IB Biology Option D.5: Phylogeny and systematics
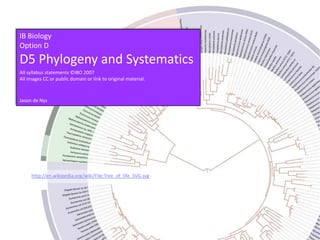
- 1. IB Biology Option D D5 Phylogeny and Systematics All syllabus statements ©IBO 2007 All images CC or public domain or link to original material. Jason de Nys http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Tree_of_life_SVG.svg
- 3. "The affinities of all the beings of the same class have sometimes been represented by a great tree... As buds give rise by growth to fresh buds, and these if vigorous, branch out and overtop on all sides many a feebler branch, so by generation I believe it has been with the great Tree of Life, which fills with its dead and broken branches the crust of the earth, and covers the surface with its ever branching and beautiful ramifications." Charles Darwin, 1859 Charlie sure could spit out a quotable piece of writing
- 5. D.5.1 Outline the value of classifying organisms Identification of Organisms Unknown organisms are easily identified if data about organisms is organised. Classification allows for the creation of keys. Remember 5.5 Classification?
- 6. Evolutionary Links Classification allows us to see evolutionary relationships. Organisms that are grouped together share a lot of similar features (homologous structures). These shared characteristics help us see how organisms have evolved from a common ancestor. e.g. Llamas were originally compared to sheep but a study of their morphology later placed them in the camel family http://www.flickr.com/photos/mrapplegate/2423991076/ http://www.flickr.com/photos/doug88888/3458057235/
- 7. Prediction of Characteristics Characteristics that are shared by organisms within a group would be expected to be found in other species that are closely related. e.g. no doubt more fossils that can be categorised in the Homo genus will be found. We can expect them to have relatively big brains (crazy “Hobbit” finds excepted!) http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Hominins_2002.png
- 10. D.5.2 Explain the Biochemical evidence provided by the universality of DNA and protein structures for the common ancestry of living organisms 1) All known organisms use DNA as genetic material The genetic code is universal. Gene sequences inserted in different organisms express the same proteins http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Bdna.gif
- 11. 2) The same 20 amino acids are used to make all proteins http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Protein_primary_structure.svg
- 12. 3) Most amino acids can exist in left or right- handed forms, i.e. as mirror images Yet all living things use left-handed amino acids It is believed that this was a chance occurrence in the oldest common ancestor The panspermia hypothesis may help explain this as more amino acids found in meteorites are left-handed than right-handed http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Chirality_with_hands.jpg
- 13. 4) Cytochrome c is a protein involved in the electron transport chain. It consists of 100-104 amino acids and is found in plants, animals, and many unicellular organisms It is too complex to have evolved independently and so must come from a common ancestor Further evidence of common descent http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Cytochromec.png
- 14. D.5.3 Explain how variations in specific molecules can indicate phylogeny Taking the example of the protein cytochrome c. It is not identical in all species because single point mutations in the DNA that codes for it can lead to different amino acids making up the protein. Both humans and chimpanzees have the identical cytochrome c molecules, while rhesus monkeys share all but one of the amino acids: the 66th amino acid is isoleucine in the former and threonine in the latter. This suggests that humans and chimpanzees are I didn’t want to be more closely related to each other than to rhesus monkeys closely related to stinking humans anyway! http://www.flickr.com/photos/stuffinhergoose/571672799
- 17. TOK Read this article: Closer to man than ape What reasons are given for including chimps in genus Homo? Do you think humans will ever be reclassified Pan?
- 18. This is part of a molecular phylogeny of all of the living primates. It clearly shows chimpanzees (Pan) as being more closely related to humans than to gorillas. It was made by comparing 34,927 base pairs sequenced from 54 genes taken from each of a single species in each genus.
