Más contenido relacionado
La actualidad más candente (20)
Similar a G6 m2-d-lesson 19-s (20)
G6 m2-d-lesson 19-s
- 1. Lesson 19: The EuclideanAlgorithm as an Applicationofthe Long Division
Algorithm
Date: 1/12/15
S.81
81
© 2013 Common Core, Inc. Some rightsreserved. commoncore.org
This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM 6•2Lesson 19
Lesson 19: The Euclidean Algorithm as an Application of the Long
Division Algorithm
Classwork
OpeningExercise
Euclid’s Algorithmis used to find the greatest common factor (𝐺𝐶𝐹) of two whole numbers.
1. Dividethe larger of the two numbers by the smaller one.
2. If there is a remainder, divideitinto the divisor.
3. Continue dividingthe lastdivisorby the lastremainder until the remainder is zero.
4. The final divisor isthe 𝐺𝐶𝐹 of the original pairof numbers.
383 ÷ 4 =
432 ÷ 12 =
403 ÷ 13 =
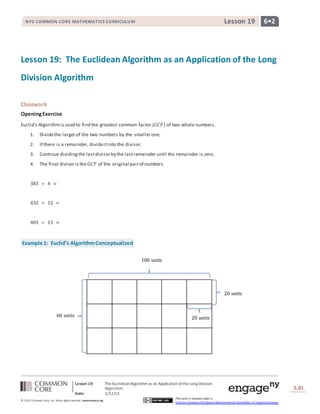
Example 1: Euclid’s AlgorithmConceptualized
100 units
20 units60 units
20 units
- 2. Lesson 19: The EuclideanAlgorithm as an Applicationofthe Long Division
Algorithm
Date: 1/12/15
S.82
82
© 2013 Common Core, Inc. Some rightsreserved. commoncore.org
This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM 6•2Lesson 19
Example 2: Lesson 18 Classwork Revisited
a. Let’s apply Euclid’s Algorithmto some of the problems from our lastlesson.
i. What is the 𝐺𝐶𝐹 of 30 and 50?
ii. UsingEuclid’s Algorithm,we followthe steps that are listed in the opening exercise.
b. What is the 𝐺𝐶𝐹 of 30 and 45?
Example 3: Larger Numbers
𝐺𝐶𝐹 (96, 144) 𝐺𝐶𝐹 (660, 840)
- 3. Lesson 19: The EuclideanAlgorithm as an Applicationofthe Long Division
Algorithm
Date: 1/12/15
S.83
83
© 2013 Common Core, Inc. Some rightsreserved. commoncore.org
This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM 6•2Lesson 19
Example 4: Area Problems
The greatest common factor has many uses. Among them, the GCF lets us find out the maximum sizeof squares that
will cover a rectangle. Whenever we solveproblems likethis,we cannot have any gaps or any overlappingsquares. Of
course, the maximum sizesquares will bethe minimum number of squares needed.
A rectangular computer table measures 30 inches by 50 inches. We need to cover it with squaretiles. Whatis the side
length of the largestsquaretilewe can use to completely cover the table, so that there is no overlap or gaps?
c. If we use squares thatare 10 by 10, how many will we need?
d. If this were a giantchunk of cheese in a factory, would itchange the thinkingor the calculationswejustdid?
e. How many 10 inch × 10 inch squares of cheese could be cut from the giant 30 inch × 50 inch slab?
- 4. Lesson 19: The EuclideanAlgorithm as an Applicationofthe Long Division
Algorithm
Date: 1/12/15
S.84
84
© 2013 Common Core, Inc. Some rightsreserved. commoncore.org
This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM 6•2Lesson 19
Problem Set
1. Use Euclid’s Algorithmto find the greatest common factor of the followingpairs of numbers:
a. 𝐺𝐶𝐹 of 12 and 78
b. 𝐺𝐶𝐹 of 18 and 176
2. Juanita and Samuel are planninga pizza party. They order a rectangular sheet pizza which measures 21 inches by
36 inches. They tell the pizza maker not to cut it becausethey want to cut itthemselves.
a. All pieces of pizza must be squarewith none left over. What is the length of the sideof the largestsquare
pieces into which Juanita and Samuel can cut the pizza?
b. How many pieces of this sizewill there be?
3. Shelly and Mickelleare makinga quilt. They have a piece of fabric that measures 48 inches by 168 inches.
a. All pieces of fabric mustbe squarewith none left over. What is the length of the sideof the l argestsquare
pieces into which Shelly and Mickellecan cut the fabric?
b. How many pieces of this sizewill there be?