Exponential growth and decay
•Download as PPT, PDF•
8 likes•68,051 views
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Recommended
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
Viewers also liked
Viewers also liked (20)
Simplifying radical expressions, rational exponents, radical equations

Simplifying radical expressions, rational exponents, radical equations
Lesson 15: Exponential Growth and Decay (Section 021 slides)

Lesson 15: Exponential Growth and Decay (Section 021 slides)
Similar to Exponential growth and decay
Call 9463138669 - ANAND CLASSES | Navy AA SSR Sailors Agniveer Bharti Recruitment Training Exam Coaching Center Academy Classes In Jalandhar Punjab9463138669|Navy AA SSR Sailors Agniveer Bharti Recruitment Training Exam Coac...

9463138669|Navy AA SSR Sailors Agniveer Bharti Recruitment Training Exam Coac...ANAND CLASSES - A SCHOOL OF COMPETITIONS
Call 9463138669 - ANAND CLASSES | CBSE ICSE Math Science Computer SST For Class 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Tuition and Coaching Center in Jalandhar. Math Tuition Center Near Me in Jalandhar for Class 4 5 6 7 8 9 10, Science Tuition Center Near Me in Jalandhar for Class 4 5 6 7 8 9 10, SST Tuition Center Near Me in Jalandhar for Class 4 5 6 7 8 9 10, Computer Tuition Center Near Me in Jalandhar for Class 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Best CBSE Tuition Center Near Me in Jalandhar for Class 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Best ICSE Tuition Center Near Me in Jalandhar for Class 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Best ICSE Math Tuition Center Near Me in Jalandhar
Best ICSE Math Tuition Classes Near Me in Jalandhar
Best CBSE Math Tuition Center Near Me in Jalandhar
Best CBSE Math Tuition Classes Near Me in Jalandhar
Best ICSE Science Tuition Center Near Me in Jalandhar
Best ICSE Science Tuition Classes Near Me in Jalandhar
Best CBSE Science Tuition Center Near Me in Jalandhar
Best CBSE Science Tuition Classes Near Me in Jalandhar. MATH SCIENCE SST ENGLISH COMPUTER FOR CLASS 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Tuition in Jalandhar, Best MATH SCIENCE SST ENGLISH COMPUTER FOR CLASS 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Tuition in Jalandhar, MATH SCIENCE SST ENGLISH COMPUTER FOR CLASS 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Tuition near me, MATH SCIENCE SST ENGLISH COMPUTER FOR CLASS 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Tuition center near me, MATH SCIENCE SST ENGLISH COMPUTER FOR CLASS 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Tuition center in Jalandhar, MATH SCIENCE SST ENGLISH COMPUTER FOR CLASS 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Tuition institute in Jalandhar, MATH SCIENCE SST ENGLISH COMPUTER FOR CLASS 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Tuition preparation in Jalandhar, MATH SCIENCE SST ENGLISH COMPUTER FOR CLASS 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Tuition classes in Jalandhar, Best MATH SCIENCE SST ENGLISH COMPUTER FOR CLASS 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Tuition near me, Best MATH SCIENCE SST ENGLISH COMPUTER FOR CLASS 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Tuition center near me, Best MATH SCIENCE SST ENGLISH COMPUTER FOR CLASS 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Tuition center in Jalandhar, Best MATH SCIENCE SST ENGLISH COMPUTER FOR CLASS 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Tuition institute in Jalandhar, Best MATH SCIENCE SST ENGLISH COMPUTER FOR CLASS 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Tuition preparation in Jalandhar, Best MATH SCIENCE SST ENGLISH COMPUTER FOR CLASS 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Tuition classes in Jalandhar, MATH SCIENCE SST ENGLISH COMPUTER FOR CLASS 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Tuition Jalandhar, Best MATH SCIENCE SST ENGLISH COMPUTER FOR CLASS 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Tuition Jalandhar, MATH SCIENCE SST ENGLISH COMPUTER FOR CLASS 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Tuition center Jalandhar, MATH SCIENCE SST ENGLISH COMPUTER FOR CLASS 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Tuition institute Jalandhar, MATH SCIENCE SST ENGLISH COMPUTER FOR CLASS 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Tuition preparation Jalandhar, MATH SCIENCE SST ENGLISH COMPUTER FOR CLASS 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Tuition classes Jalandhar, Best Tuition for MATH SCIENCE SST ENGLISH COMPUTER FOR CLASS 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12, Best Tuition for MATH SCIENCE SST ENGLISH COMPUTER FOR CLASS 4 5 6 9463138669|CBSE ICSE Math Science Computer For Class 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Tui...

