Reactions and Equilibrium
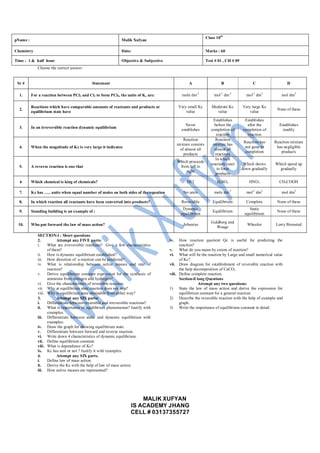
- 1. MALIK XUFYAN IS ACADEMY JHANG CELL # 03137355727 Choose the correct answer SECTION-l : Short questions 2. Attempt any FIVE parts: i. What are irreversible reactions? Give a few characteristics of them? ii. How is dynamic equilibrium established? iii. How direction of a reaction can be predicted? iv. What is relationship between active masses and rate of reaction? v. Derive equilibrium constant expression for the synthesis of ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen? vi. Give the characteristics of reversible reaction. vii. Why at equilibrium state reaction does not stop? viii. Why is equilibrium state attainable from either way? 3. Attempt any SIX parts: i. Differentiate between reversible and irreversible reactions? ii. What is importance of equilibrium phenomenon? Justify with examples. iii. Differentiate between static and dynamic equilibrium with examples. iv. Draw the graph for showing equilibrium state. v. Differentiate between forward and reverse reaction. vi. Write down 4 characteristics of dynamic equilibrium. vii. Define equilibrium constant. viii. What is dependence of Kc? ix. Kc has unit or not ? Justify it with examples. 4. Attempt any SIX parts. i. Define law of mass action. ii. Derive the Kc with the help of law of mass action. iii. How active masses are represented? iv. How reaction quotient Qc is useful for predicting the reaction? v. What do you mean by extent of reaction? vi. What will be the reaction by Large and small numerical value of Kc? vii. Draw diagram for establishment of reversible reaction with the help decomposition of CaCO3 viii. Define complete reaction. Section-ll long Questions Attempt any two questions: 1) State the law of mass action and derive the expression for equilibrium constant for a general reaction. 2) Describe the reversible reaction with the help of example and graph. 3) Write the importance of equilibrium constant in detail. pName : Malik Xufyan Class 10th Chemistry Date: Marks : 60 Time : 1 & half hour Objective & Subjective Test # 01 , CH # 09 Sr # Statement A B C D 1. For a reaction between PCl3 and Cl2 to form PCl5, the units of Kc are: mole dm-3 mol-1 dm-3 mol-1 dm3 mol dm3 2. Reactions which have comparable amounts of reactants and products at equilibrium state have Very small Kc value Moderate Kc value Very large Kc value None of these 3. In an irreversible reaction dynamic equilibrium Never establishes Establishes before the completion of reaction Establishes after the completion of reaction Establishes readily 4. When the magnitude of Kc is very large it indicates Reaction mixture consists of almost all products Reaction mixture has almost all reactants Reaction has not gone to completion Reaction mixture has negligible products 5. A reverse reaction is one that Which proceeds from left to right In which reactants react to form products Which shows down gradually Which speed up gradually 6 Which chemical is king of chemicals? HCl H2SO4 HNO3 CH3COOH 7. Kc has ….. units when equal number of moles on both sides of the equation No units mole dm-3 mol-1 dm3 mol dm3 8. In which reaction all reactants have been converted into products? Reversible Equilibrium Complete None of these 9. Standing building is an example of : Dynamic equilibrium Equilibrium Static equilibrium None of these 10. Who put forward the law of mass action? Arhenius Guldberg and Waage Whooler Lorry Bronsted
- 2. MALIK XUFYAN IS ACADEMY JHANG CELL # 03137355727 Q.1.Choose the correct answer SECTION-l : Short questions 2. Attempt any FIVE parts: i. Why H+ ion acdt as Lewis acid? ii. Define pH. What is pH of pure water? iii. Na2SO4 is a neutral while NaHSO4 is an acid salt. Justify. iv. How are the soluble salts recovered from water? v. Why a salt is neutral, explain with an example? vi. How can you justify that Pb(OH)NO3 is basic salt? vii. You are in a need of an acidic salt. How can you prepare it? viii. Define base and explain all alkalies are bases but all bases are not alkalies. 