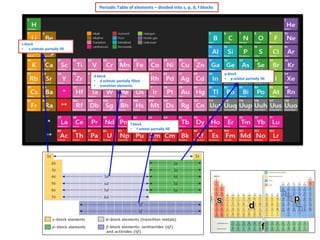
Periodic Table Elements - s, p, d, f Blocks
- 1. Periodic Table of elements – divided into s, p, d, f blocks s block • s orbitals partially fill d block • d orbitals partially filled • transition elements f block • f orbital partially fill p block • p orbital partially fill
- 2. Electron filled according to 3 Principles 1 Aufbau Principle • electron occupy orbitals of lower energy first • building up, construction from bottom up 4Be High energy - 1s2 2s2 5B - 1s2 2s2 2p1 2p 2p 2s 2s Click here to view simulation 1s 1s lower energy 2 Hund’s Principle • electron occupy orbitals singly first before pairing up 7N High energy - 1s2 2s2 2p3 8O - 1s2 2s2 2p4 2p 2s Click here to view simulation 1s 3 lower energy Pauli Exclusion Principle • each orbital occupy by 2 electron opposite spin 4Be - 1s2 2s2 High energy 10Ne - 1s2 2s2 2p6 Click here to view simulation lower energy
- 3. Electron configuration 5 B 1s2 2s2 2p1 6 C 1s2 2s2 2p2 7 N 1s2 2s2 2p3 8 O 1s2 2s2 2p4 9 F 1s2 2s2 2p5 10 Ne 1s2 2s2 2p6 11 Na 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1 12 Mg 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 13 Al 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p1 14 Si 1s2 15 P 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p3 16 S 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p4 17 CI 1s2 18 Ar 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 19 K 1s2 20 Ca 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 21 Sc 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d1 22 Ti 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d2 23 V 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d3 24 Cr 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 3d5 25 Mn 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d5 26 Fe 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d6 27 Co 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d7 28 Ni 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d8 29 Cu 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 3d10 30 Zn Electron occupy 4s first then 3d Energy level and sublevels 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 2s2 2s2 2s2 2p6 2p6 2p6 4s energy level lower than 3d 3s2 3s2 3s2 4s 3d 3p 3p2 3s 18Ar – 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 2p 2s 3p5 3p6 4s1 Electrons fill 4s first 3d 4s 1s 3p 19K – 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 3s 4s then 3d is fill 2p 3d 2s 4s 1s 21Sc 3p 3s – 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d1 2p 2s 1s
- 4. Electron Notation Atom Positive/Negative Ion s, p, d, f notation Complete configuration Noble gas notation Condensed configuration Noble gas notation Complete configuration 10 Ne 1s2 2s2 2p6 10 Ne [Ne] 10 Ne 1s2 2s2 2p6 /[Ne] 11 Na 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1 11 Na [Ne] 3s1 11 Na+ 1s2 2s2 2p6 / [Ne] 12 Mg 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 12 Mg [Ne] 3s2 12 Mg2+ 1s2 2s2 2p6 / [Ne] 13 Al 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p1 13 Al [Ne] 3s2 3p1 13 Al3+ 1s2 2s2 2p6 / [Ne] 14 Si 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p2 14 Si [Ne] 3s2 3p2 14 Si4+ 1s2 2s2 2p6 / [Ne] 15 P 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p3 15 P [Ne] 3s2 3p3 15 P3- 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 /[Ar] 16 S 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p4 16 S [Ne] 3s2 3p4 16 S2- 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 /[Ar] 17 CI 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p5 17 CI [Ne] 3s2 3p5 17 CI- 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6/ [Ar] 18 Ar 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 18 Ar [Ar] 19 [Ne] 18 Ar [Ar] K [Ar] 4s1 19 K+ 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 /[Ar] 20 Ca [Ar] 4s2 20 Ca2+ 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 / [Ar] 21 Sc [Ar] 4s2 3d1 22 Ti [Ar] 4s2 3d2 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d3 23 V [Ar] 4s2 3d3 Cr 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 3d5 24 Cr [Ar] 4s1 3d5 25 Mn 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d5 25 Mn [Ar] 4s2 3d5 26 Fe 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d6 26 Fe [Ar] 4s2 3d6 27 Co 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d7 27 Co [Ar] 4s2 3d7 28 Ni 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d8 28 Ni [Ar] 4s2 3d8 29 Cu 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 3d10 29 Cu [Ar] 4s1 3d10 30 Zn 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 30 Zn [Ar] 4s2 3d10 K 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 19 20 Ca 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 21 Sc 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d1 22 Ti 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d2 23 V 24 [Ar]
- 5. d block Exception to d block elements 4s energy level lower than 3d 3d 4s 3p Electron configuration d block 21 Sc 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d1 22 Ti V 24 Cr 25 Mn 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d5 26 Fe 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d6 27 Co Ni 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d8 29 Cu 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 3d10 30 Zn 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 3d5 4s energy level lower than 3d 2p 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d7 28 – 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d1 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d3 1s2 21Sc 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d2 23 3s 2s 1s 24Cr – 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s13d5 24Cr – 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d4 3d ✔ 4s 3p 3s ✗ Half fill energetically more stable 2p 2s 1s 29Cu 29Cu –1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 3d10 –1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d9 ✔ ✗ 4s 3p 3s Half fill energetically more stable 2p 2s 1s 3d
- 6. s block elements • s orbitals partially fill 1 H He p block elements • p orbital partially fill 5 1s2 n = 2 period 2 B [He] 2s2 2p1 6 1s1 2 Periodic Table – s, p, d, f blocks elements C [He] 2s2 2p2 7 N [He] 2s2 2p3 3 Li [He] 2s1 8 O [He] 2s2 2p4 4 Be [He] 2s2 9 F [He] 2s2 2p5 11 Na [Ne] 3s1 10 Ne [He] 2s2 2p6 12 Mg [Ne] 3s2 13 Al [Ne] 3s2 3p1 14 20 K Ca [Ne] 3s2 3p2 [Ar] 15 P [Ne] 3s2 3p3 [Ar] 4s2 16 S [Ne] 3s2 3p4 17 19 Si 4s1 CI [Ne] 3s2 3p5 18 Ar [Ne] 3s2 3p6 d block elements • d orbitals partially fill • transition elements 21 Sc [Ar] 4s2 3d1 22 Ti [Ar] 4s2 3d2 23 V [Ar] 4s2 3d13 24 Cr [Ar] 4s1 3d5 25 Mn [Ar] 4s2 3d5 26 Fe [Ar] 4s2 3d6 27 Co [Ar] 4s2 3d7 28 Ni [Ar] 4s2 3d8 29 Cu [Ar] 4s1 3d10 30 Zn [Ar] 4s2 3d10 f block elements • f orbitals partially fill Video on electron configuration Click here electron structure Click here video on s,p,d,f notation Click here video s,p,d,f blocks,
