OSCE Pediatrics KKCTH
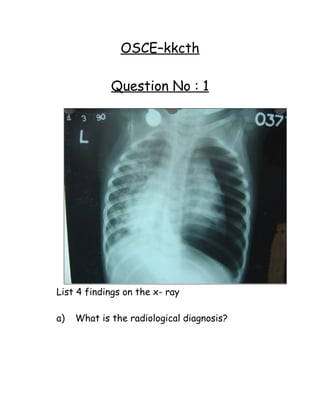
- 1. OSCE–kkcth Question No : 1 List 4 findings on the x- ray a) What is the radiological diagnosis?
- 2. b) List 4 causes for the finding in the left lung c) List 4 causes for the finding in the left lung Answer for Question No : 1 a) Mediastinal shift (L) Pneumothorax (L) Atlectasis (L) lung Bronchopnemonic changes (R) b) Pneumothorax Bronchopneumonic changes (R) (Non – homogenous opacities c) 1) Pneumonia 2) Asthma 3) Foreign body in lung 4) Trauma
- 3. 5) Cystic fibrosis 6) Tracheotomy 7) Subclavian line present 8) Thorococentesis 9) Transbronchial biopsy 10) Lymphomas & other malignancies 11) Ehlers Danlos syndrome 12) Marfan syndrome 13) Gangrene 14) Lung abscess Question No : 2 LINEZOLID 1) What group of drug is this? 2) Mode of action 3) Name 2 organisms for which this is a specific drug? 4) Dosage
- 4. 5) Mention important hematological side effect? Answer for Question No : 2 1) Oxazolidinone 2) Translation initiation by blocking, formation of protein synthesis initiation complex by binding to 50 S ribosomal RNA.
- 5. 3) MRSA vancomycin resistant Enterococci, coagulase negative staphylococci, penicillin resistant pneumococci 4) 10mg / kg / dose Q8 –12 hrs 5) Thrombocytopenia Question No : 3 QUINUPRISTIN / DALFOPRISTIN 1) What group of drug is this? 2) What is the mode of action? 3) Against which of the following organisms this is in effective?
- 6. Mycoplasma, chlamydia, staph. aureus enterococcus faecalis. Answer for Question No: 3 1) Streptogramins Strepto gramins 2) Synergistic action on bacterial ribosomal subunit to protein synthesis 3) Enterococcus faecalis.
- 7. Question No : 4 pH - 7.38 Pco2 - 38 BE -3 Hco3 - 21 Po2 - 98 1) Interpret the ABG? 2) List the indicators of compensation in ABG in following conditions.
- 8. a) Metabolic Acidosis b) Metabolic Alkalosis c) Respiratory Acidosis – Acute/ Chronic d) Respiratory Alkalosis – Acute/ Chronic Answer for Question No : 4 1) Normal ABG Met. Acidosis PCo2 = 15 x (HCo3) +8+/-2 Metabolic Alkalosis - PaCo2 increases by 7mm of Hg for each 10mq increases in the (HCo3 -) Respiratory Acidosis Acute – (HCo3) increases by 1 for each 10mm increased in Pco2. Chronic – (Hco3) increases by 3.5 for each
- 9. 10mm increase in PCo2. Respiratory Alkalosis Acute – (HCo3) fall by 2 for each 10mm Hg decrease in PCo2. Chronic – (HCo3) decreased by 4 for each 10mm of decrease in PCo2. Question No : 5 1) You are asked to counsel a mother who’s 9 month of infant has AWD regarding ORT Check list: i) Introduces himself ii) Explains that the main treatment is ORT and explains the need for rehydration. iii) Explains correctly the preparation of ORT whole packet in 1 liter of water. iv) Advises feeding by spoon discourages bottle feeding. 2) Mother asks what to do if the baby vomits v) Stop ORT for 5 – 10minutes and restart feed, give slowly spoonful every 2 – 3 minutes vi) Advise giving small aliquots of 5 – 10ml each time.
