Transport in plants 3 transpiration
- 2. Transpiration • (d) define the term transpiration; • (e) explain why transpiration is a consequence of gaseous exchange; • (f) describe the factors that affect transpiration rate;
- 3. Movement of water between cells... HYPOTONIC Water moves in ISOTONIC HYPERTONIC No net movement Water moves out
- 4. Water route (unintentional pun) • • • • • • Soil Root Xylem (root-stem-leaf) Spongy mesophyll Evaporates into air spaces Water vapour moves into external air through stomata
- 5. Why is transpiration needed • it helps in the absorption and transport of water and mineral ions from the roots to different parts of the plant. • it helps to cool the plant. • it helps to supply water to all plant cells for metabolic processes. • it helps to prevent plants from wilting by helping them to maintain cell turgidity.
- 6. Transpiration is loss of water from a plant’s surface • Water evaporates from the moist cell walls and accumulates in the spaces between cells in the leaf • When stomata open, it moves out of the leaf down the concentration gradient (there’s more water in the leaf than in the air outside)
- 7. Factors affecting transpiration rate • Light – stomata open when it gets light, so the higher the light intensity the higher the rate • Temperature – higher the temp the faster the transpiration rate. Warmer water molecules have more energy so they evaporate from the cells inside the leaf faster. • Humidity – lower the humidity the faster the transpiration rate • Wind – the windier it is, the faster the transpiration rate
- 10. 1. Water is lost from the external surfaces of the mesophyll cells of the leaves by evaporation. 2. The air spaces in the mesophyll are saturated with water vapour. 3. The air in the atmosphere outside the stomata is less saturated with water. 4. As a result, water vapour in the air spaces of the leaf diffuses from the plant cells into the atmosphere through the stomata. 5. The movement of air outside the leaf carries water vapour away from the stomata. 6. The loss of water from a mesophyll cell makes the cell hypertonic to an adjacent cell. 7. Water from the adjacent cell diffuses into the mesophyll cell by osmosis and this in turn draws water from another adjacent cell into this cell. 8. Water continues to diffuse from neighbouring cells into the adjacent cells. 9. Finally, water is drawn from the xylem vessels in the veins. 10. A pulling force is created to pull water up the xylem vessels as a result of the evaporation of water vapour and this is known as transpirational pull.
- 11. Cohesion (sticking together) of the water molecules results in a column of water with high tensile strength (unlikely to break).
- 12. Water Transport
- 13. Key terms • Osmosis – diffusion of water molecules across a partially permeable membrane, from an area of higher water potential (ie high water concentration) to an area of low water potential (ie lower concentration of water molecules) • Water potential – is the potential (likelihood) of water molecules to diffuse out of or into a solution • What solution has the highest water potential?
- 14. Water enters the plant through the root hair cells
- 15. Water has to get through the cortex and endodermis before reaching the Xylem Apoplast pathway Symplast pathway Also VACUOLAR pathway
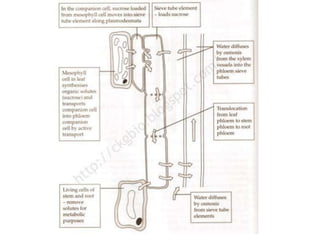
- 17. Pathways • Symplast pathway – goes through the living parts of the cell – the cytoplasm. The cytoplasm of neighbouring cells connect through plasmodesmata (small gaps in the cell walls) • Apoplast pathway – goes through the non-living parts of the root – the cell walls. The walls are very absorbent and water can simply diffuse through them, as well as passing through the spaces between them. Mineral ions also travel through this pathway. • Apoplast pathway is blocked at the Casparian strip, forcing use of the symplast pathway. This means water has to go through a cell membrane which is useful as the membrane can control whether or not substances in the water can get through. • Vacuolar pathway – osmosis carries water across the vacuoles, very little water travels this way due to high resistance
- 18. Casparian Strip • All water must enter cytoplasm at the Casparian strip. Minerals may need to do so up a concentration gradient – hence often requiring active transport. This seems to be a way to control amounts of water and minerals move from the soil into the xylem
- 19. Water moves up a plant against the force of gravity 1. 2. 3. 4. Cohesion and Tension Water evaporates from leaves at the ‘top’ of the xylem This creates tension (suction), which pulls more water into the leaf Water molecules are cohesive, so when some are pulled into the leaf others follow. This means the whole column from the leaves down to the roots moves upwards. Water enters the stem through the roots
- 20. Root pressure •Guttation – during the night droplets of water can be forced out of the leaves when transpiration rates are low, this is called guttation. •When water is transported into the xylem in the roots, it creates pressure and shoves water already in the xylem further upwards. •This pressure is weak and couldn’t move water to the top of the big plants, but it helps in young plants where leaves are developing
- 21. Root Pressure (continued) • We can see root pressure when the top of a plant is cut off • This pressure disappears if root cells are killed by steam or poisoned • This suggests root pressure is based on active transport • Root pressure is produced by the active secretion of salts from root cells into the xylem sap, increasing the concentration gradient across the root. This increases the movement of water into the cells by osmosis
- 22. Xylem and Phloem (a) explain the need for transport systems in multicellular plants in terms of size and surface area:volume ratio; (b) describe, with the aid of diagrams and photographs, the distribution of xylem and phloem tissue in roots, stems and leaves of dicotyledonous plants; (c) describe, with the aid of diagrams and photographs, the structure and function of xylem vessels, sieve tube elements and companion cells;