3. Attempt any SIX parts: i. Differentiate between acid and bases. ii. Define Arrhenius acid and base with the help of examples. iii. Write two limitations of Arrhenius Concept. iv. Differentiate between conjugate base and conjugate acid with examples. v. What do you know about an adduct? vi. What are Lewis acid and Lewis bases? Explain with examples. vii. What are best preventions from hyperacidity? viii. React salts with Sodium Hydroxide. Write at least three examples. ix. React acids with carbonates and bicarbonates. 4. Attempt any SIX parts. i. All Bronsted base are also Lewis bases but all Bronsted acids are not Lewis acids. Justify. ii. What is authorization? Give example iii. What are indicators? Why we use it? Give suitable examples. iv. How can you prepare insoluble salts? v. What are double and complex salts. Give suitable salts. vi. Write uses of some salts. vii. What do you know about acid rain? viii. What is neutralization reaction? Give example. ix. Differentiate between acid and basic radical. Section-ll long Questions Attempt any two questions: 4) Explain with examples that how soluble salts are prepared? 5) Write note on Lewis concept with the help of examples. 6) Explain with the help of examples (a) Normal salts (b) Acidic salts (c) Basic salts (d) Mixed salts 7) Explain Lowry Bronsted concept with the help of examples 8) Write main uses of salts. Name : Malik Xufyan Class 10th Chemistry Date: Marks : 60 Time : 1 & half hour Objective & Subjective Test # 02 , CH # 10 Sr # Statement A B C D 1. Which one of the following is a lewis base? NH3 BF3 H+ AlCl3 2. Which ion is the conjugate base of sulphuric acid? SO3 -2 S-2 HSO3 - HSO4 - 3. You want to dry a gas which one of the following salt you will use CaCl2 NaCl CaO Na2SiO3 4. Which one of the following species is not amphoteric ? H2O NH3 HCO3 - SO4 -2 5. Acetic acid is used for Flavouring food Making explosive Etching designs Cleaning metals 6 Which salt is used for explosive materials? NaCl Na2SO4 NaClO3 CaCl2 7. Which is universal indicator? NaCl Solution Litmus Solution pH indicator Indicator 8. Which acid is present in stomach chemicals? H2SO4 HCl HNO3 CH3COOH 9. Which base is used for Bee’s sting? NaOH Ca(OH)2 Mg(OH)2 KOH 10. Which acid is used for food preservation? Acetic aid Benzoic acid Nitric acid Sulphuric acid
- 3. MALIK XUFYAN IS ACADEMY JHANG CELL # 03137355727 Q.1. Choose the correct answer SECTION – I : Short questions 2. Attempt any FIVE parts: i. How alkyl radicals are formed? Explain with example. ii. Write classification of coal. iii. What is the importance of natural gas? iv. Write down the dot and cross formulae of n – butane and isobutene. v. Why benzene and other homologous compounds of benzene are called aromatic compounds? vi. What is difference between n – propyl and iso – propyl? Explain with structure. vii. Define functional groups. Explain with three examples. viii. Describe the test for the detection of aldehyde group. 3. Attempt any SIX parts: i. Differentiate between homocyclic and heterocyclic compounds. ii. What is meant by catenation? Explain. iii. Silicon and carbon have similar electronic configuration but carbon shows catenation while silicone does not. Justify. iv. Define isomerism. Give an example. v. Write down any fur general characteristics of organic compounds. vi. Discuss about coal gas and coke. vii. Discuss about petroleum. viii. What is vital force theory? How it disproved? ix. Write down any four uses of organic compounds. 4. Attempt any SIX parts. i. What is homologous series? Discuss its properties. ii. Discuss ester and ether linkage iii. Discuss functional groups that contain double and triple bond and carboxylic group. Also give an example. iv. Discuss the test of unsaturation. v. How primary amino group is detected? vi. How can you explain that plants are a major source of organic compounds? vii. Define molecular formula of organic compounds. viii. What is alcoholic group and aldehydic group? ix. What is sodium nitroprusside test? Section-II long Questions Attempt any two questions: 5) Write a detailed note on coal, natural gas and coal tar. 6) Discuss tests for the detection of ketonic group, carboxylic group, alcoholic group and ketonic group. 7) What are the reasons of a large diversity and magnitude of organic compounds? Explain in detail. 8) Explain the general characteristics of organic compounds in detail. 