Mth 4108-1 b (ans)
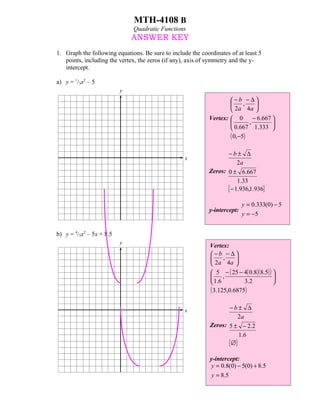
- 1. MTH-4108 B Quadratic Functions ANSWER KEY 1. Graph the following equations. Be sure to include the coordinates of at least 5 points, including the vertex, the zeros (if any), axis of symmetry and the y- intercept. a) y = 1/3x2 – 5 y −b −∆ , 2a 4a Vertex: 0 − 6.667 , 0.667 1.333 ( 0,−5) −b± ∆ x 2a Zeros: 0 ± 6.667 1.33 { − 1.936,1.936} y = 0.333(0) − 5 y-intercept: y = −5 b) y = 4/5x2 – 5x + 8.5 y Vertex: −b −∆ , 2a 4a 5 − ( 25 − 4( 0.8)( 8.5) ) , 1.6 3.2 ( 3.125,0.6875) x −b± ∆ 2a Zeros: 5 ± − 2.2 1.6 { ∅} y-intercept: y = 0.8(0) − 5(0) + 8.5 y = 8.5
- 2. Vertex: c) y = –0.2x2 + x – 3 −b −∆ , y 2a 4a − 1 − (1 − 4( − 0.2)( − 3) ) , − 0.4 − 0.8 ( 2.5,−1.75) −b± ∆ 2a Zeros: − 1 ± − 1.4 x − 0.4 { ∅} y-intercept: y = −0.2(0) + 1(0) − 3 y = −3 /30 2. Solve the following equations by factoring: a) 49x2 – 169 = 0 ( 7 x − 13) ⇒ 7 x = 13 ⇒ x = 13 7 = 1.857 ( 7 x + 13) ⇒ 7 x = −13 ⇒ x = − 13 7 = −1.857 b) 1/4x2 – 6x + 20 = 0 1 2 x − x − 5 x + 20 = 0 4 1 x( x − 4) − 5( x − 4) 4 1 1 x − 5 ⇒ x = 5 ⇒ x = 20 4 4 ( x − 4) ⇒ x = 4 /5 3. Identify the true statement(s) below: a) If ∆ = 0 for a quadratic equation, it means that there is one solution and it is equal to 0. FALSE b) If the discriminant is less than 0, it means that there are two real solutions for this equation. FALSE c) If an equation has two zeros, one postitive and one negative, it means that ∆ is negative. FALSE d) If an equation has one negative solution, it is impossible that the other solution is also negative if ∆ > 0. FALSE e) If the discriminant is equal to zero then the equation has two solutions. FALSE /5
- 3. 4. Solve the following equations using the quadratic formula. Clearly indicate the value of ∆ and round your answers to the nearest thousandth when necessary. a) 3.6x2 + 3.1x – 1 = 0 Zeros: −b± ∆ 2a − 3.1 ± ( 9.61 − 4( 3.6 )( − 1) ) 7.2 { − 1.111,0.25} b) -1x2 + 5x – 24 = 0 Zeros: 6 −b± ∆ 2a − 5 ± ( 25 − 4( − 0.1667 )( − 24 ) ) − 0.333 { 6,24} /10 5. Marjorie makes friendship bracelets and sells them for a profit of $4.50. She must sell at least 10 bracelets to break even. For each additional bracelet she sells, she can offer the buyer a discount of $0.15. The table below illustrates the her total profit as a function of how many bracelets she sells. No. of additional Number of Discount price Total profit bracelets sold bracelets sold 0 10 4.50 – (0.15 × 0) 10 × 4.50 = 45.00 1 10 + 1 = 11 4.50 – (0.15 × 1) = 4.35 11 × 4.35 = 47.85 2 10 + 2 = 12 4.50 – (0.15 × 2) = 4.20 12 × 4.20 = 50.40 x 10 + x 4.50 – (0.15 × x) (10 + x)(4.5 – 0.15x) Write the equation