9463138669|CBSE ICSE Math Science Computer For Class 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Tui...ANAND CLASSES - A SCHOOL OF COMPETITIONS
Call 9463138669 - ANAND CLASSES | Agniveer Women Army GD Soldier Clerk Technical Bharti Recruitment Training Coaching Center Academy Classes In Jalandhar Punjab.9463138669|Agniveer Women Army GD Soldier Clerk Technical Bharti Recruitment ...

9463138669|Agniveer Women Army GD Soldier Clerk Technical Bharti Recruitment ...ANAND CLASSES - A SCHOOL OF COMPETITIONS
Call 9463138669 - ANAND CLASSES | Agniveer Army GD Soldier Clerk Technical Bharti Recruitment Training Coaching Center Academy Classes In Jalandhar Punjab. Agneeveer Army Clerk SKT Exam Coaching Center in Jalandhar Punjab, Agneeveer Army Clerk SKT Exam Training Center in Jalandhar Punjab, Agneeveer Army Clerk SKT Exam Coaching Institute in Jalandhar Punjab, Agneeveer Army Clerk SKT Exam Coaching Academy in Jalandhar Punjab, Agneeveer Army Clerk Technical Exam Coaching Center in Jalandhar Punjab, Agneeveer Army Clerk Technical Exam Training Center in Jalandhar Punjab, Agneeveer Army Clerk Technical Exam Coaching Institute in Jalandhar Punjab, Agneeveer Army Clerk Technical Exam Coaching Academy in Jalandhar Punjab, Agneeveer Army GD Soldier Bharti Recruitment Exam Coaching Center in Jalandhar Punjab, Agneeveer Army GD Soldier Bharti Recruitment Exam Training Center in Jalandhar Punjab, Agneeveer Army GD Soldier Bharti Recruitment Exam Coaching Institute in Jalandhar Punjab, Agneeveer Army GD Soldier Bharti Recruitment Exam Coaching Academy in Jalandhar Punjab, Agneeveer Army Clerk SKT Bharti Recruitment Exam Coaching Center in Jalandhar Punjab, Agneeveer Army Clerk SKT Bharti Recruitment Exam Training Center in Jalandhar Punjab, Agneeveer Army Clerk SKT Bharti Recruitment Exam Coaching Institute in Jalandhar Punjab, Agneeveer Army Clerk SKT Bharti Recruitment Exam Coaching Academy in Jalandhar Punjab, Agneeveer Army Clerk Technical Bharti Recruitment Exam Coaching Center in Jalandhar Punjab, Agneeveer Army Clerk Technical Bharti Recruitment Exam Training Center in Jalandhar Punjab, Agneeveer Army Clerk Technical Bharti Recruitment Exam Coaching Institute in Jalandhar Punjab, Agneeveer Army Clerk Technical Bharti Recruitment Exam Coaching Academy in Jalandhar Punjab9463138669|Agniveer Army GD Soldier Clerk Technical Bharti Recruitment Traini...

