Infertility Treatment Options Explained
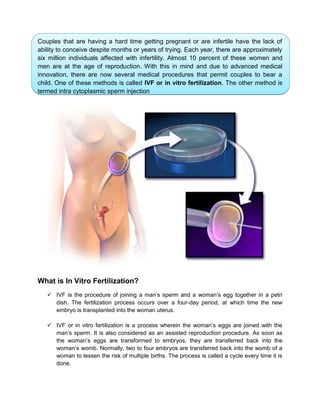
- 1. Couples that are having a hard time getting pregnant or are infertile have the lack of ability to conceive despite months or years of trying. Each year, there are approximately six million individuals affected with infertility. Almost 10 percent of these women and men are at the age of reproduction. With this in mind and due to advanced medical innovation, there are now several medical procedures that permit couples to bear a child. One of these methods is called IVF or in vitro fertilization. The other method is termed intra cytoplasmic sperm injection What is In Vitro Fertilization? IVF is the procedure of joining a man’s sperm and a woman’s egg together in a petri dish. The fertilization process occurs over a four-day period, at which time the new embryo is transplanted into the woman uterus. IVF or in vitro fertilization is a process wherein the woman’s eggs are joined with the man’s sperm. It is also considered as an assisted reproduction procedure. As soon as the woman’s eggs are transformed to embryos, they are transferred back into the woman’s womb. Normally, two to four embryos are transferred back into the womb of a woman to lessen the risk of multiple births. The process is called a cycle every time it is done.
- 2. Why In Vitro Fertilization? In-Vitro Fertilization is in most cases preformed in the following situations: • Damaged fallopian tubes • Ovulation disorders • Cervical factors • Male factors, such as low sperm count or poor-quality sperm • Surrogacies Benefits of In Vitro Fertilization Creates more families Infertile couples now have a greater chance to become pregnant Scientists are able to study fertilization and early embryonic development in an environment outside a woman’s body. Giving a greater understanding to the reasons behind birth defects In Vitro Fertilization Process In natural conception, an egg is released from the ovary into the fallopian tube in the middle of a menstrual cycle. The egg is fertilized in the fallopian tube. The fertilized egg
- 3. then begins to divide in the fallopian tube, thus becoming an early embryo. After being in the fallopian tube for several days the embryo enters the uterus where it will implant. IVF can be thought of as a bypass of the fallopian tubes. The IVF process involves stimulating the ovaries with "fertility shots" to mature multiple eggs. Development of the eggs is monitored with blood tests and vaginal ultrasounds. Once the eggs are "mature," they are removed from the ovary with a very minor surgical procedure and mild anesthesia. After the eggs are retrieved, they are put into a petri dish and exposed to the partner's sperm. The eggs are examined the following morning to see if they have been successfully fertilized by the sperm. The fertilized eggs are left in the petri dish for several days during which time they begin to divide and become early embryos (as occurs in the fallopian tubes during natural conception). The embryos are then placed in the woman's uterus with a small catheter through the cervix that is generally no more uncomfortable than a Pap test. If there are extra embryos that are viable, they may be cryopreserved (frozen) for future use. The IVF or in vitro fertilization success rates are almost the same with normal pregnancies. Remember that it is hard to get pregnant if you reach the age of 30 and above. The in vitro fertilization success rate for women below 35 years old is 37 percent while women above 35 years old is 28 percent. The success rate for women whose age is over 40 is 13 percent. Pregnancy will be impossible or not common at all to women older than that. It simply means that the younger you are, the higher the success rate is. VF or in vitro fertilization has aided hundreds and thousands of couples get pregnant and have a baby. On the other hand, this fertility treatment is also considered expensive. Before trying this procedure, you should ask your fertility specialist about the cost and find out if this is the right treatment for you. Roles of Nurses in In Vitro Fertilization The role of the infertility nurse is continually expanding and changing to meet the demands of couples undergoing