Art Periods and Movements Summary Table
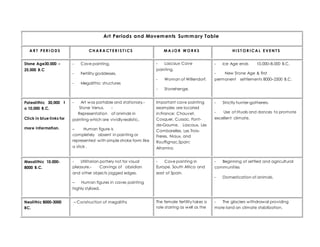
- 1. Art Periods and Movements Summary Table A R T PE R I O DS CH A R A CT E R I S T I CS M A JO R W O R KS H I S T O R I CA L E VE N T S Stone Age30,000 – 25,000 B.C - Cave painting. - Fertility goddesses. - Megalithic structures - Lascaux Cave painting. - Woman of Willendorf. - Stonehenge. - Ice Age ends 10,000–8,000 B.C. - New Stone Age & first permanent settlements 8000–2500 B.C. Paleolithic 30,000 t o 10,000 B.C. Click in blue links for more information. - Art was portable and stationary.- Stone Venus. - Representation of animals in painting which are vividly realistic. – Human figure is completely absent in painting or represented with simple stroke form like a stick . Important cave painting examples are located in:France: Chauvet, Cosquer, Cussac, Font- de-Gaume, Lascaux, Les Combarelles, Les Trois- Freres, Niaux, and Rouffignac.Spain: Altamira. - Strictly hunter-gatherers. - Use of rituals and dances to promote excellent climate. Mesolithic 10.000- 8000 B.C. - Utilitarian pottery not for visual pleasure.- Carvings of obsidian and other objects jagged edges. – Human figures in caves painting highly stylized. - Cave painting in Europe, South Africa and east of Spain. - Beginning of settled and agricultural communities - Domestication of animals. Neolithic 8000-3000 BC. – Construction of megaliths The female fertility takes a role starring as well as the - The glaciers withdrawal providing more land an climate stabilization.
- 2. – Stylized pictographs. goddess mother. The figurines are now clay and baked. - Humans were settling in agrarian societies. Prehistoric Art. Cooper, Bronze & Iron Ages. Cooper Age: - Was one of the first metal using by mans in its natural state due to not know how to melted. Bronze Ages. 2500-800 B.C. - Intensification of trades. - Labor specialization. - Social differentiation. Iron Ages 2000-1500 B.C. – The last period of prehistory prior to the beginning of the story with the Cooper age: - Elaboration of cuneiform glass and ceramic rope pottery. - Spirals of gold. - Abundant so-called “Palmela” arrows. - Triangular daggers in copper. - Perforated plates. Bronze Age mayor work: - The petro glyphs, paint on smaller objects, sculptures and steles, make frequent use of ornament and artistic images for decoration of tools and household goods. Cooper age: - The man perfected the techniques of pottery allowing to experiment with metallurgical processes. - Most manufactured items were tools. Bronze Age: - Spread of agriculture and animal husbandry. – Mastery of metal developing new alloys. Iron Ages: - Assyria originate and impressive
- 3. invention of writing. – Development of the artistic skills due to better use of time when the man have improve tools elaborated with iron. – Developing of the military technology and strong weapons. Iron Ages - Iron is a good material for the manufacture of saws, axes, adzes and nails. - Nordic petro glyphs. military technology. - The iron replaced bronze as the material of manufacture of instruments and weapons. - Celtic and Nordic people star using iron for tools & weapons. Minoan Culture - Pacific inclines. - Decoration with nature motive. - Proportional human body representation. - Politeist religion. Matriarcal sociaty. - Found for Physical activities. - Important trades activities. - Taurocatapsia representation in painting & relieves. - Goddess of serpents. - Ostentatious jewelry. Skilled goldsmith. – Dancing woman widely represented in art. – Dolphins fresco at the Quing chamber’s. Minoan historical events:-Development as a Matriarchal society.- Foundation of the first palaces. – Sudden disappearance due to conquests and natural disasters. Mesopotamian3500– 539 B.C. Sumerian Culture: Sumerian Culture: - The most ancient civilization in this region with clay figurine representation, cuneiform tablets and Sumerian: - Ubaid Art. - Clay feminine Sumerians: - Invention of writing around 3400 B.C. - The dynasty of Sargon between (2300