9463138669|Agniveer Army GD Soldier Clerk Technical Bharti Recruitment Traini...ANAND CLASSES - A SCHOOL OF COMPETITIONS
Call 9463138669-ANAND CLASSES | Airforce Airman Group X & Y Agniveer Vayu Bharti Recruitment Training Exam Coaching Center Academy Classes In Jalandhar Punjab. Airforce Airman Group X & Y Agniveer Vayu Bharti Recruitment Training Exam Coaching Center in Alawalpur, Airforce Airman Group X & Y Agniveer Vayu Bharti Recruitment Training Exam Coaching Center in Kartarpur, Airforce Airman Group X & Y Agniveer Vayu Bharti Recruitment Training Exam Coaching Center in Jandiala, Airforce Airman Group X & Y Agniveer Vayu Bharti Recruitment Training Exam Coaching Center in Kapurthala, Airforce Airman Group X & Y Agniveer Vayu Bharti Recruitment Training Exam Coaching Center in Phagwara, Airforce Airman Group X & Y Agniveer Vayu Bharti Recruitment Training Exam Coaching Center in Nakodar, Airforce Airman Group X & Y Agniveer Vayu Bharti Recruitment Training Exam Coaching Center in Nurmahal, Airforce Airman Group X & Y Agniveer Vayu Bharti Recruitment Training Exam Coaching Center in Dhilwan, Airforce Airman Group X & Y Agniveer Vayu Bharti Recruitment Training Exam Coaching Center in Begowal, Airforce Airman Group X & Y Agniveer Vayu Bharti Recruitment Training Exam Coaching Center in Shahkot, Airforce Airman Group X & Y Agniveer Vayu Bharti Recruitment Training Exam Coaching Center in Phillaur, Airforce Airman Group X & Y Agniveer Vayu Bharti Recruitment Training Exam Coaching Center in Hoshiarpur, Airforce Airman Group X & Y Agniveer Vayu Bharti Recruitment Training Exam Coaching Center in Banga, Airforce Airman Group X & Y Agniveer Vayu Bharti Recruitment Training Exam Coaching Center in Hariana, Airforce Airman Group X & Y Agniveer Vayu Bharti Recruitment Training Exam Coaching Center in Moga, Airforce Airman Group X & Y Agniveer Vayu Bharti Recruitment Training Exam Coaching Center in Goraya, Airforce Airman Group X & Y Agniveer Vayu Bharti Recruitment Training Exam Coaching Center in Kartārpur, Airforce Airman Group X & Y Agniveer Vayu Bharti Recruitment Training Exam Coaching Center in Adampur, Airforce Airman Group X & Y Agniveer Vayu Bharti Recruitment Training Exam Coaching Center in Jandu Singha, Airforce Airman Group X & Y Agniveer Vayu Bharti Recruitment Training Exam Coaching Center in Jandiāla, Airforce Airman Group X & Y Agniveer Vayu Bharti Recruitment Training Exam Coaching Center in Jalandhar Cantt, Airforce Airman Group X & Y Agniveer Vayu Bharti Recruitment Training Exam Coaching Center in Khambra, Airforce Airman Group X & Y Agniveer Vayu Bharti Recruitment Training Exam Coaching Center in Sansarpur, Airforce Airman Group X & Y Agniveer Vayu Bharti Recruitment Training Exam Coaching Center in Sufipind, Airforce Airman Group X & Y Agniveer Vayu Bharti Recruitment Training Exam Coaching Center in Dhina, Airforce Airman Group X & Y Agniveer Vayu Bharti Recruitment Training Exam Coaching Center in Beas, Airforce Airman Group X & Y Agniveer Vayu Bharti Recruitment Training Exam Coaching Center in Bhegoawal9463138669|Airforce Airman Group X & Y Agniveer Vayu Bharti Recruitment Train...

9463138669|Airforce Airman Group X & Y Agniveer Vayu Bharti Recruitment Train...ANAND CLASSES - A SCHOOL OF COMPETITIONS
Call 9463138669 - ANAND CLASSES | Agniveer Army Nursing Assistant Bharti Recruitment Training Coaching Center Academy Classes In Jalandhar Punjab9463138669|Agniveer Army Nursing Assistant Bharti Recruitment Training Coachi...

9463138669|Agniveer Army Nursing Assistant Bharti Recruitment Training Coachi...ANAND CLASSES - A SCHOOL OF COMPETITIONS
Similar to Exponential growth and decay (20)
9463138669|Navy AA SSR Sailors Agniveer Bharti Recruitment Training Exam Coac...

9463138669|Navy AA SSR Sailors Agniveer Bharti Recruitment Training Exam Coac...
9463138669|CBSE ICSE Math Science Computer For Class 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Tui...

9463138669|CBSE ICSE Math Science Computer For Class 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Tui...
ANAND CLASSES-CBSE ICSE Math Science Computer For Class 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 ...

ANAND CLASSES-CBSE ICSE Math Science Computer For Class 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 ...
9463138669|Agniveer Women Army GD Soldier Clerk Technical Bharti Recruitment ...

9463138669|Agniveer Women Army GD Soldier Clerk Technical Bharti Recruitment ...
9463138669|Agniveer Army GD Soldier Clerk Technical Bharti Recruitment Traini...

