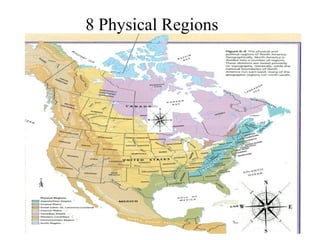
Physical regions
- 2. Topography: Appalachian Region -Made up of different moutain ranges -Old mountains formed 300,000,000 years ago -once sharp now rolling moutains, hills -Contains fertile plateaus and river valleys Vegetation: Climate: -Affected by two ocean currents -Labrador current causes freezing in winter Economic activity: -Originally heavily forested -205, 000 square mile region -Deciduous, coniferous trees -once depended on minning, forestry, -Could survive in mountain soils agriculture, chemical industries Environmental concerns: -Now include a variety of manufacturing -Over the past decads the hobe 21 mountain top removal coal minning opreration has obliterated 23 square miles of the high land -minning operation clear cut the hillsides and "fill"the mountain hollows to the brim -extends more than 1000 miles
- 3. Topography: The Coastal PlainsClimate: - Average evalation of less then 200 meters -In the north it has cold, snowy above sea level winters -Surface mostly flat or gently rolling -Hot humid summers -Many swamps, marshes - In the south it is a subtropical -Wide belt of fertile agriculture climate -subject to hurricanes Vegetation: Economic activity: -Soils are mainly sandy -Magor crops:cotton,tobacco, corn, -Some areas lush jungles developed peanuts, broilers, eggs, cagttle -originally pine forests -Cotton is the jumber one crop Enviromental concerns: -Population of 4.5 million -Soils are mostly clay and clay looms -Covers 13 million acres tracking the gulf of mexico -Over years farmland has been converted to pine plantations
- 4. The great lakes St. Lawrence lowland Topography: Climate: -Rolling land scape, created by glaciation -Humid continental climate -Flat plains broken by hills and deep river -humid because of great lakes valleys -lakes cool temperature in summer -St. Lawrence section, flat plains on both -winters vary from cool to cold sides of river -summers warm to hot Vegetation: Economic activity: -originally heavily treed -Farming poultry, dairy, meat, specialty crop -because of soil and climate -Manufacturing cars, carparts, steel, iron, -in the great lakes portion maple, beech, textiles, clothing hickory and black walnut trees thrived -minning minerals, copper, iron, silver, lead, -elsewhere it is a mixed forest zinc, coal Environmental concerns: -Alot of waste and population -fresh water baisins are third most densly poluted -the weather is beginning to get hotter and hotter -lots of air polution
- 5. The interior plains Climate: -in the U.S the plains are divided into the central Topography: lowland and the great plains -the northern boundary of the central lowland formed by Canadian sheild, great lakes, st. Lawrence river -great plains rise frlm 600-1500 meters above sea level Vegetation: -originally central lowland was covered with mixed deciduous trees -great plains-prairie grasses -northern portion of interior plains boreal forest grows Environmental concerns: -farm polutants seeping into the groundand waters -lumber harvesting -disposing waste into landfills -continental climate -climate of extremes -long, hot summers -Cold winters, little precipitation -farther noth, short cool summers, longer, colder winters Economic activity: -agriculture, minning -cattle, pigs, poultry, wheat, barley, oats, flax, canola, potatoes, corn, and sugar beets -large amount of minerals -oils, gas, gypsum and coal
- 6. Topography: The canadian sheild -During iceage glaciers removed most soil Climate: -leaving barren of rock surface -North winters are long and cold -evalation 100 meters above sea level in north -summers are shorter and cooler - In south the evalation is 500 meters above Vegetation: Economic activity: -Dominated by the minning of metals and -covered mostly by boreal forest minerals -North of the tree line no trees can grow - 1900's Hudson bay company used land as Environmental concerns: -Acid rain ruining forests crops, buildings - once acid rain hits the amount and diversity of vegetation, zoo, plankton, amphibians and fish decrease fur resources -logging of the boreal forest
- 7. Topography: The western cordillera Climate: -new mountains -Maritime climate -twice as high as the Appalachian -west coast is moist and mild mountains -winters qbove freezing -Rocky mountains to the east -summers are cooler than the interior -all rivers east of rockies flow east -valleys are warmer then mountain slopes Vegetation:one side of mountain to other -varies hugely from -on moist side, douhlas fir, western hemlock, western red cedar, -slme grow as high as 30 story office buildings -on the leeward sloppes grasses and cactus grow Environmental concerns: -slope erosion -harmful metals in water -lost wild habitat for lads for agriculture Economic activity: -pupl and paper industry -minning -copper, gold, lead, diamond, nickel, platinum -fishing
- 8. The Intermountain region Topography: -flows brackish lakes -some disappear into desert lakes -some rivers find a way into the ocean Vegetation: -Sparse grassland to plants -survive in semi deserts or deserts Economic activity: -cattle ranching -minning -fruits -vegitables Climate: -affected by its location and elevation -winters cooland wet or hot and dry -southern portions winters are short and warm -northern portions winters are moist and hot, dry summers Environmental concerns: -eleven bird species are endangered -forest fires because of dry air forests
- 9. The arctic Climate: Topography: -severe because it is far from the equator -near the ocean is very flat -winter lasts 10 months in the north -mountains far north are -summers are short amd nlt very hot formed by glaciers - is a desert because of the little Vegetation: -very few life forms -trees cannot grow on the tundra -climate is to vold so thawing ocvurs during the summer -small shrubs, mosses, lichens only grow Environmental concerns: -climate change -changes in biological diversity -use of toxic substances -thawing of perma forest precipitation Economic activity: -natural resources oil, gas, minerals -their "occupation" is hunting and fishing -furs, meat
- 10. Bibliography cranny, M. (1947). Crossroads a meeting of nations. (pp. 160-177). Great lakes st.lawrence lowlands. (n.d.). Retrieved from http://abishop4.tripod.com/ St Lawrence Great Lakes Lowland - Pollution." St Lawrence Great Lakes Lowland - Pollution. N.p., n.d. Web. 18 Feb. 2014 Conservation History , A. O. T. (2007). Texas legacy project. Retrieved from http://www.texaslegacy.org/bb/regions/c oastalplain.html