NC Human Impact Unit
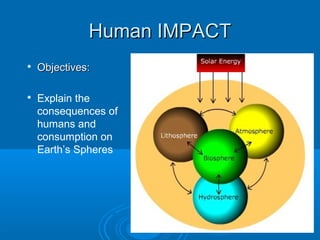
- 1. Human IMPACT Objectives: Explain the consequences of humans and consumption on Earth’s Spheres
- 2. Humans and Nature: An Overview “The environmental crisis is an outward manifestation of a crisis of mind and spirit. There could be no greater misconception of its meaning than to believe it is concerned only with endangered wildlife, human-made ugliness, and pollution. These are part of it, but more importantly, the crisis is concerned with the kind of creatures we are and what we must become in order to survive.” ~ Lynton K. Caldwell
- 3. If you really got a hold of anything in the Universe, you find out that it’s hitched to everything else.— John Muir, Founder, Sierra Club Diagram makes it clear that environmental science is multidisciplinary and interdisciplinary. That is, “it takes all kinds” of observations and inputs to “do” environmental science.
- 4. The Human Impact Problem? Several themes—recurring and inter-connected Human population x demand for resources = root problem. (Problem for each other as individuals, communities, nations; for the rest of the ecosphere.) The impact of environment on human health
- 5. Assignment – Cats of Borneo A simple exercise to get you thinking about the interconnectedness of man, environment and how one decision can cause a domino effect in the scheme of environment! Complete “Cats of Borneo” activity You will receive an envelope with 13 statements which are numbered. Your job as a group is to order them by event (not numerically!) Based on a true story
- 6. Change in the Biosphere = change in the environment Changes in the Lithosphere •Leads to local and global health issues •Competition for resources •Destruction of habitats and upheaval of human populous
- 7. Changes in the Atmosphere Increased global temperatures – greenhouse effect? Normal or enhanced? Loss of ozone due to chlorfluorocarbons (CFCs) Increase of natural gases (Sulfur and CO2) due to volcanic eruptions
- 8. The Great American Hypocrite
- 9. Aquatic and marine resources— longneglected, overexploited, directly and indirectly* impacted. Changes in the hydrosphere *remember, water flows downhill—The 1st Law of Ecology
- 10. What characteristics of Earth make life possible? Water Air (nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide and water vapor) Soil Sun – driving force behind all life processes.
- 11. Biosphere (Ecosphere) All the parts of Earth that support and contain life. Reaches from the floor of the ocean to the tops of the mountains. Approximately 20 km (12.4 mi) thick. If the earth were an apple, the ecosphere would be no thicker than the apple’s skin!
- 12. Environment Everything that surrounds a particular organism.
- 13. Ecology Study of the interaction between organisms and their environment, composed of abiotic (NON-Living) and biotic (living) factors
- 14. Ecosystem Structure Food Web – a network of food chains representing the feeding relationships among the organisms in an ecosystem (complicated).
- 16. Biological Magnification The increasing concentration of a pollutant in organisms at higher trophic levels in a food web. Ex. In 1972 the US banned the use of DDT. By 1991 bald eagle population rebounded 4X.
- 17. Diversity and Stability A deciduous forest is an example of a stable ecosystem that has a food web with many links. A small disturbance has a small effect on a deciduous forest. Conversely, a tundra has few links in the web, therefore a small disturbance can have a larger impact.
- 18. Energy in the Ecosystem The ultimate and only significant source of energy in most ecosystems is that radiated by the sun. This energy is the driving force of photosynthesis. Of the total sunlight received on the earth, only 20-25% is available for photosynthesis because only the longer wavelengths are used in photosynthesis.
- 19. Key players in ECOLOGY: Producers, Consumers and Decomposers All biomes (and ecosystems within biomes) contain three different kinds of living things: 1) Decomposers 2) Producers 3) Consumers
- 20. Producers (Autotrophs) Organisms that make their own food from inorganic molecules and energy. EX. - Plants
- 21. Consumers (Heterotrophs) 1) Cannot produce their own food (animals, humans- any living thing that does not have chlorophyll) 2) Must eat other organisms (plants and/or animals) to get their energy and food. EX: animals, fungi, protists and bacteria
- 22. Bacteria and fungi that consume the bodies of dead organisms and other organic wastes. Decomposers complete the cycle of matter in the ecosystem.
- 23. Trophic Level What scientists call the different feeding levels of organisms in a ecosystem. From the root “troph” – meaning to feed or nourish.
- 24. Trophic Levels Number pyramid the higher one moves, each consecutive layer or level contains fewer organisms than the level below it.