- 19. D.5.4 Discuss how biochemical variations can be used as an evolutionary clock An evolutionary clock involves calculating the time since species diverged by comparing the number of differences in their DNA and/or protein sequences. Scientists who originated the idea calibrated the amino acid differences in haemoglobin with times derived from the fossil record. http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Nature_Clock.gif
- 20. The assumption is that these changes occur at a regular rate. (which may not always be the case) Therefore if species A had 5 differences from species B and 10 differences from species C, then the lineages for A and C must have split twice as long ago as for A and B C B A Time
- 21. D.5.5 Define clade and cladistics Cladistics (From the ancient Greek for "branch") is a method of classifying species of organisms into groups called clades, which consist of an ancestor organism and all its descendants (and nothing else). Wikipedia http://www.flickr.com/photos/aussiegall/4149475009/
- 22. For example, birds, dinosaurs, crocodiles, and all descendants (living http://www.flickr.com/photos/kev http://www.flickr.com/photos/mo http://www.flickr.com/photos/tam or extinct) of their om/photos/emraya/2929959881/ most recent common ancestor form a clade Wikipedia
- 23. Characteristics change over time, thus the amount of change can help determine relationships Groups of organisms are descended from a common ancestor There is a branching pattern in the evolution of species and when a split occurs, two distinct species eventuate.
- 24. Hair Shelled eggs Each clade Amniotic Egg is determined by Four Limbs common characteristics Bony Skeleton of its members that are different from that of the Vertebrate other species from which it has diverged http://bridgeurl.com/xrmmmk/all
- 25. These traits which tie the clades together are called shared derived characters http://www.flickr.com/photos/29448992@N08/2970804257/
- 26. D.5.6 Distinguish, with examples, between analogous and homologous characteristics Homologous structures are inherited from a common ancestor http://www.flickr.com/photos/opoterser/4189239614/
- 27. e.g. The fly on the previous page and the mosquito on this page have mouthparts adapted to their food sources but the basic components were inherited from a common ancestor Other examples include pentadactyl limbs and finches’ beaks http://www.flickr.com/photos/kclama/102002644/
- 28. Analogous structures have similar form and function due to convergent evolution, they do not stem from a common ancestor Bats… http://www.flickr.com/photos/tjt195/105694980/
- 29. …birds… http://www.flickr.com/photos/patrickwilken/112947862/
- 30. …and bugs all have wings for flight that evolved independently Other examples include: -Streamlined shape for dolphins , sharks and ichthyosaurs -Long snout and tongue for capturing ants on the anteater and echidna http://www.flickr.com/photos/hhoyer/3758550410/sizes/o/in/photostream/
- 31. D.5.7 Outline the methods used to construct cladograms and the conclusions that can be drawn from them AND D.5.8 Construct a simple cladogram • These two cladograms are identical (although they don’t look it) • The shape and the order of the terminal nodes does not matter. • The only information to be gathered from the cladograms below is the order of nesting of sister clades and the relative relatedness of species http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Identical_cladograms.svg
- 32. Out group: Defines the ancestral Terminal nodes Sister clades: have a characters common ancestor Human Chimp Gorilla Chimp Human Gorilla Nodes: Common ancestors Root
- 33. Branches on a cladogram can be scaled or unscaled. If the branches are scaled, the length of the branch often indicates how much evolutionary change has occurred in a species since it split from it’s sister clade at the last node http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/About/primer/phylo.html
- 34. Rooted cladograms show evolutionary relationships. Unrooted trees just show the relationships between clades http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/About/primer/phylo.html
- 35. Cladograms are made by compiling data on homologous characteristics shared by species. These characteristics can be structural, physiological and/or biochemical. With increasing taxa comes increasing complexity. Number of taxa 23 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 N Possible number of rooted 1 3 15 105 945 10,395 135,135 2,027,025 34,459,425 1*3*5*7*...*(2N-3) cladograms So software is often used to find the best possible tree that has the fewest evolutionary steps.