9) Differentiate between aromatic and alicylic compounds and also between the condensed formula and electronic formula of organic compounds. Name : Malik Xufyan Class 10th Chemistry Date: Marks : 60 Time : 1 & half hour Objective & Subjective Test # 03 , CH # 11 Sr # Statement A B C D 1. Main component of natural gas is: Methane Propane Butane Propene 2. Which one of the following is a synthetic fiber? Cotton Wool Nylon Silk 3. Coal gas is a mixture of CO and CH4 CO, CH4, CO2 CO, CH4, H2 CO, H2 and CO2 4. Natural gas contains 85% ___________. Methane Ethane Propane Propene 5. Which one of the following does not contain protein? Pulses Potatoes Beans Eggs 6 General formula of alkyl radical is: CnH2n + 2 CnH2n – 2 CnH2n + 1 CnH2n 7. Bituminous contain carbon contents about: 80% 85% 90% 95% 8. Organic compounds is not soluble in: Alcohol Ether Benzene Water 9. Urea is prepared from: Ammonia Ammonium hydrate Ammonium cyanate Ammonium nitrate 10. The strong heating of coal in the absence of air is called: Simple distillation Destructive distillation Fractional distillation Dry distillation
- 4. MALIK XUFYAN IS ACADEMY JHANG CELL # 03137355727 Name: Class: 10th Date: Paper: Chemistry Objective + Subjective Part Marks: 60 Time: 2:40 Test: 4 Chapter No. 12 Choose the correct answers. 10 × 1 = 10 Sr # Statements A B C D 1. The reduction of alkyl halides take place in the presence of Zn / HCl Na / HCl Mg / HCl Cu / HCl 2. Alkenes are prepared from alcohols, this phenomenon is called: Dehydrogenation Dehalogenation Dehydration Dehydrohalogenation 3. Which one of these is a saturated hydrocarbon? C2H4 C3H6 C4H8 C5H12 4. The end product of oxidation of acetylene is Oxalic acid Glycol Glyoxal None of these 5. Substituent reaction is a characteristic of Alkanes Alkenes Alkynes None of these 6. Dehydrogenation of alcohols can be carried out with: NaOH KOH HCl H2SO4 7. Oxidation of alkenes produce Glyoxal Glycol Oxalic acid Formic acid 8. The general formula of saturated hydrocarbons is CnH2n + 1 CnH2n + 2 CnH2n – 1 CnH2n – 2 9. Alkanes are also called Olefins Parafins Both None 10. Reduction means addition of Nascent hydrogen Hydrogen molecule Hydrogen gas None SECTION – I Q 2. Give the answers of any FIVE questions. 6 × 2 = 10 i. Define hydrocarbons. ii. Define open chain and closed chain hydrocarbons with an example. iii. Differentiate between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons. iv. How alkanes are prepared by reduction of alkyl halides? Give equations with conditions. v. Describe the sources of alkanes. vi. Discuss the uses of methane and ethane. vii. Why hydrocarbons are soluble in organic solvents? viii. Identify propane from propene with a chemical test. Q 3. Give the answers of any SIX questions. 6 × 2 = 12 i. Why alkenes are called olefins? ii. How alcohols and alkyl halides prepared alkenes? Just give equations. iii. Discuss physical properties of alkanes. iv. Prepare glycol from alkene and KMnO4. v. Discuss uses of ethene. vi. How alkynes are prepared from vicinal dihalides? vii. Discuss about photochemical industry and synthetic fiber industry. viii. How hydrocarbons are used as fuel? Discuss. ix. Explain briefly that why butane undergoes substitution reactions? Q 4. Give the answers of any SIX questions. 6 × 2 = 12 i. What happens? When ethyne burnt in the presence of air. ii. Why alkynes are more reactive than alkanes? Discuss. iii. Discuss oxidation of alkyne with KMnO4. Give chemical equation. iv. Describe physical properties of alkynes. v. How alkenes are prepared from alcohols? vi. Write down the occurrence of alkenes. vii. Describe any four uses of acetylene. viii. What happens when ethyne is passed through bromine water? ix. Discuss the physical properties of alkanes. SECTION – II Give the answers of any TWO questions. 8 × 2 = 16 Q 5. What type of reactions is given by alkanes? Explain with the reference to halogenation of alkanes. Q 6. Prepared a) Alkynes from tetrahalides. b) Alkenes from dehydrohalogenation of alkyl halides. c) Alkanes from hydrogenation of alkenes and alkyne and by reduction of alkyl halides. Q 7. Write down reactions: a) Alkyne with halogen. b) Hydrogenation and hydrohalogenation of alkenes. c) Combustion of alkanes. Q 8. Write down the chemical properties of alkanes, alkenes and alkynes in detail.