- 10. vii) Explains the danger signs of dehydration and explains when she should seek medical attention Does not become better in 3 days or develops danger Signs (Seizure / unconscious / rapid breathing etc). viii) Encourage continuance of breast feeds / normal feeds / home available feeds. ix) Checks, whether the mother has understood or not. x) Ask the mother whether there are any doubts. Answer for Question No : 5 1) You are asked to counsel a mother who’s 9 month of infant has AWD regarding ORT Check list: a. Introduces himself b. Explains that the main treatment is ORT and explains the need for rehydration. c. Explains correctly the preparation of ORT whole packet in 1 liter of water. d. Advises feeding by spoon discourages bottle feeding. 2) Mother asks what to do if the baby vomits v) Stop ORT for 5 – 10minutes and restart feed, give slowly spoonful every 2 – 3 minutes vi) Advise giving small aliquots of 5 – 10ml each time.
- 11. vii) Explains the danger signs of dehydration and explains when she should seek medical attention Does not become better in 3 days or develops danger Signs (Seizure / unconscious / rapid breathing etc). viii) Encourage continuance of breast feeds / normal feeds / home available feeds. ix) Checks, whether the mother has understood or not. x) Ask the mother whether there are any doubts. Question No : 6 6 yrs old boy is brought for bed-wetting. His frequency in day time is normal. He is dry in the day. He is never been dry in the night. 1) Define this problem? What type is it?
- 12. 2) Is it complicated or uncomplicated? Enumerate 4 differences between complicated and uncomplicated. 3) Name 3 drugs and dosage for the pharmacological therapy of this condition. Name 3 non – pharmacological measures for the management of this condition. Answer for Question No : 6 1) Nocturnal Enuresis. Primary Nocturnal Enuresis 2) Uncomplicated Uncomplicated Complicated Onset Primary Secondary Daytime symptoms absent + Stream Normal Abnormal
- 13. Physical Normal Abnormal Urine analysis Normal Abnormal 3) Drug “ODI!!!” Dose DDAVP 10 – 40 mcg/day Nasal spray Oxybutinin 10 - 20 mg/day PO Imipramine 0.9 – 1.5 mg/kg/day Non-pharmacological Behavioral modification, Bladder exercises, alarm device. Question No : 7 List 3 abnormalities in this ECG 1) What is the ECG Diagnosis? 2) List 4 causes for the same
- 14. 3) Drug of choice 4) Mention 1 complication Answer for Question No : 7 1) Fibrillary waves Absence of P waves Irregular Ventricular response / rhythm 2) Atrial Fibrillation 3) Rheumatic Valvular disease
- 15. Thyrotoxicosis Following cardiac surgery Pulmonary embolism Pericarditis WPW syndrome Mitral regurgitation 4) Digoxin 5) Stroke / Thromboembolism Question No: 8
- 16. 1) Identify the organism? 2) Name the method and steps used for the preparation for the smear?
- 17. Answer for the Question No: 8 Acid-fast bacilli Ziehl neelsen technique CSEWM Heat and dry. Fix the smear. Add strong carbol fushcin Heat approximately for 5mins. Do not boil. Decolorise the smear with 20% sulphuric acid Decolorise with ethanol Wash with water Counter stain with methylene blue
- 18. Question No : 9 1) Describe the pedigree 2) What is the mode of inheritance? 3) Give 4 examples.
- 19. Answer for Question No : 9 1) 3 generation pedigree chart showing All daughters of the affected males have the disease Sons of the affected males are normal Affected females affect ½ of the males and ½ of the daughters 2) X- linked dominant inheritance 3) Hypophosphatemic rickets ( Vit.D resistant) Incontinentia pigmenti XD RHIO Oro facial digital syndrome Rett syndrome
- 20. Question No : 10 The following food substances, which contain Vit.A, need to be arranged based on Vitamin A content from high to low. Papaya, Guava Amaranth Drumstick leaves Egg Human milk Carrot
- 21. Answer for Question No : 10 VIT A : CADEPM Carrot 1167 Amaranth 515 Drumstick leaves 300 Egg 140 Papaya 118 Human Milk 38 Guava 0
- 22. Question No : 11 1) Vitamin A prophylaxis programme in India - Mention the dosage and schedule. 2) Daily requirement of Vitamin A. 3) Name two manifestation of hypervitaminosis A?