assisted reproduction. Infertility nurses play a major role in ovulation induction programmes. The extended role of infertility nurse practitioners allows more continuity of care and better understanding of patients’ needs and results in the involvement of fewer people in the overall care. One of the more positive aspects of IVF is actually having regular contact with the IVF nurse. The nurse takes the client through the whole IVF treatment process step by step. She will repeat everything that she has told to make sure that the client understands everything that is going on. The nurse is the person who will check blood test and ultrasound appointments. She will be the client’s first port of call if anything goes wrong during the treatment – like breaking a vial of medicine, like having unusual
- 4. pain when client shouldn’t. The nurses offer solace and advice when unusual things happen during the treatment process. They will lend their ear in times of distress. They will recognize when client is close to breaking point and arrange to meet with a counselor if need be. The nurses are the unsung heroes of the whole process. The successes achieved in this still evolving field are in large part attributable to the pivotal role played by nurses. IVF nurses are bright, intelligent, and individuals who have found their calling helping those in search of compassionate family achieve their long-held dream of parenthood. Nurses are problem solvers and multitaskers who take on a multitude of responsibilities. IVF nurses must wear many hats. They must understand embryology, andrology, endocrinology, gynecology, obstetrics, genetics, oncology, information technology, and of course psychology. They are the most important bridge between highly technical information and physician prescriptions and their patients’ ability to understand and implement the treatment. IVF nurses must learn not just the science of reproduction but also the art of telling a patient empathically of her pregnancy test is negative.
- 5. Family planning Family planning is sometimes used as a synonym for the use of birth control. It is most usually applied to a female- male couple who wish to limit the number of children they have and/or to control the timing of pregnancy (also known as spacing children). Family planning may encompass sterilization, as well as abortion. There are sterilization procedures for both men and women. These are permanent and for the most part irreversible (or intended to be). What Is Male Sterilization? Male sterilization is achieved through a surgical procedure, called a vasectomy, that is intended to be a permanent method of birth control (there is no guarantee that it can be reversed). How is the procedure performed? A vasectomy is a quick, 30-minute surgical procedure performed in the physician's
- 6. office in which the vas deferens (the tubes that carry sperm out of the penis) is cut or tied, and then the ends are cauterized (burned). This prevents sperm from coming out in the ejaculate or getting into the vagina. Recovery from vasectomy usually requires only that the patient refrain from physical activity for approximately 48 hours. Back-up contraception needs to be used until two follow-up semen tests show no sperm. What Is Female Sterilization? Permanent female sterilization can be achieved through two procedures: 1. Tubal ligation: This is a surgical procedure performed in a hospital, usually with no over night stay. It involves cutting the fallopian tubes and then tying and cauterizing the cut ends, so the egg does not get out of the tube into the uterus to be fertilized. 2. Hysteroscopic sterilization (Essure procedure): A hysteroscope, a lighted telescopic instrument, is inserted into the uterus through the cervix. The hysteroscope is used to insert spring-like coils called micro-inserts in the opening of the fallopian tubes. During the following months, scar tissue will form around the inserts and essentially plug the tubes which will keep sperm from fertilizing an egg. A follow-up visit to the doctor is required to make sure that the tubes are completely blocked. 3. Back-up contraception must be used until blockage is confirmed. This is a minor surgical procedure and requires anesthesia.