- 7. Periodic Table – s, p, d, f blocks elements Electron structure Chromium d block (Period 4) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 3d5 [Ar] 4s1 3d5 d block – d partially filled Electron structure Cadmium d block (Period 5) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d104s2 4p6 5s2 4d10 [Kr] 5s2 4d10 d block – d partially filled Electron structure Germanium p block, Gp 4 (Period 4) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p2 [Ar] 4s2 3d10 4p2 Gp 4 -4 valence electron Electron structure Mercury d block (Period 6) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d104s2 4p6 5s2 4d10 5p6 6s2 4f14 5d10 [Xe] 6s2 4f14 5d10 d block – d partially filled Electron structure Iodine p block, Gp 7 (Period 5) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d104s2 4p6 5s2 4d10 5p5 [Kr] 5s2 4d10 5p5 Gp 7 - 7 valence electron Electron structure Lead p block, Gp 4 (Period 6) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d104s2 4p6 5s2 4d10 5p6 6s2 4f14 5d106p2 [Xe] 6s2 4f14 5d10 6p2 Gp 4 -4 valence electron
- 8. Periodic Table – s, p, d, f blocks elements s block elements • s orbitals partially fill 1 H He 5 1s2 n = 2 period 2 B [He] 2s2 2p1 6 1s1 2 p block elements • p orbital partially fill C [He] 2s2 2p2 7 N [He] 2s2 2p3 3 Li [He] 2s1 8 O [He] 2s2 2p4 4 Be [He] 2s2 9 F [He] 2s2 2p5 11 Na [Ne] 3s1 10 Ne [He] 2s2 2p6 12 Mg [Ne] 3s2 13 Al [Ne] 3s2 3p1 14 Si [Ne] 3s2 3p2 15 P [Ne] 3s2 3p3 16 S [Ne] 3s2 3p4 17 CI [Ne] 3s2 3p5 18 Ar [Ne] 3s2 3p6 19 K 20 1 Ca [Ar] [Ar] 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d104s2 4p6 5s2 4d10 5p6 6s2 4f14 5d106p2 [Xe] 6s2 4f14 5d10 6p2 4s1 4s2 Identify position elements P, Q, R, S and T Electron configuration : P – 3s2 3p6 Q – 4s2 4p5 R – 3s2 3p6 4s2 S – 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d3 4s2 T – 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p6 Answer 2 Write electron configuration for X, Y and Z Element Group Period X 2 3 Y 15 2 Z 18 3 Answer Element Group Period Classification P 8/18 3 Noble gas Q 7/17 4 p block R 2 4 s block S 5 4 d block T 8/18 4 Noble gas X – 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 Y – 1s2 2s2 2p3 Z – 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3 Write electron structure for ions: • • • • • • O - 1s2 2s2 2p4 O2- V - 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d3 V3+ Cu - 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d9 Cu2+ - Answer Write electron structure for ions: • • • • • • O - 1s2 2s2 2p4 O2- -1s2 2s2 2p6 V - 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d3 V 3+ - 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s0 3d2 Cu - 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d9 Cu 2+ - 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s23p6 4s0 3d9
- 9. Four Quantum Numbers • • • Electrons arrange in specific energy level and sublevels Orbitals of electrons in atom differ in size, shape and orientation. Allow states call orbitals, given by four quantum number 'n', 'l', 'm l' and ’ms’ - (n, l, ml, ms) 1 Principal Quantum Number (n): n = 1, 2, 3,.. ∞ • Energy of electron and size of orbital/shell • Distance from nucleus, (higher n – higher energy) • Larger n - farther e from nucleus – larger size orbital • n=1, 1stprincipal shell ( innermost/ground shell state) 2 Angular Momentum Quantum Number (l): l = 0 to n-1. • Orbital Shape • Divides shells into subshells/sublevels. • Letters (s, d, p, f) s orbital p orbital No TWO electron have same 4 quantum number 3 4 Magnetic Quantum Number (ml): ml = -l, 0, +l. • Orientation orbital in space/direction • mℓ range from −ℓ to ℓ, • ℓ = 0 -> mℓ = 0 –> s sublevel -> 1 orbital • ℓ = 1 -> mℓ = -1, 0, +1 -> p sublevel -> 3 diff p orbitals • ℓ = 2 -> mℓ = -2, -1, 0, +1, +2 -> d sublevel -> 5 diff d orbitals • (2l+ 1 ) quantum number for each ℓ value Spin Quantum Number (ms): ms = +1/2 or -1/2 • Each orbital – 2 electrons, spin up/down • Pair electron spin opposite direction • One spin up, ms = +1/2 • One spin down, ms = -1/2 • No net spin/cancel out each other– diamagnetic electron writing electron spin electron spin up/down d orbital