- 23. Answer for Question No : 11 1) 5 doses 9 months – 3 yrs Oral retinol palmitate 1lakh 9 months (along with measles) 2lakh 1½ yrs 2lakh 2 yrs 2lakh 2 ½ yrs 2lakh 3 yrs 2) 400mg to 600mg of requirement Retinal / RE B –carotene I.U 0-1yr 350mcg 1200mcg 1166.67 1-6yrs 400mcg 1600mcg 1333.33 >7yrs 600mcg 8400mcg 2000 1mcg = 3.3 IU 1 IU of vitamin A = 0.3mcg at retinal 3) Nausea, vomiting, anorexia, sleep distress, irritability Skin desquamation Hepatomegaly Pseudo tumor cerebri (diplopia/ papilledema /cranial N.Palsy) Alopecia, seborrhea,
- 24. cutaneous leisions craniotabes Tender bony swellings Fissures at corners and mouth Question No : 12 Match the following: 1) BCG - Toxoid & killed bacteria 2) OPV - Live attenuated bacteria 3) DPT - Bacterial sub unit 4) Hib - Viral Antigen 5) Hep B Vaccine – Live attenuated viral 6) Typhoid V I - Killed virus 7) Hep A Vaccine – Capsular polysaccharide 8) Acellular pertusis – Capsular polysaccharide
- 25. Question No : 13 Answer the following: What is the Diluent for BCG? What is the Diluent for MMR? How long can reconstituted BCG be used? How long can reconstituted MMR be used? Name 5 vaccines which should not be frozen What does IAP recommend at 5 yrs - (DPT/DT)?
- 26. Answer for Question No: 12 1) BCG - Live attenuated bacteria 2) OPV - Live attenuated viral 3) DPT - Toxoid & killed bacteria 4) Hib - Capsular poly saccharide 5) Hep B Vaccine - Viral Antigen 6) Typhoid V I - Capsular poly saccharide 7) Hep A Vaccine - Killed virus 8) Acellular pertusis - Bacterial sub unit
- 27. Answer for Question No : 13 Diluent for BCG is Sterile NS Diluent for MMR is Distilled water Reconstituted BCG can be used for 3 hrs Reconstituted MMR can be used for 1 hr. DPT, Hepatitis A & B, Varicella, Hib, TT IAP recommends DPT at 5 yrs.
- 28. What are indications for Acellular pertusis – vaccine? Mention 4 indications for pneumococcal vaccine?
- 29. Answer for Question No : 13 Indications are: Persistent / inconsolable Cry 3 or more hrs in 48 hrs. Temperature > 40º within 48 hrs Collapse / shock with (HHE within 48 hrs) Convulsions with or without fever within 72 hrs of immunization. Encephalopathy within 7 days, behavioral problems. 3) Indications: Prior to splenectomy, HIV CSF Rhinorrhea Sickle cell Asplenia
- 30. CRF Chronic lung / heart disease Question No : 14 A 6 year old girl has been referred for evaluation of anemia. Answer the questions after seeing the peripheral smear? a) What is your diagnosis?
- 31. b) What would be the confirmatory test to clinch your diagnosis ? c) What is the definitive treatment of this condition ? Answer for Question No : 14 1) Hereditary spherocytosis 2) Incubated osmotic fragility 3) Splenectomy
- 32. Question No : 15 You are asked to resuscitate a newborn with the provided equipments. Please ask questions regarding status of infant – wherever necessary. 1) Check the following equipments before proceeding further Bag mask valve Laryngoscope 2) Get information about the infant from the observer before proceeding to resuscitate and at each step whenever necessary Answer for Question No : 15
- 33. 1) Check list for observer. Bag mask valve…does he - attach reservoir? - check pop off valve? - check for leak? Laryngoscope – Checks bulb & handle Does candidate ask the following 5 questions? Meconium staining of liquor or not? Term or preterm? Crying well – breathing well or not? Pink or blue colour? Good muscle tone? The Observer Should Say Baby Is Not Breathing Does he clear airway/provide warmth/ position dry infant? 1..5 marks and then ask status of baby Observer Says: Baby Still Not Breathing well Does he give PPV for 30 seconds? Correct position EC clamp technique Chest expansion and then ask status of baby Observer Says Hr- 50/Min, Blue Does he start chest compressions? Correct technique?
- 34. Question No : 16 1) What is the diagnosis? 2) This infant is 8 months old, what is the most likely type? 3) What is the earliest sign of this disorder? 4) What is the first radiological change that occurs in response to specific therapy? 5) How could this have been prevented? 6) What are the non – specific urinary findings
- 35. in this disorder? (at least 2) Answer for Question No: 16 1) Rickets 2) Vitamin D deficiency 3) Craniotabes 4) Appearance of provisional zone of calcification 5) Supplement of 400IU of vitamin D 6) Generalized aminoaciduria Glycosuria Phosphaturia Elevated urinary citrate
- 36. Impaired renal acidification. Question No : 17 You have performed ICD on a child with empyema. How will you dispose the used items given below? Scalpel blade, hypodermic needles, trochar, used ampoules Cotton, gauze, linens, suture material, surgical mask, gloves Pus, 3 way connector Syringe, plastic covers of gloves and ICD bag cover
- 37. Answer for Question No : 17 Blue / white transparent puncture proof container Yellow bag Red bag Black plastic bag.