- 36. This cladogram for bacteria is computer generated
- 38. 1) Compile a table of the characters being compared Characters Shark Frog Kangaroo Human Vertebrae X X X X Two pairs of limbs X X X Mammary glands X X Placenta X Modified from: http://www.bu.edu/gk12/eric/cladogram.pdf
- 39. 2) Use the data to construct a Venn diagram, Vertebrae: Start with the Shark characteristic Two Pairs of shared by all Limbs: Frog taxa in the Mammary biggest circle Glands: and work Kangaroo inwards Placenta: Human
- 40. 3) Convert the Venn diagram into a cladogram Shark Frog Kangaroo Human Placenta Mammary Glands Lungs Vertebrae
- 41. Now you try! Make a Venn diagram for this data. Characters Sponge Jellyfish Flatworm Earth- Snail Fruit fly Starfish Human worm Cells with flagella X X X X X X X X Symmetry X X X X X X X Bilateral symmetry X X X X X X Mesoderm X X X X X Head develops first X X X Anus develops first X X Segmented body X X Calcified shell X Chitinous Exoskeleton X Water Vascular system X Vertebrae X
- 42. It should look Cells with flagella: Sponge something Symmetry: Jellyfish like this: Bilateral symmetry: Flatworm Mesoderm Head develops first Anus develops first Segmented Body: Earthworm Water Calcified Vascular Vertebrae: Shell: system: Human Chitinous Snail Starfish exoskeleton: Fruit fly now make the cladogram
- 43. It should look something like this: Flat- Sponge Jellyfish worm Snail Earthworm Fruit fly Starfish Human Calcified Water shell Chitinous vascular shell system Vertebrae Segmented body Head develops first Anus develops first Some of the characteristics in the data table were unnecessary Mesoderm for the construction of this Bilateral symmetry cladogram. Symmetry Flagella Can you identify them?
- 44. Unnecessary to use two characteristics to differentiate between Starfish and Human. Either would do the trick Flat- Sponge Jellyfish worm Snail Earthworm Fruit fly Starfish Human Calcified Water shell Chitinous vascular shell system Vertebrae Segmented body Head develops first Anus develops first Unnecessary to differentiate Snail. Snail is the only species with head Unnecessary to use Mesoderm develops first and without two characteristics Bilateral symmetry to split lineages segmented body Symmetry Flagella
- 45. D.5.9 Analyse cladograms in terms of phylogenetic relationships A B C D Of the three nodes, 3 is most recent and 1 3 occurred earliest. Node 3 is the most recent 2 common ancestor for C and D Node 2 is the most recent common 1 ancestor for B and C Node 3 is the common ancestor of all taxa And so on…
- 46. D.5.10 Discuss the relationship between cladograms and the classification of living organisms Mammals have the unique homologous characteristic of producing milk They form a clade http://www.flickr.com/photos/chavals/3720930469/
- 47. Likewise, birds share the common characteristic of feathers They too form a clade http://www.flickr.com/photos/bestrated1/47581481/
- 48. Lizard Tortoise Reptiles, as a group, consist of the crocodilians, lizards and snakes, tortoises and turtles and tuatara. However, they are not a clade. One of them is actually more Tuatara closely related to birds. Crocodile Care to guess which one? http://www.flickr.com/photos/audreyjm529/155024495/ http://www.flickr.com/photos/mg-muscapix/3288435589/ http://www.flickr.com/photos/8363028@N08/2665814123/ http://www.flickr.com/photos/sidm/5253662054/
- 49. Crocodiles are more closely related to birds than to lizards! Monophyletic: A recent common ancestor and all it’s descendants Paraphyletic: Does not include all descendants from a common ancestor Polypheletic: A group of organisms that does not What this doesn’t include the most recent common ancestor show is that birds are the last descendants of the dinosaurs! http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Phylogenetic-Groups.svg
- 50. *ornithologists study birds, herpetologists study amphibians and reptiles ‘herp’ is a polyphylatelic grouping whereas birds are monophylatelic Fish are paraphylatelic Dinosaurs are paraphylatelic http://xkcd.com/867/
- 51. Further information: ↑An excellent series that covers most of the content ↑The tree of life ↑Sir David Attenborough ↓Amazing site, not to be missed! + BBC = Brilliant