- 7. MALE CONDOMS – Mostly made of fine latex rubber. – Silicon used nowdays to produce semi- dry, pre-lubricated forms. – Spermicidal – coated with nonoxynol 9 on inner and outer surfaces. ADVANTAGE: • Simple spacing method • No side effects • Easily available, safe & inexpensive • Protects against STDs DISADVANTAGE: • Chances of slip off and tear off • Penis must be withdrawn immediately after ejaculation • Failure rate: 16% FEMALE CONDOM – Advantages – Woman controlled method – Prevents STDs including HIV/AIDS – Not damaged by oils and other chemicals
- 8. Disadvantages – High motivation – Only women who can use diaphragms can use female condom – Slippage occurs – Expensive – Failure rate 21% with typical use and 5% with correct and consistent use Pills – Most combination pills come in either a 21-day pack or a 28-day pack. One hormone pill is taken each day at about the same time for 21 days. Depending on your pack, you will either stop taking birth control pills for 7 days (as in the 21-day pack) or you will take a pill that contains no hormones for 7 days (the 28-day pack). A woman has her period when she stops taking the pills that contain hormones. Some women prefer the 28-day pack because it helps them stay in the habit of taking a pill every day. It prevents ovulation by inhibiting FSH It decreases permeability of cervical mucus - Contain Synthetic hormone, Progestin which suppresses ovulations, thickens cervical mucus.
- 9. Advantages: Reversible, no need for daily intake, does interfere, no estrogen related effects, does not affect breastfeeding. A breastfeeding woman can use LAM to space her next birth and as a transition to another contraceptive method. She may start LAM at any time if she meets all 3 criteria required for using the method. There is only a 2% chance of pregnancy at this time. A woman may choose another family planning method at any time—but preferably not a method with estrogen while her baby is less than 6 months old. Methods with estrogen include combined oral contraceptives, monthly injectables, the combined patch, and the combined vaginal ring.
- 10. - Abstaining from sexual intercourse during fertile (wet) days - Billings: senses vaginal wetness ; spinnbarkeit, mucus Advantage: can be used by any woman of repro. Age Disadvantage: not applicable with medical conditions How to use: - Recording of menstruation and dry days - Inspecting underwear regularly for presence of mucus - Recording the most fertile observation at the end of the day From day 6-10 of menstrual cycle to identify thermal shift ( the three consecutive temp. above the cover line labeled as days 1,2,3 intercourse is allowed only from 4th day thermal shift until the end of the cycle. - Women resting body temperature (morning or before activity) - 1 degree higher- time of ovulation - ½ degree higher – day before ovulation - Ovulation: A slight dip then sudden rise in temp
- 11. Statistics for 1995 reveal that 56.9 babies were born for every 1000 females between the ages of 15 and 19. Although these rates appear to be dropping, pregnant adolescents are at risk physically, emotionally, and socially. The impact of adolescent pregnancy on the individual has far-reaching consequences, which may restrict or limit future opportunities for the adolescent and the child(ren). Educational goals may be altered or eliminated, thus limiting potential for a productive life. The client frequently may be of lower socioeconomic status, with the pregnancy perpetuating financial dependence and lowered self-esteem. Statistically, the obstetric hazards for adolescents and their infants include increased mortality and morbidity rates. Therefore, individualized prenatal nursing care for the adolescent client/family/partner that incorporates developmental needs and health education with prenatal needs has the potential to contribute positively to prenatal, intrapartal, and postpartal outcomes. In addition, neonatal outcomes associated with better Apgar scores, lower incidence of resuscitation, and fewer LBW infants can also be expected. NURSING PRIORITIES 1.Promote optimal physical/emotional well-being of client. 2. Monitor fetal well-being. 3. Provide information and review the available options. 4. Facilitate positive adaptation to new and changing roles. 5. Encourage family/partner participation in problem-solving. DISCHARGE GOALS Inpatient care is not required unless complications develop necessitating hospitalization (refer to appropriate plans of care.)