- 38. Question No : 18 This child has fever with URI 1) What is the diagnosis? 2) What is the causative organism? 3) Name one serious hematological complication in this disease. 4) Name one orthopedic complication. 5) Name one cause for intrauterine fetal demise.
- 39. 6) What treatment is recommended for severe hematological complications? Answer for Question No : 18 1) Erythema Infection or fifth disease 2) Parvovirus B 19 3) Transient aplastic crisis 4) Arthropathy 5) Non – immune fetal hydrops 6) IvIg
- 40. Question No : 19 Calculate the mean, median, mode and mean deviation of the diastolic pressures given below. 83,75,81,79,71,95,75,77,84
- 41. Answer for Question No : 19 Mean = 80, Median = 79, Mode = 75 and Mean deviation = 5.1 The average of the deviations from arithmetic mean MD = ∑ (x -xˉ)/n ∑ = summation x = item values xˉ = Mean x - xˉ = deviation from mean n = No. of items
- 42. Question No :20 Take relevant history from this parent whose child is suspected to have urinary tract infection for the first time.
- 43. Answer for Question No : 20 Introduces himself History of fever History of constipation History of urgency History of malodorous urine History of suprapubic pain History of loin pain Details of coevute toilet training Wiping from back to front History of incontinence History of threadworm infection Family history of renal disease / stones
- 44. Family history of UTI / VUR Note of thanks Question No : 21 You are asked to perform rapid sequence intubation. Write the steps sequentially. Mention the names of drugs wherever necessary.
- 45. Answer for Question No : 21 Brief history and assessment Assemble equipment, medications, etc. Preoxygenate patient Premedicate with lidocaine atropine Sedation and analgesia induced Pretreat with nondepolarizing paralytic agent Administer muscle relaxants Sellick maneuver Endotracheal intubation Secure tube, verify position with roentgenogram Begin mechanical ventilation Step – 5 : Sedatives: Thiopental Diazepam Ketamine Analgesics: Fentanyl Morphine Succinylcholine Vecuronium or Pancuronium or rocuronium
- 46. Question No : 22 A 2 year child presents with the following 5 episodes of abscesses in 6 months Photosensitivity Light skin and silvery hair Peripheral smear shows large inclusions in all nucleated blood cells. 1) What is the diagnosis? 2) What is the cause for the lighten hair? 3) What is the mode of inheritance? 4) Name one life threatening hematological complications? 5) What is the neurological manifestation?
- 47. 6) Which drug is indicated? Answer for Question No : 22 1) Chediak – Higashi syndrome 2) Melanosomes or melanocytes are oversized. Failure to properly disperse the giant melanosomes to keratinocytes and hair follicles. 3) Autosomal recessive. Mutated gene for CHS Chromosome 1q2-q44. 4) Accelerated phase of a lymphoma like syndrome characterized by pancyopenia. 5) Peripheral neuropathy and ataxia Motor Sensory 6) High – dose ascorbic acid 200mg / 24hrs for infants 2,000mg/24hrs for adults. (2g !)
- 48. Question No : 23 Perform Hand Washing
- 49. Answer for Question No : 23 a) Remove ornaments / watch etc. hand sleeves above elbows. b) Perform six steps of hand washing 1) Palm to Palm 2) (i) Right palm over left dorsum (ii) Left palm over right dorsum 3) Fingers interlace palm to palm 4) Back of fingers to opposing palms 5) (i) Rotational rubbing of right thumb (ii) Rotational rubbing of left thumb 6) (i) Rotational rubbing of left palm (ii) Rotational rubbing of right palm c) Perform in 2 minutes d) Air dry / dry with sterile towel / paper e) Discard towel in black cover.
- 50. Question No : 24 1) A Lumbar puncture is performed and the CSF is xanthochromatic. What are the four possible causes? 2) CSF protein levels are 400mg/dl. What are the three possible causes for the same? 3) CSF Glucose in 200mg/dl and blood glucose is 112mg/dl. List five causes for the same. 4) CSF is also cloudy, what does it imply?