- 4. Babylonian Culture: Assyrian Culture: seals. Babylonian Culture: - Glazed brick decoration. - cuneiform writing tables and seals. - Hammurabi’s code of laws. - Gilgamesh Epic representation in Art pieces. Assyrian Culture: – Warrior people with art and narration in stone relief predominant Lion representation and winged Sphinxes. figurines, - Standard of Ur. Babylon: - Gate of Ishtar. - Diorite Stele of Hammurabi’s Code. - Gilgamesh’s Epic flood tablet story. Assyria: Nimrud or Jursabad doors with winged Sphinxes The construction of Ziggurats. – 2223 BC) build ziggurats and clay seals. - Rule of Naramsin 2230 BC. Babylon: - Hammurabi writes his code of laws 1780 B.C. - Abraham founds monotheism. - King Nebuchadnezzar palace is builder in Babylon. Assyria: About 884 BC Assyria gets at the head of the power in a vast region under Ashur- Nassir-Pal reign. Aqueménida Period (550-330) B.C.- Monumental style with sculptures in relief attached to architectural joints with profuse but simple decoration. – Metalwork representation evading the ambiguous, obscure or clumsy. Same principal of simplicity apply to Aqueménida Period - Glazed brick are use to decorated in Darius palace. - Palace of Persepolis. - Relief on the palace - During the reign of Cyrus the Great, Persia expands to the West and Northwest beyond the borders of what is today Iran to include Babylonia, some of the Aegean Islands and Anatolia.- Dario’s Government (522 to 486 BC) .The rule of Darius covers many
- 5. Persian Culture painting. – Use of low reliefs glazed brick from Babylon;s technique. – Simplicity of the messages avoiding complications, the dark or confuse. Sassanid Period – Architectural decorations in carved stone, walls covered with stucco decorated with vivid and contrasting colors. – Attractive and deeply expressive with refined decoration, emotional & imaginative. – Representation of abstract ideas without violating the terms of the visual aspects. Islamic Period – Stoning architecture. – Calligraphy & decoration of walls representing the power of rulers. - Important metalwork in weapons decorations. Sassanid Period. - Spectacular glaze decorations. - Detailed metal work in daily used objects and weapons. - Drapery and jewelry mastery. - Islamic architecture. - Calligraphy and decoration of manuscript. cultures. He and his son used foreign artists to promote and strengthenits image of power. Sassanid Period - Greatest achievements of Persian culture, the last great Iranian Empire before the Islamic conquest of Persia. - The conquest of Persia by Alexander the great began the spread of Hellenistic art into Western Asia. Islamic Period - The adoption of the Islam as a religion throughout the territory resulted in important changes in the Persian culture. - The Persians became the main
- 6. manuscripts. – Decoration of the walls with stucco and covered with figurative colored and detailed paints. - Handmade Persian rugs. - Pottery with influence of Chinese ceramic. - Metalwork with arabesques. instrument of the expansion of Islam in most of the rest of the Asian territory. Egyptian 3100 – 30 B.C. - Art with an afterlife focus with destination to the Church:- Pyramids and tomb painting.- Reverence to pharaohs.- The artist is more a craftsman, completely anonymous.- Hieratic & utilitarian sculptures. – The image carries a symbolism and a message; it is not with the intention of showing beauty. – The figures show position of frontality; is a fixed concept which is repeated. - Imhotep, – Step Pyramid – The great pyramid of Giza, built by King Cheops about 4,500.- Bust of Nefertiti, – Mask of Tutankhamen. – Sculpture of the scribe. – The Sphinges. - King Narmer unites Upper/Lower Egypt (3100 B.C).- Ramses II battles the Hittites 1274 B.C.- Persian domination of Egypt.1085-333: Persian domination of Egypt.- The domain of Egypt under the Greek and the Roman.- Cleopatra dies 30B.C. Greek and Hellenistic 850 –31 B.C. - Greek dealism of balance, perfect proportions and mathematical measures applied to all manifestation of art. Representation of an idilic art oriented to be decorative an highlighting the beauty of the forms. - Architectural orders (Doric, - Construction of the Parthenon. - The Korai and the Kouroi archaic sculpture. - Masters sculptures artist individually highlight like Myron, Phidias, Polycleitus, - Athens defeats Persia at Marathon 490 B.C.- Peloponnesian Wars (431–404) B.C. - Alexander the Grate’s conquests Greece 336 -323 B.C - Hellenistic Period: 4th century (B.C) from the reign of Alexander the great (336-323 BC) until the conquest of Greece by Rome, in the middle of the