in the form ax2 + bx + c which illustrates this situation. (10 + x )( 4.5 − 0.15 x ) 45 + 1.5 x + 4.5 x + 0.15 x 2 y = 0.15 x 2 + 6 x + 45 /10 6. Without calculating, write the equation in the form ax2 + bx + c which illustrates the following situation: The sum of the squares of two consecutive even numbers is 1060. What are the two numbers? Let x = 1st number Let x + 1 = 2nd number x 2 + ( x + 1) = 1060 2 /5 x 2 + x 2 + 2 x + 1 = 1060 2 x 2 + 2 x − 1059 = 0
- 4. 7. Answer the following questions using the graph below: y = –x2 + 2x + 8 y x a) What are the coordinates of the vertex? Vertex: − b − ∆ − 2 − ( 4 − 4( − 1)( 8) ) , ⇒ , ⇒ (1,9 ) 2a 4a − 2 −4 b) What is the equation of the axis of symmetry? x=1 c) Is there a maximum or a minimum? Maximum of 9 d) What are the zeros? −b± ∆ − 2 ± 36 Zeros: ⇒ ⇒ { − 2,4} 2a −2 e) What is the y-intercept? y-intercept: y = −1(0) + 2(0) + 8 ⇒ y = 8 /5 8. The small diagonal of a rhombus measures 2 cm more than one quarter of the large diagonal. The area of the rhombus is 66.56 cm2. What are the measurements of the small diagonal and the large diagonal of this rhombus? Let x = LARGE diagonal Let ¼x + 2 = small diagonal −b± ∆ ( x 1 x+2 ) 2a 4 2 = 66.56 −2± 4−4 1 ( 4 )( − 133.12) 1 x 2 + 2 x = 133.12 Zeros: 0.5 4 1 x 2 + 2 x − 133.12 = 0 − 3 ± 137.12 4 0.5 { − 29.4196,17.4196} 0.25(17.4196) + 2 = 6.3549 ANS: 17.4196 cm and 6.3549 cm /5
- 5. 9. A school superintendent is deciding on how many students per class there should be. The classes are 120 minutes long, with a certain number of students in each room. If 10 students are added to the classes, the time spent per student declines by 1 minute. How many students are in the room? Let x = number of students in the classroom −b± ∆ 120 120 −1 = 2a x x + 10 120 − x 120 − 10 ± 100 − 4(1)( − 1200 ) = Zeros: 2 x x + 10 120 x + 1200 − x 2 − 10 x = 120 x − 10 ± 70 2 x 2 + 10 x − 1200 = 0 { − 40,30} ANS: There are 30 students in the classroom. /10 10. A hot air balloon lifts off the ground from the point (2, 0). The equation of the height (y) of the balloon in metres is: y = –t2 + 38t – 72 where t represents the time in minutes. a) What is the maximum height obtained by the balloon? Vertex: − b − ∆ − 38 − (1444 − 4( − 1)( − 72 ) ) , ⇒ , ⇒ (19,289 ) 2a 4a − 2 −4 b) After how many seconds is the maximum height obtained? Vertex: − b − ∆ − 38 − (1444 − 4( − 1)( − 72 ) ) , ⇒ , ⇒ (19,289 ) 2a 4a − 2 −4 c) How many minutes is the balloon in the air? −b± ∆ − 8.75 ± 1444 − 4( −1)(−72) − 38 ± 1156 ⇒ ⇒ Zeros: 2a −2 −2 { 2,36} ANS: The balloon is in the air for 34 minutes. Round your answers to the nearest hundredth. /15