Denunciar
Compartir
Recomendados
Más contenido relacionado
La actualidad más candente
La actualidad más candente (20)
Relative Velocity Method for Velocity and Acceleration analysis 

Relative Velocity Method for Velocity and Acceleration analysis
General Curvilinear Motion &Motion of a Projectile

General Curvilinear Motion &Motion of a Projectile
Velocity and Acceleration analysis in kinematics of mechanism

Velocity and Acceleration analysis in kinematics of mechanism
Moment of inertia concepts in Rotational Mechanics

Moment of inertia concepts in Rotational Mechanics
Lecture 1 Introduction to statics Engineering Mechanics hibbeler 14th edition

Lecture 1 Introduction to statics Engineering Mechanics hibbeler 14th edition
Chapter 3. velocity analysis (IC,GRAPHICAL AND RELATIVE VELOCITY METHOD)

Chapter 3. velocity analysis (IC,GRAPHICAL AND RELATIVE VELOCITY METHOD)
Destacado
Destacado (17)
Engineering mechanics dynamics (7th edition) j. l. meriam, l. g. kraige

Engineering mechanics dynamics (7th edition) j. l. meriam, l. g. kraige
Engineering mechanics statics j.l.meriam-l.g.kraige-solution manual (5th ed)

Engineering mechanics statics j.l.meriam-l.g.kraige-solution manual (5th ed)
Similar a 006 relative motion
Similar a 006 relative motion (20)
lec09_part1.pptx PLANAR KINEMATICS OF RIGID BODIES

lec09_part1.pptx PLANAR KINEMATICS OF RIGID BODIES
Velocityofmechasnismbygraphical 130217105814-phpapp02 (1)

Velocityofmechasnismbygraphical 130217105814-phpapp02 (1)
Velocityofmechasnismbygraphical 130217105814-phpapp02

Velocityofmechasnismbygraphical 130217105814-phpapp02
Más de physics101
Más de physics101 (20)
006 relative motion
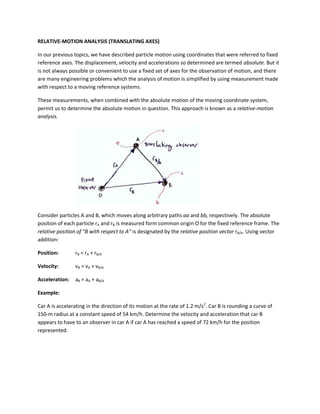
- 1. RELATIVE-MOTION ANALYSIS (TRANSLATING AXES) In our previous topics, we have described particle motion using coordinates that were referred to fixed reference axes. The displacement, velocity and accelerations so determined are termed absolute. But it is not always possible or convenient to use a fixed set of axes for the observation of motion, and there are many engineering problems which the analysis of motion is simplified by using measurement made with respect to a moving reference systems. These measurements, when combined with the absolute motion of the moving coordinate system, permit us to determine the absolute motion in question. This approach is known as a relative-motion analysis. Consider particles A and B, which moves along arbitrary paths aa and bb, respectively. The absolute position of each particle rA and rB is measured form common origin O for the fixed reference frame. The relative position of “B with respect to A” is designated by the relative position vector rB/A. Using vector addition: Position: rB = rA + rB/A Velocity: vB = vA + vB/A Acceleration: aB = aA + aB/A Example: Car A is accelerating in the direction of its motion at the rate of 1.2 m/s 2. Car B is rounding a curve of 150-m radius at a constant speed of 54 km/h. Determine the velocity and acceleration that car B appears to have to an observer in car A if car A has reached a speed of 72 km/h for the position represented.
- 3. Problem: 1. A train travelling at a constant speed of 60 mi/h, crosses over a road as shown in the figure. If automobile A is travelling at 45 mi/h along the road, determine the magnitude and direction of the relative velocity of the train with respect to the automobile. [Ans. 42.5 mi/h, 48.5o]
- 4. 2. Plane A is flying along straight-line path whereas plane B is flying along a circular path having a curvature of rB = 400 km. Determine the velocity and acceleration of B as measured by the pilot of A. [100 km/h, 912 km/h2] 3. For the instant represented, car A has an acceleration n the direction of its motion and car B has a speed of 72 km/h which is increasing. If the acceleration of B as observed from A is zero for this instant, determine the acceleration of A and the rate at which the speed of B is changing.