slide Next
- 28. Final Quiz: 1) Is this animal a herbivore, carnivore, or omnivore? a)Carnivore b) Herbivore c) Omnivore Previous slide Next
- 29. 2) True or False Plants are consumers? a) True b) False Next
- 30. 3) True or False – Humans are omnivores? a) True b) False Next
- 31. 4)What is the correct food chain order these living things? 2 3 1 4 5 a)3,4,1,2,5 b) 3,5,4,1,2 Next
- 32. 5) Is this animal a herbivore, carnivore, or omnivore? a)Carnivore b)herbivore c)omnivore Next
- 33. 6) Which two organisms in the food web are both secondary and tertiary consumers? a) Rabbit and Fox b) Bird and Squirrel c) Snake and Eagle Next
- 34. Congratulations!!! You have successfully completed this PowerPoint. You now understand how food chains and food webs work. We will start our human food web project. • Each student will create their own food web. Previous slide
Notas del editor
- 13 Summary of Classification of Living things | Biology Notes for ...All living things have 7 ... igbiologyy.blogspot.com - 375 × 337 - More sizes
- Five Essential Daily Nutrients [INFOGRAPHIC] | Harrisburg Physical ...Here is a list of five essential nutrients that we challenge you to ...maddenptblog.com - 2174 × 1442 - More sizes
- Web of LifeAs a matter of fact, most animals are herbivores. www.kidsplanet.org - 300 × 270 - More sizes Ms. Taylor's Magic School Bus Blog: Food Chains and WebsHere are some examples of different omnivores. When animals and plants die, ... rge5thgradescience.blogspot.com - 291 × 400 - More sizes
- What IS Photosynthesis? And WHY should I care?Photosynthesis chart www.homestead-farm.net - 814 × 499 - More sizes
- Elephant - Wikipedia, the free encyclopediaElephanten.wikipedia.org - 220 × 330 - More sizes RhinocerosRhinoceros.www.math.msu.edu - 1000 × 647 - More sizes