- 5. MALIK XUFYAN IS ACADEMY JHANG CELL # 03137355727 Name: Class: 10th Date Paper: Chemistry Objective + Subjective Part Marks: 60 Time: 2:40 Test: 5 Chapter no: 13 Q.1.Choose the correct answers. 10 × 1 = 10 Sr # Statements A B C D 1. Which of the following is a disaccharide? Glucose Fructose Sucrose Starch 2. Which one of the following is a reducing sugar? Glucose Maltose Sucrose Starch 3. Deficiency of vitamin E causes: Rickets Scurvy Anemia in babies Night blindness 4. Which one of the following is a water soluble vitamin? Vitamin A Vitamin C Vitamin D Vitamin E 5. Night blindness is because of deficiency of Vitamin A Vitamin E Vitamin C Vitamin D 6. Which one of the following is a fat soluble vitamin? A E K All of these 7. _____ is a permanent storage place for genetic information in the nucleus of cell. RNA DNA Nucleosomes Nucleopores 8. _______ consists of glucose and galactose. Sucrose Maltose Lactose None 9. Animal fats used in making: Vegetable oil Soap Fats Gasoline 10. Which one of the following is triglyceride? Carbohydrates Proteins Lipids Vitamins SECTION – I Q 2. Give the answers of any FIVE questions. 6 × 2 = 10 i. How is gelatin formed? ii. What is the function of DNA? iii. How you justify RNA works like a messenger? iv. Why the ten amino acids are essential for us? v. What do you mean by genetic code of life? vi. Write down the significance of vitamins. vii. Give the characteristics of polysaccharides. viii. Justify that water soluble vitamins are not injurious to health. Q 3. Give the answers of any SIX questions. 6 × 2 = 12 i. Define lipids. Give the general formula of triglycerides. ii. Define fatty acids. Give any two names and formulas of fatty acids. iii. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. Justify it by giving equation. iv. Differentiate between essential and non – essential amino acids. v. Carbohydrates are a source of energy. Justify it. vi. Write down the structural formula of glucose and fructose. vii. What are oligosaccharides? What do you know about this? viii. Discuss sources and uses of vitamin D. Also give the name of diseases that caused due to its deficiency. ix. Give the uses of lipids. Q 4. Give the answers of any SIX questions. 6 × 2 = 12 i. Differentiate between glucose and fructose. ii. How vegetable oil is prepared by hydrogenation? iii. Define proteins and amino acids. iv. Give the source of sucrose, lactose and maltose. And also give the components of these. v. Briefly explain RNA. vi. Differentiate between ghee and oil. vii. Plants are the source of oils. Justify it. viii. What are the advantages of water soluble vitamins? ix. Give the sources and uses of vitamin A. also give the names of diseases that caused due to its deficiency. SECTION – II Give the answers of any TWO questions. 8 × 2 = 16 Q 5.what are carbohydrates? How monosaccharides are prepared? Give their general characteristics. Q 6. Define vitamins. Also give its different types in detail. Also give their importance. Q 7. Describe about DNA in detail. Q 8. Give the sources and uses of carbohydrates, lipids and proteins in detail.
