Denunciar
Compartir
Más contenido relacionado
La actualidad más candente
La actualidad más candente (20)
Chemical and physical features of seawater and the

Chemical and physical features of seawater and the
20100414 Herman Ridderinkhof Zeeonderzoek Aan Boord

20100414 Herman Ridderinkhof Zeeonderzoek Aan Boord
Similar a Earth science 15.1
Similar a Earth science 15.1 (20)
Oceanography Lecture_025553.pptx my one of best presentation

Oceanography Lecture_025553.pptx my one of best presentation
1603638128-lecture-26-compartmentalization-of-ecosystem.pptx

1603638128-lecture-26-compartmentalization-of-ecosystem.pptx
Chemical characteristics of Marine Environment.pdf

Chemical characteristics of Marine Environment.pdf
1 10 ocean composition-location Water in Earth’s Processes

1 10 ocean composition-location Water in Earth’s Processes
Implementing and learning from nutrition-sensitive fish agri-food systems, e....

Implementing and learning from nutrition-sensitive fish agri-food systems, e....
Más de Tamara
Más de Tamara (20)
Earth science 15.1
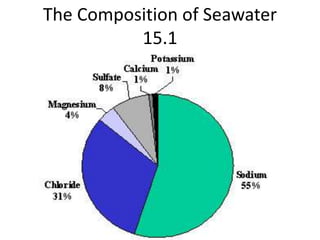
- 1. The Composition of Seawater 15.1
- 2. Salinity • The proportion of dissolved salts to pure water, usually expressed in parts per thousand.
- 3. Thermocline • A layer of water in which there is a rapid change in temperature with depth.
- 4. Density • Mass per unit volume of a substance, usually expressed as grams per cubic centimeters.
- 5. Pycnocline • A layer of water in which there is a rapid change of density with depth.
- 6. Mixed Zone • An area of the ocean surface with uniform temperatures created by the mixing of water by waves, currents, and tides.
- 7. Key Concept • What units are used to express the salinity of ocean water? –Oceanographers typically express salinity in parts per thousand.
- 8. Key Concept • What are the sources of salt in Ocean Water? –Most of the salt in seawater is sodium chloride, common table salt. Chemical weathering of rocks on the continents is one source of elements found in seawater.
- 9. Key Concept • What factors affect the density of ocean water? –Seawater density is influenced by two main factors: salinity and temperature.
- 10. Key Concept • What are the three main zones of the open ocean? –Oceanographers generally recognize a three-layered structure in most parts of the open ocean: a shallow surface mixed zone, a transition zone, and a deep zone.