- 10. Principal and Angular Momentum Quantum numbers • • • Electrons arrange in specific energy level and sublevels Orbitals of electrons in atom differ in size, shape and orientation. Allow states call orbitals, given by four quantum number 'n', 'l', 'm l' and ’ms’ - (n, l, ml, ms) 1 Principal Quantum Number (n): n = 1, 2, 3, …, ∞ • Energy of electron and size of orbital /shell • Distance from nucleus, (higher n – higher energy) • Larger n - farther e from nucleus – larger size orbital • n=1, 1stprincipal shell ( innermost/ground shell state) 2 Angular Momentum Quantum Number (l): l = 0, ..., n-1. • Orbital Shape • Divides shells into subshells (sublevels) • Letters (s,p,d,f) • < less than n-1 Sublevels, l Quantum number, n and l l=1 2p sublevel l=0 2s sublevel n= 2 n= 1 1 Principal Quantum #, n (Size , energy) l=0 2 1s sublevel Angular momentum quantum number, l (Shape of orbital) 2p sublevel – contain 2p orbital 2nd energy level Has TWO sublevels 2s sublevel – contain 2s orbital 1st energy level Has ONE sublevel 1s sublevel – contain 1s orbital 1 Principal Quantum Number (n) 2 Angular Momentum Quantum Number (l)
- 11. Electronic Orbitals Simulation Electronic Orbitals n = 1, 2, 3,…. Allowed values l = 0 to n-1 Allowed values ml = -l, 0, +l- (2l+ 1 ) for each ℓ value ml =+2 ml =+1 ml = 0 l=1 3px orbital ml = 0 3s sublevel 3py orbital 3s orbital ml =+1 l=0 3pz orbital ml = 0 3p sublevel 3dxy orbital ml =-1 l=1 3dxz orbital ml =+1 n= 3 3dz2 orbital ml =-2 3d sublevel 3dyz orbital ml =-1 l=2 Energy Level 3dx2 – y2 orbital 2py orbital ml = 0 2p sublevel 2pz orbital ml =-1 n= 2 2px orbital l=0 1 Principal Quantum #, n (Size , energy) 2 2s sublevel ml =0 1s sublevel ml =0 Click here to view simulation 2s orbital l=0 n= 1 Click here to view simulation 1s orbital Angular momentum quantum number, l (Shape of orbital) 3 Magnetic Quantum Number (ml) (Orientation orbital) Click here to view simulation
- 12. Quantum Numbers and Electronic Orbitals ml =+2 3dx2 – y2orbital Simulation Electronic Orbitals Energy Level ml =+1 3d sublevel ml = 0 3dz2 orbital ml =-1 l=2 3dyz orbital 3dxz orbital Click here to view simulation n= 3 ml =-2 3dxy orbital ml =+1 3p sublevel ml = 0 3pz orbital ml =-1 l=1 3py orbital 3px orbital Click here to view simulation l=0 2p sublevel n= 2 ml = 0 3s orbital ml =+1 l=1 3s sublevel 2py orbital ml = 0 2pz orbital ml =-1 2px orbital l=0 n= 1 2s sublevel ml =0 2s orbital l=0 1s sublevel ml =0 1s orbital Click here to view simulation
- 13. Concept Map No TWO electron have same 4 quantum number Quantum number Quantum number = genetic code for electron What are these 4 numbers? (1, 0, 0, +1/2) 0r (3, 1, 1, +1/2) 4 numbers n l ml ms Size/distance Shape Orientation Electron has special number codes Electron spin Number + letter 1 Electron with quantum number given below (n,l,ml,,ms) – (1, 0, 0, +1/2) (n,l,ml,,ms) – (3, 1, 1, +1/2) 2 1s orbital 3py orbital What values of l, ml, allow for n = 3? How many orbitals exists for n=3? Video on Quantum numbers For n=3 -> l = n -1 =2 -> ml = -l, 0, +l -> -2, -1, 0, +1, +2 • mℓ range from −ℓ to ℓ, • ℓ = 0 -> mℓ = 0 –> s sublevel -> 1 orbital • ℓ = 1 -> mℓ = -1, 0, +1 -> p sublevel -> 3 diff p orbitals • ℓ = 2 -> mℓ = -2, -1, 0, +1, +2 -> d sublevel -> 5 diff d orbitals • (2l+ 1 ) quantum number for each ℓ value Answer = nine ml values – 9 orbitals/total # orbitals = n 2 Click here video on quantum number Click here video on quantum number