- 25. Biomass The total amount of organic matter present in a trophic level. Potentially food for the next trophic level. As organisms do work, they use energy, and must continue to take in additional fuel to continue doing work
- 26. Cycles of Matter Chemical composition of human body Water Cycle Carbon Cycle Nitrogen Cycle
- 27. Water Cycle – All the water on Earth which is continually cycled from hydrosphere to atmosphere and lithosphere
- 28. Carbon Cycle Plants use CO2 and sunlight to make sugars and starches during photosynthesis
- 30. Nitrogen Cycle Organisms require nitrogen in order to make amino acids, the building blocks of proteins. 80% of Earth's atmosphere is made up of nitrogen in its gas phase. Plants take up the nitrates and convert them to proteins that then travel up the food chain through herbivores and carnivores. When organisms excrete waste, the nitrogen is released back into the environment.
- 32. Competitive Exclusion The extinction of a population due to direct competition with another species for a resource. If two species try to share the same niche in the same habitat, they will compete for resources. If one is better than the other, one will have to move to another area or extinction may occur.
- 33. Population Growth Exponential Growth – population growth in which the rate of growth in each generation is a multiple of the previous generation.
- 34. City Lights from Space Geospatial demographers, such as Deborah Balk, use satellite images of the Earth at night to estimate population densities.
- 35. Human Population on the 50th Earth Day The following is from an insert to a solicitation letter from the group Zero Population Growth. In the seconds it takes you to read this sentence, 24 people will be added to the Earth’s population. Before you’ve finished this letter, that number will reach 1,000. Within an hour ... 11,000. By day’s end ... 260,000. Before you go to bed two nights from now, the net growth in human numbers will be enough to fill a city the size of San Francisco. It took four million years for humanity to reach the 2 billion mark. Only 30 years to add a third billion. And now we’re increasing by 95 million every single year. No wonder they call it the human race.
- 36. Carrying Capacity The number of individuals of a species that can be supported by an ecosystem. As population grows, it takes more from its habitat. Resources such as food and living space become scarce. As resources become scarce, individuals begin to compete.
- 38. Ecological Succession Change is a fact of life! Living things have evolved in response to change. As an environment changes, the community changes with it. In many cases, different communities follow one another in a definite pattern.
- 39. Evolution and Adaptation Ecosystems change over time and changes in the environment affect the evolution of populations.
- 40. Interdependence Health depends on resources. Good health depends on accessibility to sustainable resources.
- 41. Interdependence Bad health results from inaccessibility to sustainable resources or exposure to a hazard. Both exist in the environment. Therefore, quality of health depends on the environment.
- 42. Community Action and the Environment What are the environmental problems that we face as communities, as states, as a country, and as part of the global community? How many environmental problems are you aware of?
- 43. Human Population and Carrying Capacity What impact does an ever increasing population have on global health issues?
- 44. What characteristics of life allow it to influence the environment on the global scale? 1. Life spreads exponentially 7 BILLION The environmental problems we face – population growth, wasteful use of resources, destruction and degradation of wildlife habitats, extinction of plants and animals, poverty, and pollution – are interconnected and are growing exponentially.
- 45. More People = More Competition According to the United Nations, world population reached 7 billion on October 31, 2011 According to the most recent estimates, world population is expected to reach 8 billion people in the spring of 2024. What matters is that we are competing for essential resources
- 46. Which leads to global environmental problems like…. Competition Resource Depletion Pollution Risk, Toxicology and Human Health Climate, Global Warming and Ozone Depletion Water resources and water quality Solid and hazardous waste disposal
- 48. Global Warming? TRUE or NOT??? Regardless of whether you believe that man is enhancing global warming or we are just in a “normal” warming period – the ensuing environmental changes will have an impact on both animals and humans! 60 Minutes Video on evidence in Antartica
- 49. What impact will climate change (global warming) have on the human species? Food shortages Loss of fresh water Increase in disease 6 of Change! o
- 50. Climate Change and Food Climate Change and Food Security: Out of
- 51. Now that scientists agree? What do we do….. How to feed the world in 2050: actions in a changing climate
- 52. Climate and Human Human Health What impact will global warming have on our human health? Think about disease and the spread of disease – can you make a connection between climate change and the spread of diseases?
- 53. Kinds of health impacts resulting from climate change: Direct- result from weather extremes. Consequences from ecological disruption. Consequences resulting from climate-induced economic disruption, e.g. traumatic, infectious, nutritional, psychological
- 54. Social factors affecting health Population density Level of economic development of the country Food availability Pre-existing health status Availability of health care
- 55. Human Population Dynamics What have we learned about the impact of population on: •Resources? •Global Health? •Global Warming? :28
Notas del editor
- Those most affected by heat extremes are the socially isolated elderly and poor. Populations living at the margins of malaria and dengue habitat, without effective primary health care, will be the most affected if these diseases expand their geographic range.