9463138669|Agniveer Army GD Soldier Clerk Technical Bharti Recruitment Traini...
9463138669|Airforce Airman Group X & Y Agniveer Vayu Bharti Recruitment Train...

9463138669|Airforce Airman Group X & Y Agniveer Vayu Bharti Recruitment Train...
9463138669|Agniveer Army Nursing Assistant Bharti Recruitment Training Coachi...

9463138669|Agniveer Army Nursing Assistant Bharti Recruitment Training Coachi...
Growth Models 173 © David Lippman Creative Commons BY.docx

Growth Models 173 © David Lippman Creative Commons BY.docx
More from Jessica Garcia
More from Jessica Garcia (20)
How do fractions apply to unit rates?7th daily 10 14-14 complex fractions and...

How do fractions apply to unit rates?7th daily 10 14-14 complex fractions and...
7th daily 10 10-14 proportions vocabulary and long division

7th daily 10 10-14 proportions vocabulary and long division
7th daily 10 10-14 proportions vocabulary and long division

7th daily 10 10-14 proportions vocabulary and long division
Recently uploaded
Recently uploaded (20)
ICT Role in 21st Century Education & its Challenges.pptx

ICT Role in 21st Century Education & its Challenges.pptx
Russian Escort Service in Delhi 11k Hotel Foreigner Russian Call Girls in Delhi

Russian Escort Service in Delhi 11k Hotel Foreigner Russian Call Girls in Delhi
Seal of Good Local Governance (SGLG) 2024Final.pptx

Seal of Good Local Governance (SGLG) 2024Final.pptx
Measures of Central Tendency: Mean, Median and Mode