- 6. MALIK XUFYAN IS ACADEMY JHANG CELL # 03137355727 Name: Class: 10th Paper: Chemistry Objective + Subjective Part Marks: 60 Time: 2:40 Test: 6 Chapter no: 14 Choose the correct answers. 10 × 1 = 10 Sr # Statements A B C D 1. The composition of nitrogen in the atmosphere is 78.09 78.99 79.09 79.99 2. Normally rain water is weakly acidic because of SO3 gas CO2 gas SO2 gas NO2 gas 3. Iron and steel structures are damaged by Carbon mono oxide Sulpher dioxide Methane Carbon dioxide 4. Which one of the following is not an air pollutant? Nitrogen Carbon monoxide Nitrogen dioxide Ozone 5. Just above the earth’s surface is: Mesosphere Stratosphere Thermosphere Troposphere 6. Which gas protects the earth’ surface from ultra violet radiations? CO2 CO N2 O3 7. About 99% atmosphere’s mass lies within: 30 km 35 km 11 km 15 km 8. Acid rain affects the aquatic life by closing fish gills because of: Lead metal Chromium metal Mercury metal Aluminium metal 9. Which one of the following is not a secondary pollutant? HNO3 HF PAN CH4 10. Accumulation of CO2 in air is resulting in increasing temperature about ______ every year. 0.07 o C 0.04 o C 0.05 o C 0.08 o C SECTION – I Q 2. Give the answers of any FIVE questions. 6 × 2 = 10 i. Explain the phenomenon of decreasing temperature in troposphere. ii. CO is a hidden enemy, explain its action. iii. How acid rain increases the acidity of soil? iv. Why is 75% of the atmospheric mass lies within the troposphere? v. How ozone layer is being depleted by chloroflorocarbons? vi. State the major sources of CO and CO2 emission. vii. What threats are to human health due to SO2 gas as air pollutant? viii. Which air pollutant is produced on anaerobic decomposition of organic matter? Q 3. Give the answers of any SIX questions. 6 × 2 = 12 i. Differentiate between primary and secondary pollutants. ii. Define acid rain. iii. Write any three effects of ozone depletion. iv. Why CO2 is called a green house gas? v. Burning in open air is preffered. Comment. vi. How combustion of fossil fuels in internal combustion engine produces oxides of nitrogen? vii. Define pollutants and pollution. viii. Discuss oxides of carbon. ix. Describe the composition of atmosphere. Q 4. Give the answers of any SIX questions. 6 × 2 = 12 i. What is troposphere? Write about it in short. ii. Where the ozone layer exists? iii. Why the temperature of upper stratosphere is higher? iv. How the temperature of atmosphere is maintained? v. Differentiate between atmosphere and environment. vi. Give the effects of global warming. vii. How aquatic life is affected by acid rain? viii. How acid rain damages buildings? ix. How ozone is beneficial to human health? Discuss. SECTION – II Give the answers of any TWO questions. 8 × 2 = 16 Q 5. Write a note on green house effect and global warming. Q 6. What is acid rain? Give its effects in detail. Q 7. What are nitrogen compounds? How the pollute the environment? Discuss in detail. Q 8. Discuss stratosphere in detail.
- 7. MALIK XUFYAN IS ACADEMY JHANG CELL # 03137355727 Name: Class: 10th Paper: Chemistry Objective + Subjective Part Marks: 60 Time: 2:40 Test: 7 Chapter no: 15 Choose the correct answers. 10 × 1 = 10 Sr # Statements A B C D 1. A disease that cause bone and tooth damage is: Fluorosis Hepatitis Cholera Jaundice 2. Temporary hardness is because of: Ca(HCO3)2 CaCO3 MgCO3 MgSO4 3. Permanent hardness is removed by adding: Na2 zeolite Soda lime Lime stone Lime water 4. Specific heat capacity of water is: 4.2 kJg-1 K-1 4.2 Jg-1 K-1 2.4 kJg-1 K-1 2.4 Jg-1 K-1 5. Which one of the following diseases causes liver inflammation? Typhoid Jaundice Cholera Hepatitis 6. Which one of the following ions does not cause hardness in water? Ca2+ Mg2+ SO4 2- Na+ 7. Ground water contains about ______ water. 2.1% 0.001% 0.6% 0.2% 8. Soap is the sodium salt of a long chain ___________. Carbonic acid Carboxylic acid Propanoic acid Acetic acid 9. Hepatitis is a __________ inflammation. Heart Kidney Liver Stomach 10. Swimming pools are cleaned by ________ process. Chlorination Bromination Fluorination Iodination SECTION – I Q 2. Give the answers of any FIVE questions. 6 × 2 = 10 i. How detergents make the water unfit for drinking? ii. How water borne disease can be prevented? iii. What are the causes of hardness in water? iv. Which forces are responsible for dissolving polar substances in water? v. How limestones dissolve in water? vi. How water rises in plants? vii. What are the effects of temporary hardness in water? viii. How water dissolves in water? Q 3. Give the answers of any SIX questions. 6 × 2 = 12 i. What is meant by Fluorosis? ii. Write down the name of bacteria that causes the cholera. iii. Write down the function of fertilizers. iv. Define industrial effluents. Give its any two causes or effects. v. Differentiate between hard and soft water. vi. How we remove temporary hardness with the help of Clark’s method? Give equations. vii. Give the disadvantages of hard water. viii. Give the names of salts that cause the hardness of water. ix. Why we use water as a solvent? Give reasons. Q 4. Give the answers of any SIX questions. 6 × 2 = 12 i. Write down any four properties of water. ii. Differentiate between temporary and permanent hardness. iii. Why non – ionic polar compounds are soluble in water? Explain. iv. What is dysentery? v. Discuss jaundice and typhoid. vi. How decaying plants consume oxygen? vii. Write down the effects of water pollution. viii. Discuss hepatitis and cryptosporidium. ix. Write down the dual effects of agricultural effluents. SECTION – II Give the answers of any TWO questions. 8 × 2 = 16 Q 5. How we remove permanent hardness? Explain in detail. Q 6. Explain in detail that water acts as a solvent. Q 7. Write a note on treatment of sewage water. Q 8. A) Justify that household water is the reason of water pollution B) How domestic effluents cause water pollution. Write detailed note.