- 7. Ionic, Corinthian) - Great Pottery, red ceramic, black figure ceramic. Praxiteles, scopas, Lisipo. - The Athena Farnese. second century B.C). Roman 500 B.C– 476 A.D) – Roman realism: practical and utilitarian very down to earth.- Introduction of new techniques in Art, but still with Greek influences.- Art to the services of the propaganda of the Roman’s Empire power. – It addresses both the idealism and realism in the art. – Central themes in Roman sculpture are portraits. – Mayor accomplishments in architecture – Erotic & sensual content in painting. – Anonymous Illusionist or stages painting. - Augustus of Primaporta.- Roma’s Coliseums. – Trajan’s Column. – The Discobolo of Myron. – Caracalla Thermals’. – Caracalla Mosaics. – Constantine Emperor Sculpture. – City of Pompeii & Herculaneum paint’s Julius Caesar is assassinated 44 B.C. Augustus proclaimed Emperor 27 B.C. Diocletian splits Empire 292 A.D. Rome falls 476 A.D. Emperor Constantine adopted Christianisms. India Culture: - Dynamic colorful multi-ethnic and multicultural features.- Buddhism temples carving in the mountains.- Serene, meditative & solemner art in Buddhism & Jainism. – Erotic & symbolisms in Hinduism - Polychrome sculptures. - Taj Majal. - Alora Cave. - Khajuraho Temple. - Templo Jaina de Vimala - Dravidians develop advances urbanisms & culture. - The Brahmanism prosperous social cast & religious made an important statement in India. - The Buddhism & Jainism prosper.
- 8. sculpture. – Sensuality, dramatics, movement & symbolisms in Hinduism painting. – Splendor in jewelry and textiles. – Nature & their polytheist religious pantheon are the main elements of representation in their art. Vasahi en el monte Abu. - Ajanta Budhist Temple. Maharastra. - The Mahabharata and the Ramayana, two major Sanskrit epics manuscripts of ancient Indiath India region Temples. - The Hinduism modify the ancestor polytheist Brahmanism pantheon. - Persia Invade India been the last conquest by the Mughal very important for the art in India. - The England Indian’s Company establishes a colony beginning from the littorals of India and then extended. Chinese, and Japanese 653 B.C–1900 A.D. - Serene, meditative art.- Arts of the Floating World. – Represent idealist lanscape with realistic detail. – Homenage to nature and to the lanscaping in painting. – After a colourful period in painting this one is reduced to duo tones color representation in furthers periods. – Important ceramic production using porcelain made with caolin. – Detailed painting in paper, wood and fabrics. – Abundant use of caligraphy in paints been as much important as the paint itself. – Magnificent works in ivory amd jade. Painters- Gu Kaizhi.- – Li Cheng. – Guo Xi. – Hokusai. – Hiroshige. Birth of Buddha 563 B.C;Silk Road opens (1st century B.C. Buddhism spreads to China 1st–2nd centuries A.D and Japan 5th century A.D
- 9. – Architecture addresed to practical use not ornamental and intedrated to the lanscape around the building. Wooden structure with repetitive plant. – Wide representation of Budda images with particular Asiatic feature and postures. Byzantine and Islamic 476–1453 A.D - The symbolic character of the works becomes more important over even its expression and aesthetic, responding to the theology and ecclesiastical power representation.– They do not imitate the image of the man and the nature in details, they made instead a rational representation of the concept of those images.- – Rich materials in Byzantine.Mosaic’s, with abundance in the use of gold. (Glowing sensation). - Heavenly Byzantine mosaics.- Islamic architecture and amazing maze-like design.- Mural Painting.- Wood & Ivory diptychs.- Hagia Sophia Cathedral. – San Vitale of Ravenna – Andrei Rublev. – Mosque of Córdoba. – Tthe Alhambra in Spain. - Justinian partly restores Western Roman Empire (533– 562). A.D. - Iconoclast controversy 726– 843 A.D. - Birth of Islam 610 A.D. - Muslim Conquests 632–732 A.D.
- 10. Art Appreciation Art Periods and Movements Summary Submit t ed by: John Lawrence S. Ting Ronald P.Castillo Myla A.Viray Jeric L. Hernandez Jacques Cymon E. Mendoza Aldrin M. Manalo Submit t ed t o: Ms. Leslee B. Manguerra
