Reading 3
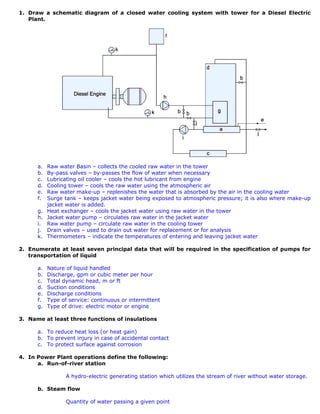
- 1. 1. Draw a schematic diagram of a closed water cooling system with tower for a Diesel Electric Plant. a. Raw water Basin – collects the cooled raw water in the tower b. By-pass valves – by-passes the flow of water when necessary c. Lubricating oil cooler – cools the hot lubricant from engine d. Cooling tower – cools the raw water using the atmospheric air e. Raw water make-up – replenishes the water that is absorbed by the air in the cooling water f. Surge tank – keeps jacket water being exposed to atmospheric pressure; it is also where make-up jacket water is added. g. Heat exchanger – cools the jacket water using raw water in the tower h. Jacket water pump – circulates raw water in the jacket water i. Raw water pump – circulate raw water in the cooling tower j. Drain valves – used to drain out water for replacement or for analysis k. Thermometers – indicate the temperatures of entering and leaving jacket water 2. Enumerate at least seven principal data that will be required in the specification of pumps for transportation of liquid a. Nature of liquid handled b. Discharge, gpm or cubic meter per hour c. Total dynamic head, m or ft d. Suction conditions e. Discharge conditions f. Type of service: continuous or intermittent g. Type of drive: electric motor or engine 3. Name at least three functions of insulations a. To reduce heat loss (or heat gain) b. To prevent injury in case of accidental contact c. To protect surface against corrosion 4. In Power Plant operations define the following: a. Run-of-river station A hydro-electric generating station which utilizes the stream of river without water storage. b. Steam flow Quantity of water passing a given point
- 2. c. Spinning reserve Part of the generating capacity that can be activated on decision of the system operator d. Hot reserve Reserve generating capacity that is in operation but not in service e. Cold reserve Reserve generating capacity that is available for service but not in operation f. Prime power Maximum potential power constantly available for transformation into electrical power g. Firm power Power intended always to be available under emergency conditions 5. Define the following: a. Maintenance chart A typical time schedule chart indicating the equipment and the maintenance activities to be accomplished such as lubrication or replacement of parts. b. Preventive maintenance Periodic, time-scheduled inspections to detect wear and tear in advance of actual equipment breakdown with subsequent replacement of worn-out parts before they fail in order to minimize interference in operations. c. Corrective maintenance Improvements or minor changes in design and substitution of more suitable components or improve materials of construction to eliminate a problem. d. Routine maintenance Consists of the regular maintenance activities like lubrication, recharging of batteries and replacement of certain parts. e. Inspection schedule A typical weekly schedule of servicing an equipment to detect possible defect. 6. Define the following: a. Fossil Fuel Plants In fossil fuel plants, the main source of energy is heat energy from the combustion of fossil fuels such as coal, petroleum products or natural gas. The neat energy is converted to mechanical energy by the use of internal combustion engines or steam turbine which drives generators. b. Pressurized Water Reactors A pressurized water reactor is a type of nuclear power plant in which the heat generated from fission of Uranium is absorbed by the pressurized water coolant. The coolant in turn heats the circulating feed water in a heat exchanger, generating steam in the process. The generated steam proceeds to release its energy to the turbine which drives the generator.
- 3. c. Terrestrial Heat Plants Terrestrial heat, which is another term for geothermal energy, makes use of steam or hot water harnessed from the earth to drive steam turbines. Wells are dug into the steam or hot water reservoir and the steam (or flashed steam) is fed into the steam turbine-generator to generate electricity. d. Magneto Hydro Dynamic Plants In a magneto hydro dynamic generator, combustion gasses produced in a combustion chamber at high pressure and temperature and seeded with metal vapor to increase its electrical conductivity, is passed through an expansion tube lined with a strong magnetic field. This induces an electric voltage in the gas conductor and affects the flow of electrons through the electrodes along the magnetic field, thereby generating electricity. e. Low Thermal Head Plants Low thermal head plant, otherwise known as Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion, makes use of the temperature difference between the ocean surface water and the water at the sea bottom. Surface water which is at relatively high temperature is pumped to an evaporator where the water evaporates into saturated steam. This steam drives a single stage turbine thereby producing electricity, and exhaust to a jet condenser maintained at the saturation pressure of the subsurface water temperature pumped from the sea bottom. 7. Give four (4) sources of air pollution, briefly explain each, and give example for each. a. Exhaust gases from combustion Exhaust gases from engines or boilers which results from the combustion of fuel and which contains dust, fumes and carbon monoxide. b. Chemical Industries Dust, mist, fumes and chemical spray which result from chemical processes c. Mineral Processes Principally dust and sometimes fumes which result from crushers and mills such as in ore milling and cement industry. d. Food Processing Dust and mist and other odorous material resulting from food production. 8. Some equipment normally used now for pollution control are as follows: a. Chimney or smoke stack Provides effective atmospheric dispersion of gaseous and particulate pollutants with acceptable ground level concentrations. Stacks or chimneys are high enough to produce sufficient draft to dispose gases at safe heights. b. Cyclone dust collector In this type of industrial dust collector, the gas is passed tangentially into a vertical cylinder with a conical bottom. The gas follows a spiral path, with most of the separation taking place in the smaller sections. c. Spray Scrubbers Tower type, the gas passing upward concurrently as the descending liquid. Sets of sprays are placed in the top zone, with various materials used in the layers to channel and mix the gas and water. d. Electrostatic Precipitator Dust particles are electrically charged and are attracted to the electric field of the electrostatic precipitator.
- 4. 9. With an aid of a diagram, describe briefly how an ice is manufactured. In the Can System of ice manufacture, standard size ice cans are immersed in a brine solution, which is cooled by the refrigerant in the evaporator coils, and which in turn freezes the water in the ice cans. The common refrigerant used in ice plants is ammonia. 10. Three principal types of evaporator according to construction: a. Horizontal tube evaporator Consists of vertical cylindrical body; two rectangular steam chests in the lower section contain tube sheets; primarily suitable for non-viscous liquids that do not deposit salt or scale during evaporation. b. Standard vertical tube evaporator Consists of vertical cylindrical shell with flat, dished or conical bottom, most widely used type, can be used for liquids that deposit salt or scale during evaporation. c. Long-tube, natural-circulation vertical evaporator Consists of long tubes so that the liquor passes through the evaporator but once; used with non-salting or non-scaling liquids; can be used with high viscosities; one of the cheapest types. 11.Enumerate principal points to consider when designing a chimney. • Minimum height of chimney • Flue gas temperature • Chimney should be located with reference to nearby higher buildings. • Gas flue should be as straight as possible from base to top outlet and should have no opening except boiler smoke pipe. • Outlet must not be capped so that its area is less than the flue gas • Best location for a chimney is near the center of a building, as all walls then are kept warm. • The best practices uses fireclay linings for small and medium-sized flues.