- 51. Answer for Question No : 24 1) a) Hyperbilirubinemia b) Subarachnoid hemorrhage c) Markedly elevated CSF protein d) Carotenemia 2) a) TB Meningitis b) GBS c) Tumors of spinal cord / brain d) Degenerative disorders e) Vasculitis f) Multiple sclerosis 3) a) Bacterial meningitis b) TBM c) Fungal meningitis d) Aseptic meningitis f) Neoplasms of meninges 4) Elevated WBC or RBC count
- 52. Question No : 25 An adolescent presents with history of ingestion insecticides and has clinical features of organophosphorus poisoning. 1) Mention 2 methods of decontamination needed. 2) What is the mode of action of 2 antidotes used? 3) What 2 laboratory parameters are used to confirm the diagnosis of organophosphorus poisoning?
- 53. Answer for Question No : 25 1) Activated charcoal for gastric decontamination. Skin decontamination by removal of clothes stained with organophosphorus. 2) Atropine – blocks acetylcholine receptor. Reverses the muscarinic and CNS effects. Pralidoxime (PAM) – breaks the bond between the organophosphate and the enzyme, liberating the enzyme and degrading the organophosphate. 3) Red cell cholinesterase and pseudo cholinesterase levels.
- 54. Question No : 26 Answer the following questions after seeing the X-ray. 1) What are the findings? 2) Name 5 aerobic organisms, which can cause this?
- 55. Answer for Question No : 26 1) Air and fluid filled cyst. Lung abscess, pneumatocele 2) Streptococcus Staphylococcus aureus Escherichia coli Klebsiella Pseudomonas
- 56. Question No : 27 Dobutamine 1) What is the mode of action? 2) 7kg child requires Dobutamine infusion. How do you prepare the infusion? What is the dose? 3) What is T ½ of the drug / peak action? 4) Mention 3 contraindications? 5) Mention at least 6 adverse effects?
- 57. Answer for Question No : 27 1) Act on the β1 adrenergic receptors of the myocardium. It increases stroke volume – increased COP – causes peripheral vasodilatation – decreases the sympathetic vascular tone – decreases the after load and there by improving the myocardial function. 2) Dose 2.5 – 15mcg/kg/min. infusion rate of 6mg/kg in 100ml normal NS, 1ml/hr will give 1mcg/kg/min. 3) T ½ - 2min, peak action 10 – 20min. ( Dobu2min ! ) 4) IHSS, atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter, sulfite sensitivity, hypotension. 5) Increase myocardial O2 demand tachycardia, ectopic heartbeat, angina / palpitations / tachyarrythmias, tingling sensation, parasthesia and leg cramps, diarrhoea and abdominal cramps.
- 58. Question No : 28 4 year old child is being evaluated for syncope. 1) Identify the ECG? 2) Mention 2 acquired causes for the above abnormality? 3) Drug of choice. 4) What should be taught to parents?
- 59. Answer for Question No : 28 1) Prolonged QT interval - > 0.45secds. 2) Myocarditis / electrolyte abnormality like calcium, mitral valve prolapse and drug induced. 3) Beta adrenergic antagonist- β blockers 4) Parents should be taught cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
- 60. Question No : 29 1) a) List the components of IMNCI? b) List the components of reproductive and child health programme? 2) Mention 4 highlights of the Indian adaptation of IMNCI? 3)Which vaccine project has been introduced as a part of pilot project in IMNCI?
- 61. Answer for Question No : 29 1a) Family planning Child survival and safe motherhood Client approach to health care Prevention and management of RTI /STD/ AIDS b) Improvement in case management skills of health staff, through provision of locally adopted guidelines and activities to promote their care. Improvement in overall health system Improvement in family and community health care system. 2) Inclusion of 0-7 days age in the programme Incorporating national guidelines on malaria Anemia, Vit.A supplementation, and immunization schedules Training of the health personnel begins with sick young infants upto 2 months Proportion of training time devoted to sick young infant and sick child is almost equal 3) Hepatitis B vaccine Question No : 30
- 62. 1) What is the diagnosis? 2) What is the confirmatory test? 3) What neurological complications can occur? 4) Mode of inheritance? 5) What antibiotic is prescribed for this as prophylaxis?
