Shoulder pain & problems
- 1. SHOULDER PAIN & PROBLEMS
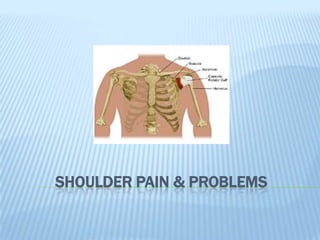
- 2. Shoulder Pain and Problems What is the shoulder? The shoulder is made up of several layers, including the following: Bones - the collarbone (clavicle), the shoulder blade (scapula), and the upper arm bone (humerus). Joints - facilitate movement, including the following: Sternoclavicular joint (where the clavicle meets the sternum) Acromioclavicular (AC) joint (where the clavicle meets the acromion) Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) - a ball-and-socket joint that facilitates forward, circular, and backward movement of the shoulder. Ligaments - a white, shiny, flexible band of fibrous tissue that binds joints together and connects various bones and cartilage, including the following: Joint capsule - a group of ligaments that connect the humerus to the socket of the shoulder joint on the scapula to stabilize the shoulder and keep it from dislocating. Ligaments that attach the clavicle to the acromion Ligaments that connect the clavicle to the scapula by attaching to the coracoid process
- 3. Acromion - the roof (highest point) of the shoulder that is formed by a part of the scapula. Tendons - the tough cords of tissue that connects muscles to bones. The rotator cuff Tendons are a group of tendons that connect the deepest layer of muscles to the humerus. Muscles (to help support and rotate the shoulder in many directions) Bursa - a closed space between two moving surfaces that has a small amount of lubricating fluid inside; located between the rotator cuff muscle layer and the outer layer of large, bulky muscles. Rotator cuff - composed of tendons, the rotator cuff (and associated muscles) holds the ball of the glenohumeral joint at the top of the upper arm bone (humerus). Shoulder pain may be localized in a specific area or may spread to areas around the shoulder or down the arm. What are some of the different types of shoulder problems? Common shoulder problems include the following: Dislocation The shoulder joint is the most frequently dislocated major joint of the body - often caused by a significant force that separates the shoulder joint's ball (the top rounded portion of the upper arm bone, or humerus) away from the joint's socket (glenoid).
- 4. Separation. The shoulder becomes separated when the ligaments attached to the collarbone (clavicle) are torn, or partially torn, away from the shoulder blade (scapula). Shoulder separation may be caused by a sudden, forceful blow to the shoulder, or as a result of a fall. Bursitis Bursitis often occurs when tendonitis and impingement syndrome cause inflammation of the bursa sacs that protect the shoulder. Impingement syndrome Impingement syndrome is caused by the excessive squeezing or rubbing of the rotator cuff and shoulder blade. The pain associated with the syndrome is a result of an inflamed bursa (lubricating sac) over the rotator cuff, and/or inflammation of the rotator cuff tendons, and/or calcium deposits in tendons due to wear and tear. Shoulder impingement syndrome can lead to a torn rotator cuff. Tendonitis Tendonitis of the shoulder is caused when the rotator cuff and/or biceps tendon become inflamed, usually as a result of being pinched by surrounding structures. The injury may vary from mild inflammation to involvement of most of the rotator cuff. When the rotator cuff tendon becomes inflamed and thickened, it may become trapped under the acromion. Rotator cuff tear A rotator cuff tear involves one or more rotator cuff tendons becoming inflamed from overuse, aging, a fall on an outstretched hand, or a collision.
- 5. Adhesive capsulitis (frozen shoulder) Frozen shoulder is a severely restrictive condition frequently caused by injury that, in turn, leads to lack of use due to pain. Intermittent periods of use may cause inflammation and adhesions to grow between the joint surfaces, thus restricting motion. There is also a lack of synovial fluid to lubricate the gap between the arm bone and socket that normally helps the shoulder joint to move. This restricted space between the capsule and ball of the humerus distinguishes adhesive capsulitis from the less complicated condition known as stiff shoulder. Fracture A fracture is a partial or total crack or break through a bone that usually occurs due to a impact injury. What causes shoulder problems? Although the shoulder is the most movable joint in the body, it is also an unstable joint because of its range-of-motion. Because the ball of the upper arm is larger than the socket of the shoulder, it is susceptible to injury. The shoulder joint must also be supported by soft tissues - muscles, tendons, and ligaments - which are also subject to injury, overuse, and under use.
- 6. Degenerative conditions and other diseases in the body may also contribute to shoulder problems, or generate pain that travels along nerves to the shoulder. How are shoulder problems diagnosed? In addition to a complete medical history and physical examination (to determine range-of- motion, location of pain, and level of joint instability/stability), diagnostic procedures for shoulder problems may include the following: X-ray - a diagnostic test which uses invisible electromagnetic energy beams to produce images of internal tissues, bones, and organs onto film. Arthrogram - a test in which dye is injected into the shoulder joint and x-rays are taken to outline structures of the shoulder. When the fluid leaks into an area that it does not belong, disease or injury may be considered, as a leak would provide evidence of a tear, opening, or blockage. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) - a diagnostic procedure that uses a combination of large magnets, radiofrequencies, and a computer to produce detailed images of organs and structures within the body; can often determine damage or disease in a surrounding ligament or muscle. Computed tomography scan (Also called a CT or CAT scan.) - a diagnostic imaging procedure that uses a combination of x-rays and computer technology to produce cross- sectional images (often called slices), both horizontally and vertically, of the body. A CT scan shows detailed images of any part of the body, including the bones, muscles, fat, and organs. CT scans are more detailed than general x-rays.
- 7. Electromyogram (EMG) - a test to evaluate nerve and muscle function. Ultrasound - a diagnostic technique which uses high-frequency sound waves to create an image of the internal organs. Laboratory tests (to determine if other problems may be the cause) Arthroscopy - a minimally-invasive diagnostic and treatment procedure used for conditions of a joint. This procedure uses a small, lighted, optic tube (arthroscope) which is inserted into the joint through a small incision in the joint. Images of the inside of the joint are projected onto a screen; used to evaluate any degenerative and/or arthritic changes in the joint; to detect bone diseases and tumors; to determine the cause of bone pain and inflammation. Treatment of shoulder problems: Specific treatment of shoulder problems will be determined by your physician based on: your age, overall health, and medical history extent of the condition your tolerance for specific medications, procedures, or therapies expectations for the course of the condition your opinion or preference
- 8. Treatment may include: activity modification rest physical therapy medications surgery POSTED BY ATTORNEY RENE G. GARCIA: For more information:- Some of our clients have suffered these kinds of injuries due to a serious accident. The Garcia Law Firm, P.C. was able to successfully handle these types of cases. For a free consultation please call us at 1-866- SCAFFOLD or 212-725-1313. http://medicalcenter.osu.edu/patientcare/healthcare_services/orthopaedics/joint/shoulder_pain_problem s/Pages/index.aspx
