Structural analysis (method of joints)
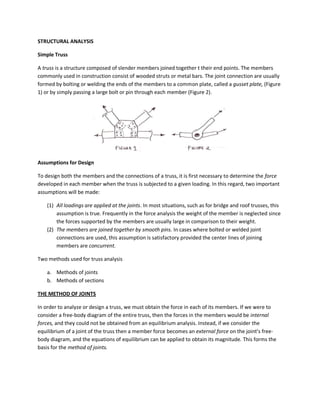
- 1. STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS Simple Truss A truss is a structure composed of slender members joined together t their end points. The members commonly used in construction consist of wooded struts or metal bars. The joint connection are usually formed by bolting or welding the ends of the members to a common plate, called a gusset plate, (Figure 1) or by simply passing a large bolt or pin through each member (Figure 2). Assumptions for Design To design both the members and the connections of a truss, it is first necessary to determine the force developed in each member when the truss is subjected to a given loading. In this regard, two important assumptions will be made: (1) All loadings are applied at the joints. In most situations, such as for bridge and roof trusses, this assumption is true. Frequently in the force analysis the weight of the member is neglected since the forces supported by the members are usually large in comparison to their weight. (2) The members are joined together by smooth pins. In cases where bolted or welded joint connections are used, this assumption is satisfactory provided the center lines of joining members are concurrent. Two methods used for truss analysis a. Methods of joints b. Methods of sections THE METHOD OF JOINTS In order to analyze or design a truss, we must obtain the force in each of its members. If we were to consider a free-body diagram of the entire truss, then the forces in the members would be internal forces, and they could not be obtained from an equilibrium analysis. Instead, if we consider the equilibrium of a joint of the truss then a member force becomes an external force on the joint’s free- body diagram, and the equations of equilibrium can be applied to obtain its magnitude. This forms the basis for the method of joints.
- 2. Example 1: Determine the force in members GE, GC and BC of the truss shown in the figure. Indicate whether the members are in tension or compression. SOLUTION:
- 4. __________________________ Example 2: Determine the force in members in BF, BG and AB, and state if the members are in tension or compression.
- 5. SOLUTION:
- 6. Hence, reactions at A and G;