- 63. Answer for Question No : 30 1) Sickle cell anemia 2) Hemoglobin electrophoresis or HPLC 3) Stroke 4) Autosomal recessive 5) Penicillin
- 65. Question No : 31 These lesions are tender 1) What is the diagnosis? 2) What 2 common infections and drugs can trigger this? 3) What 2 non – infectious systemic disorders can trigger this?
- 66. Answer for Question No : 31 1) Erythema Nodosum 2) TB, Streptococcus Sulfa, Phenytoin, Oral contraceptives 3) IBD, Spondylo arthropathy, Sarcoidosis
- 67. Question No : 32 You are asked to provide prophylaxis for bacterial endocarditis for 2 children with the following clinical details. Child 1: 8 year old boy with rheumatic mitral regurgitation is to undergo dental extraction tomorrow. 1) What is the drug of choice? 2) Dosage and timing Child 2: 2 years old male with VSD is to undergo Cystocopy tomorrow. 1) What is the drug of choice? 2) Dosage and timing. Child 3 :3 year old who has undergone PDA ligation 2 years back is to undergo dental extraction. What is the appropriate advice? Child4: 2 year old with TOF is to undergo circumcision. What is the appropriate advice?
- 68. Answer for Question No : 32 1) Oral amoxycillin 50mg/kg 1hr before surgery (or) Ampicillin IV/IM 50mg/kg ½ hr before surgery 2) IV Ampicillin 50mg/kg + gentamycin 1.5mg/kg 30mins before surgery followed 6hrs later by IV/oral Ampicillin/amoxycillin 25mg/kg 3) No prophylaxis needed 4) No need for anti microbial prophylaxis.
- 69. Question No : 33 Pedigree chart: 1) Identify the Mode of inheritance? 2) Give 3 examples of clinical disorders? 3) What is the significance of the pedigree symbols used in this?
- 70. Answer for Question No : 33 1) Autosomal dominant 2) Neurofibromatosis, Huntington’s chorea, Myotonic dystrophy. 3) - Normal Male - Normal female - Affected male - Affected female - Proband - Dead
- 71. Question No : 34 Pneumococcal 7 valent conjugate vaccine 1) What is the protein conjugate? 2) Route of administration? 3) Youngest age for administration? 4) Dosing interval? 5) Primary immunization schedule for infants < 6 months of age? 6) Dose if started at 12 – 23 months of age? 7) Dose if started > 24 months to 9 yrs of age?
- 72. Answer for Question No : 34 1) Diphtheria CRM 197 protein 2) IM 3) 6 weeks 4) 4 to 8 weeks 5) 3 doses < 1 year 1 dose 12 to 15 months 6) 2 doses 7) 1 dose
- 73. Question No : 35 A study was carried out to assess the utility of IgM Elisa test in the diagnosis of Leptospirosis. Blood culture positive cases were considered the gold standard for diagnosis. A total of 100 cases were studied. Leptospira were grown in blood culture in 40 of these cases. IgM Elisa was positive in 70 out of 100 cases. Out of these 70 cases, Leptospira were cultured in 30. IgM Elisa was negative in 30 cases, out of this 30, Leptospira was grown in culture in 10 cases. Calculate the following for IgM Elisa as a diagnostic test for Leptospirosis. 1. Specificity 2. Sensitivity 3. Positive Predictive Value 4. Negative Predictive Value
- 74. Answer for Question No : 35 Blood c/s Blood c/s + - IgM elisa + 30 (a) 40 (b) 70 IgM elisa - 10 (c) 20 (d) 30 40 60 100 1) Specificity: d x 100 20 x 100 = 33.3% d+b 20 + 40 2) Sensitivity: a x 100 30 x 100 = 75% a+c 30 + 10 3) Positive predictive value: a x 100 30 x 100 = 42.85% a+b 30 + 40 4) Negative Predictive value: d x 100 20 x 100 = 66.6% c+d 10 + 20 Question No: 36
- 75. A 2 year old child presents with biphasic fever, severe arthragia and rash tourniquet test is negative. Platelet count is normal. Hb is 10.28gm. 1) What is the most probable diagnosis? a) Dengue hemorrhagic fever b) Measles c) Chikunguniya fever d) Roseola infantum 2) List 2 criteria for case definition of this probable case and4 criteria for confirmed case 3) What neurological complication can develop? 4) What family does this virus belong to? Answer for Question No : 36