- 12. Nursing diagnosis of teen pregnancy: Body Image disturbance/Role Performance, altered/Personal Identity disturbance/Self Esteem (specify) may be related to situational and maturational crises, fear of failure at life events, biophysical changes, absence of support systems possibly evidenced by self-negating verbalizations, expressions of shame/guilt, hypersensitivity to criticism, fear of rejection, lack of follow-through and/or nonparticipation in care. Desired Outcomes: 1. Identify feelings and methods for coping with negative perception of self/abilities. 2. Verbalize increased sense of self-esteem in relation to current situation. 3. Demonstrate adaptation to changes/events as evidenced by setting of realistic goals and active participation in meeting own needs. Nursing intervention with rationale: 1. Establish a therapeutic nurse-client relationship. Rationale: Adolescent client needs a caring, nonjudgmental adult with whom to talk. Important to establish trust and cooperation so that the client is free to hear the information available. 2. Assess use of terms/language used by the client/significant other(s). Rationale: Terminology may be specific to the adolescent culture, and words may have different meanings for client and nurse. 3. Determine developmental level and needs relative to age as early, middle, or late adolescence. Rationale: Cognitive development during this period moves from concrete to abstract thinking (formal operations). The younger client may see control of the situation as external and beyond her grasp, and have little ability to understand the consequences of her behavior. With maturity, the abilities to understand possible consequences and to accept individual responsibility develop. 4. Identify client’s self-perception as positive or negative. Rationale: Helps client become aware of how she views herself and to begin to increase her self-esteem. Until late adolescence, body image is still formative. The client is dealing with adolescent developmental tasks, establishing an adult identity. Low self-worth may lead to feelings of hopelessness about the future and inability to visualize a successful outcome. 5. Elicit the client’s feelings about sexual identity/roles. Rationale: May have difficulty seeing herself as a mother. The adolescent must make a
- 13. role transition from child/daughter to adult/mother, which can create conflicts for the client and significant other(s). 6. Discuss concerns and fears about body image and transitory changes associated with pregnancy; discuss personal value system. Rationale: Establishes a basis for future learning. Conflicts may exist regarding how client has previously seen herself, what her expectations of pregnancy had been, and what the realities of pregnancy are. By midpregnancy, the enlarging abdomen and the increasing size of breasts andbuttocks may prompt the teenager to try to control her appearance by dieting, with adverse consequences for fetal health and her own growth needs. 7. Discuss ways to promote positive self-image (e.g., clothing style, makeup) and recognition of positive aspects of the situation. Rationale: Assists in coping with changes in appearance and presenting a positive image. 8. Discuss appropriate adaptation techniques and the communication skills to implementthese techniques. Rationale: Role playing and active listening can be used to learn skills of communication and adaptation. Helps client learn information necessary to development of improved self-esteem. Nutrition and the Pregnant Adolescent The nutritional needs of pregnant adolescents are the greatest at a time when it is most difficult to meet them. Dieting, skipping meals, snacking, eating away from home, consuming fast foods, and trying unconventional diets are common eating behaviors among adolescents, which relate to their changing lifestyles of increased independence, busy schedules, search for self-identity, peer influence, group conformity, and body image dissatisfaction. Total nutritional needs of pregnant adolescents who are at least 2-year post-menarche are similar to those of pregnant adults. But, because of their poor dietary habits, they usually enter pregnancy with reduced nutrient stores and increased risk of nutritional deficiencies. All pregnant teens, therefore, should have their dietary habits assessed along with special dietary counseling, and vitamin-mineral supplements should be recommended if their usual nutritional intake is below standard. Also, the weight-gain pattern should be monitored to ensure that energy intakes are sufficient to support a gain of about 0.4 kg (1 lb) per week in the second and third trimester.