Measures of Central Tendency: Mean, Median and Mode
Exponential growth and decay
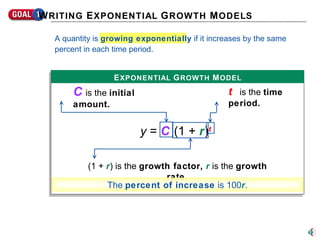
- 1. C is the initial amount. t is the time period. (1 + r ) is the growth factor, r is the growth rate. The percent of increase is 100 r . y = C (1 + r ) t E XPONENTIAL G ROWTH M ODEL W RITING E XPONENTIAL G ROWTH M ODELS A quantity is growing exponentially if it increases by the same percent in each time period.
- 2. C OMPOUND I NTEREST You deposit $500 in an account that pays 8% annual interest compounded yearly. What is the account balance after 6 years? S OLUTION M ETHOD 1 S OLVE A S IMPLER P ROBLEM Find the account balance A 1 after 1 year and multiply by the growth factor to find the balance for each of the following years. The growth rate is 0.08 , so the growth factor is 1 + 0.08 = 1.08 . A 1 = 500 ( 1.08 ) = 540 Balance after one year A 2 = 500 ( 1.08 )( 1.08 ) = 583.20 Balance after two years A 3 = 500 ( 1.08 )( 1.08 )( 1.08 ) = 629.856 A 6 = 500 ( 1.08 ) 6 793.437 Balance after three years Balance after six years Finding the Balance in an Account • • • • • •
- 3. S OLUTION M ETHOD 2 U SE A F ORMULA C OMPOUND I NTEREST You deposit $500 in an account that pays 8% annual interest compounded yearly. What is the account balance after 6 years? Use the exponential growth model to find the account balance A . The growth rate is 0.08 . The initial value is 500 . E XPONENTIAL G ROWTH M ODEL C is the initial amount. t is the time period. (1 + r ) is the growth factor, r is the growth rate. The percent of increase is 100 r . y = C (1 + r ) t E XPONENTIAL G ROWTH M ODEL 500 is the initial amount. 6 is the time period. (1 + 0.08 ) is the growth factor, 0.08 is the growth rate. A 6 = 500 ( 1.08 ) 6 793.437 Balance after 6 years A 6 = 500 (1 + 0.08 ) 6 Finding the Balance in an Account
- 4. A population of 20 rabbits is released into a wildlife region. The population triples each year for 5 years. Writing an Exponential Growth Model
- 5. So, the growth rate r is 2 and the percent of increase each year is 200%. 1 + r = 3 A population of 20 rabbits is released into a wildlife region. The population triples each year for 5 years. a. What is the percent of increase each year? S OLUTION The population triples each year, so the growth factor is 3. 1 + r = 3 Reminder: percent increase is 100 r . So, the growth rate r is 2 and the percent of increase each year is 200%. So, the growth rate r is 2 and the percent of increase each year is 200% . 1 + r = 3 Writing an Exponential Growth Model The population triples each year, so the growth factor is 3.
- 6. A population of 20 rabbits is released into a wildlife region. The population triples each year for 5 years. b. What is the population after 5 years? S OLUTION After 5 years, the population is P = C (1 + r ) t Exponential growth model = 20 (1 + 2 ) 5 = 20 • 3 5 = 4860 Help Substitute C , r , and t . Simplify. Evaluate. There will be about 4860 rabbits after 5 years. Writing an Exponential Growth Model
- 7. G RAPHING E XPONENTIAL G ROWTH M ODELS Graph the growth of the rabbit population. S OLUTION Make a table of values, plot the points in a coordinate plane, and draw a smooth curve through the points. P = 20 ( 3 ) t Here, the large growth factor of 3 corresponds to a rapid increase A Model with a Large Growth Factor t P 4860 60 180 540 1620 20 5 1 2 3 4 0 0 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 1 7 2 3 4 5 6 Time (years) Population
- 8. A quantity is decreasing exponentially if it decreases by the same percent in each time period. C is the initial amount. t is the time period. (1 – r ) is the decay factor, r is the decay rate. The percent of decrease is 100 r . y = C (1 – r ) t W RITING E XPONENTIAL D ECAY M ODELS E XPONENTIAL D ECAY M ODEL
- 9. C OMPOUND I NTEREST From 1982 through 1997, the purchasing power of a dollar decreased by about 3.5% per year. Using 1982 as the base for comparison, what was the purchasing power of a dollar in 1997? S OLUTION Let y represent the purchasing power and let t = 0 represent the year 1982. The initial amount is $1. Use an exponential decay model. = ( 1 )(1 – 0.035 ) t = 0.965 t y = C (1 – r ) t y = 0.965 15 Exponential decay model Substitute 1 for C , 0.035 for r . Simplify. Because 1997 is 15 years after 1982, substitute 15 for t . Substitute 15 for t . The purchasing power of a dollar in 1997 compared to 1982 was $0.59. 0.59 Writing an Exponential Decay Model
- 10. G RAPHING E XPONENTIAL D ECAY M ODELS Graph the exponential decay model in the previous example. Use the graph to estimate the value of a dollar in ten years. S OLUTION Make a table of values, plot the points in a coordinate plane, and draw a smooth curve through the points. Your dollar of today will be worth about 70 cents in ten years. y = 0.965 t Help Graphing the Decay of Purchasing Power 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1 12 3 5 7 9 11 Years From Now Purchasing Power (dollars) 2 4 6 8 10 t y 0.837 0.965 0.931 0.899 0.867 1.00 5 1 2 3 4 0 0.7 0.808 0.779 0.752 0.726 10 6 7 8 9
- 11. G RAPHING E XPONENTIAL D ECAY M ODELS y = C (1 – r ) t y = C (1 + r ) t E XPONENTIAL G ROWTH M ODEL E XPONENTIAL D ECAY M ODEL 1 + r > 1 0 < 1 – r < 1 An exponential model y = a • b t represents exponential growth if b > 1 and exponential decay if 0 < b < 1 . C is the initial amount. t is the time period. E XPONENTIAL G ROWTH AND D ECAY M ODELS C ONCEPT S UMMARY (1 – r ) is the decay factor, r is the decay rate. (1 + r ) is the growth factor, r is the growth rate. (0, C) (0, C)
- 13. Graphs A 0 A 0
- 20. E XPONENTIAL G ROWTH M ODEL C is the initial amount. t is the time period. (1 + r ) is the growth factor, r is the growth rate. The percent of increase is 100 r . y = C (1 + r ) t
- 21. E XPONENTIAL D ECAY M ODEL C is the initial amount. t is the time period. (1 – r ) is the decay factor, r is the decay rate. The percent of decrease is 100 r . y = C (1 – r ) t