- 76. 1) Chikunguniya 2) • Features of suspect case-Fever with chills / arthralgia / rash / rheumatic manifestations. • Case definition – features of suspect case and positive serology in acute and convalesce phase. • Confirmed case – probable case with any of the following : a) 4 fold rise in antibodies in paired sera b) Positive IgM c) Virus isolation from serum d) Positive RT PCR in serum e) Positive RT PCR in serum 3) Meningo encephalitis 4) Toga viridiae Question No : 37
- 77. A 10 year old female weighing 30kg; diagnosed case of IDDM on insulin therapy as follows: 10 (regular) Morning: 40 units 30 (lente) 7 (regular) Evening: 20 units 13 (lente) Her recent morning blood sugars are becoming high. (Blood sugar at 7.00 am 280 mg%) 1) What is Somogyi and Dawn phenomenon? 2) How will you differentiate these two in this case? 3) How will you treat in either case? Answer for Question No : 37
- 78. 1) Somogyi phenomenon: Hyperglycemia begetting hypoglycemia due to counter regulating hormones in response to insulin induced hypoglycemia. Dawn phenomen: Hyperglycemia (early morning) without preceding hypoglycemia due to decreased availability of insulin and increased GH release. 2) Measure blood sugar at 3 am, 4 am, and 7 am. • If blood sugar > 80mg/dl in 1st two sample, and high in 3rd Diagnosis – Dawn phenomenon • If blood sugar <60mg/dl in first two sample and high in 3rd. Diagnosis – Somogyi phenomenon 3) Treatment- • Dawn phenomenon – increased evening dose of Lente insulin by 10 – 15% • Somogyi phenomenon – decreased evening dose of Lente insulin by 10-15%. Question No : 38
- 79. Councell the mother of a child who is being discharged from your hospital following acute severe asthma. Answer for Question No : 38
- 80. 1) Introduces himself 2) Clearly explains about asthma as hyperactive airway disease and not infective. 3) Explains that there is no curative treatment and treatment reduces the severity and complications. 4) Explains how to use MDI. 5) Explains preventive strategies at home. 6) Explains danger signs / warning signs of acute attack. 7) Tells the treatment at home and reach nearest hospital. Tells difference between Rescue and prophylactic inhalers. 8) Explains other alternatives, and ask for any doubts and clears it. 9) Need for regular follow up. 10) Note of thanks and availability.
- 81. Question No : 39 1) A child has massive GI bleed. His clotting time is 12 mins. His PT test is 40 secs, control 14secs and PTT test is 60 secs, control is 30 His Hb is 11gm and Platelet count is 2.5lakhs. What blood product would you transfuse? And how much? 2) List 4 other indications for transfusion with this blood product? 3) List 4 clotting factors deficiencies, which will be corrected by this transfusion? 4) Name 2 parasitic disease transmitted by blood transfusion?
- 82. Answer for Question No : 39 1) Fresh Frozen Plasma - 15ml/kg 2) a) Severe clotting factor deficiency and bleeding b) Severe clotting factor deficiency and invasive procedure. c) Emergency reversal of warfarin effects d) Dilutional coagulopathy and bleeding. e) Anticoagulant protein (AT – III, protein C, Protein S, FTTP) 3) II, V, X and XI 4) Malaria / Chagas disease
- 83. Question No : 40 A 13 year old HIV positive boy is seen in OPD for abrasions injuries over left thigh following RTA 2 days back. He was vaccinated with TT at age of 10 yrs. 1) What immunization advice is appropriate? 2) Mention the dose and route? 3) What is the amount of Tetanus toxoid present in DPT, DT and TT? 4) What is the preservative in TT? 5) What is the role of Aluminum Phosphate in TT?
- 84. Answer for Question No : 40 1) a) Clean the wound with soap and water. b) Administer TT & TIG c) Advice booster dose. 2) a) TT 0.5ml IM on one buttock b) TIG 500U IM on opposite buttock 3) 10 Lf of TT component. 4) Thiomerosol 0.01% w/v 5) TT is adsorbed on to aluminum compounds and increases potency, by reaching high titers. It also gives long lasting immunity.