- 14. Criteria for a Healthy Prenatal Diet • Provides enough calories for adequate weight gain • Is well-balanced and follows the Food Guide Pyramid • Tastes good and is enjoyable to eat • Spaces eating in intervals throughout the day • Provides adequate amounts of high fiber foods • Includes 8 cups of fluid daily • Limits beverages that contain caffeine (2-3 servings or fewer daily) • Is moderate in fat, saturated fat, cholesterol, sugar and sodium • Stable and continuous food supply • Excludes alcohol A woman’s attitude toward a pregnancy depends a great deal on psychological aspects: • The environment in which she was raised • The messages about pregnancy her family communicated to her as a child • The society and culture in which she lives as an adult • Whether the pregnancy came at a good time in her life Mother’s Reactions • Initial reaction includes wide range of emotions • May be surprised, pleased, disturbed, disapp ointed, frightened • There is element of surprise in every pregnancy • As the pregnancy progresses they must reach an acceptance
- 15. PSYCHOLOGICAL ADAPTATION OF ADOLESCENT PREGNANCY First Trimester Uncertainty ı Unsure of pregnancy, looks for confirmation Ambivalence ı Mixed feelings even of pregnancy planned ı Often feel unprepared for permanent life style changes ı Wonders about ability to parent ı Worries about how this will affect relationships with others Self focus ı Looks for physical changes in self Nurses’ role ı Reassure changes are normal, do not indicate problem ı Maternal Responses continued ı Second Trimester Physical changes more evident ı Physically feels better Makes attempts to ensure healthy fetus ı Keeps appointments, eats healthy, stops smoking, etc. Primary focus now fetus ı Fetus becomes real with quickening ı Becomes a separate entity from her Introversion ı Turning in as she contemplates health of newborn, her ability to provide for and protect infant
- 16. Body Image ı May be welcome signs confirming pregnancy ı Appearance and discomforts may contribute to negative body image for others Changes in sexuality ı May increase, decrease, or remain unchanged ı Intercourse ok in pregnancy unless complications ı Interest decreased in early preg d/t nausea, fear of SAB ı Pelvic congestion may increase sensitivity in 2nd trimester resulting in more intense orgasms ı In 3rd trimester may need to alter positions for comfort ı May also feel less sexy as become larger, males may be turned on or off by her appearance ı Concern about harming fetus Nurses’ role ı Educate about potential reactions ı Encourage open and honest communication by couple ı Maternal Responses continued ı Third Trimester Vulnerability ı Worries about fetus, becomes very cautious Increasing dependence ı Insists that partner be readily available at all times ı Seeks help in making decisions ı Needs much reassurance
- 17. Upset because partner doesn’t understand her feelings Birth preparation ı Concerned about ability to recognize labor, get to hospital on time ı Worried about coping with labor ı Begins to nest ı Maternal Role Transition ı Transition into mother begins in pregnancy and continues as pregnancy progresses Relationships ı Becomes more self aware ı Alterations in relationship with father as both prepare for parenthood ı Examines relationship with own mother ı Looks for example of what she perceives as mothering behaviors ı Must develop relationship with fetus Maternal Tasks in Pregnancy ı Seeking safe passage For herself and fetus by following cultural practices to ensure health of fetus, self ı Securing acceptance Involves reworking relationships so that those important to expectant woman accepts her as a mother, welcomes baby ı Especially her mother, her partner and sibs of baby ı Learning to give of self Derives enjoyment from giving to others Receiving gifts from others enhances woman’s ability to give ı Committing Herself to Unknown Child
- 18. Developing attachment to baby begins in early pregnancy Increases with quickening, ultrasound showing “parts” Integrates role of mother into her self image ı Becomes comfortable idea of herself as mother
- 19. REFERRENCES: http://www.slideshare.net/rachaellaw/ivf-presentation http://my.clevelandclinic.org/fertility-center/fertility-lab/ivf-procedures.aspx http://globalhandbook.atendesigngroup.com/when-can-woman-use-lam http://www.slideshare.net/niyamatpAli/in-vitro-fertilization-embryo-transfer http://www.epi.umn.edu/let/pubs/nmpa.shtm http://www.epi.umn.edu/let/pubs/img/NMPA_37-46.pdf http://www.slideshare.net/reynel89/psychological-changes-of-pregnancy-6691873 http://www.cotc.edu/faculty-and-staff/ FacultySites/nphillis/Documents/psychosocial%20adaptions%20to%20pregnancy.p df
- 20. Republic of the Philippines Laguna State Polytechnic University Santa Cruz, Laguna College of Nursing and Allied Health