- 8. MALIK XUFYAN IS ACADEMY JHANG CELL # 03137355727 Name: Class: 10th Paper: Chemistry Objective + Subjective Part Marks: 60 Time: 2:40 Test: 8 Chapter no: 16 Choose the correct answers. 10 × 1 = 10 Sr # Statements A B C D 1. When NaHCO3 is heated it forms: CO2 Ca(OH)2 CaCO3 CaO 2. Crude oil is heated in the furnace upto: 300 o C 350 o C 400 o C 450 o C 3. The nitrogen present in urea is used by plants to synthesize Sugar Proteins Fats DNA 4. Organic compound found in gasoline is C2H4 C3H8 C8H18 C12H26 5. Matte is a mixture of: FeS and CuS Cu2O and FeO Cu2S and FeS CuS and FeO 6. In Solvay’s process slaked lime is used to Prepare CO2 Prepare quick lime Recover ammonia Form Na2CO3 7. Urea contains nitrogen ______. 48.8% 46.6% 46.8% 48.8% 8. Gravity separation is based on the differences in ______ of metallic ore and the gangue particles. Intensities Wavelength Densities Frequencies 9. Urea is prepared from: Ammonium cyanate Ammonium carbamate Both None 10. ___________ is used as jet oil. Diesel oil Kerosene oil Gasoline Fuel oil SECTION – I Q 2. Give the answers of any FIVE questions. 6 × 2 = 10 i. What role is played by pine oil in the froth flotation process? ii. Explain the process of electrorefining. iii. How NaHCO3 is converted into Na2CO3? iv. Give the principle of Solvay’s process. v. What id refining of petrolium? How it can be carried out? vi. What happen when ammonical brine is carbonated? vii. How is roasting carried out? viii. How is ammonia prepared for the synthesis of urea? Q 3. Give the answers of any SIX questions. 6 × 2 = 12 i. What is meant by metallurgy? Give the names of different process. ii. How forth floatation process occurred? Explain. iii. How concentration of crushed ore is carried out by electromagnetic separation? Explain. iv. Draw flow sheet diagram of Solvay’s process for the manufacturing of sodium carbonate. v. How CO2 is prepared in the Solvay’s process? vi. Differentiate between diesel oil and fuel oil. vii. Describe formation of petrolium. viii. Give the reactions of formation of ammonia in the process. ix. What type of raw materials used in the manufacturing of sodium carbonate? Give names. Q 4. Give the answers of any SIX questions. 6 × 2 = 12 i. Give the advantages of Solvay’s process. ii. What happens when ammonium carbamate is heated with steam? iii. Differentiate between crude oil and residual oil. iv. Write down the composition, boiling range and temperature of gasoline, petrolium ether and petrolium gas. v. Draw flow sheet diagram of urea. vi. How ammonia is prepared by Haber’s process? Give equation. vii. Discuss bassemerization by giving a suitable example. viii. Define minerals and ores. ix. What is the principle of fractional distillation? SECTION – II Give the answers of any TWO questions. 8 × 2 = 16 Q 5. Discus smelting by giving suitable example and how refining of metal is done? Explain. Q 6. Discuss Solvay’s process in detail. Q 7. Give the process for the manufacturing of urea. Also give its importance. Q 8. Write a note on fractional distillation of petroleum.