- 85. Question No : 41 An infant is being evaluated for ambiguous genitalia. You find clitoral hypertrophy and other signs of virilization. On investigations Sr. cortisol levels are low. ACTH & PRA are markedly elevated. ACTH skin stimulation test reveals markedly increased 17 – OH progesterone. Serum testosterone is also elevated. Child also has severe hyponatremia. 1) What is your diagnosis? 2) What is the mode of inheritance? 3) What is pre-natal diagnosis? 4) What advice will you give her for the next pregnancy? 5) What treatment you offer for this baby?
- 86. Answer for Question No: 41 1) Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21 hydroxylase deficiency 2) Autosomal recessive 3) 1sttrimesterCVS,2ndtrimester amniocentesis for DNA common mutations or polymorphic micro satellite markers if affected siblings samples are available for comparison. 4) Dexamethasone 20mg/kg pre pregnancy maternal wt in two – three divided doses. Prefer CVS. continue treatment if female child. 5) Hydrocortisone 10 to 20mg/m2/day tds. (Increase in stress situation) Mineralo corticoids 0.1 – 0.3mg/day BD Sodium supplements 1 – 3gm. Surgical correction.
- 87. Question No : 42 Drug: Carbamzepine 1) Mention 4 clinical indications? 2) In which type of seizures it is avoided? 3) What is therapeutic drug levels in blood and recommended time to draw sample? 4) Mention 4 common drugs, which increases its toxicity? 5) What dose adjustment is needed in ARF? 6) What is the standard concentration in suspension? 7) Mention dosage of frequency of suspension? 8) What & how frequent lab monitoring is needed? 9) Mention 4 life threatening complications? 10) What is treatment of toxicity?
- 88. Answer for Question No : 42 1) GTCS, partial seizures, trigeminal neuralgia, bipolar disorders. 2) Myoclonic seizures 3) 4 –12mg/L, 30min. before oral dose. 4) Erythromycin, INH, TCA, clozapine, itraconazole, cimetidine. 5) Mild, mod forms - dose adjustment is not necessary, severe (Creatnine clearance < 10; decrease dose by 75%) 6) 5ml = 100mg 7) 10-20mg/kg/day, increased 100mg/day at 1 week interval (BD/QD). 8) CBC, SGOT, SGPT every monthly for first 3-4 months and then as needed. 9) Hyper sensitivity reactions, aplastic anemia, pancytopenia, hepatic toxicity, thrombocytopenia. 10) Gastric lavage repeated dose of activated charcoal, hemoperfusion or hemodialysis.
- 89. Question 1 ½ year old male with acute gastroenteritis develops anuria. His Hb is 8.9, Platelet count 90,000 & Pt – 24/20, PTT – 28/30. His PS is shown below. 1) Describe PS 2) Mention two MC D/D for it. 3) Which single test will help differentiate your D/B? 4) This baby’s renal functions de--erated after 2 units of FFP. What would be the possibility? 5) What are indications of steroids in this scenario? 6) Which other conditions here similar PS findings?
- 90. Answer 1) Microangiopath--- hemolytic anemia with helmetcells, burn cells, he------- RBCs 2) HUS, RVT 3) Doppler USG ------- 4) HUS due to strep pneumonia 5) Seizures 6) Malignment HTN, SLE
- 91. Question A 10 year old male with acute onset progressive lower limb weakness. On detailed CNS examination you find he is cons--- alert and normal cranial nerve examinations. No bowel / bladder involvement. His knee and ankele re--- are brisk and has grade II power on both lower limbs. You also notice abdominal reglesses below ----- is absent alibbus sensory system normal. 1) what is your progressive diagnosis? 2) Mention 4 conditions where you get hypotension and diminished referes in UMN lesion? 3) Mention 3 major points to differentiated extra modular from intramedially lesions? 4) Mention a congential conditions leading to non compressive myelopathy?
- 92. Question No : 43 A 8 year old boy is brought because his mother feels he is short for his age. His height is 80cm. His father’s height is 160cm and mother’s height is 148cm. His US/LS ratio is 1. 4: 1 1) What type of short stature does this child have? 2) What is the mid parenteral height of this child? 3) Name 3 causes for the short stature in this child? 4) What is the normal US/LS ratio at this age? 5) Name 3 conditions in which there is advanced US/LS ratio?
- 93. Answer for Question No : 43 1) Dysproportionate dwarfism 2) 160cm 3) Achandroplasia, cretinism, short limb dwarfism. 4) 1.1:1 5) Arachynodactyl, chandrodystrophy, spinal deformity and eunochodism
- 94. Question No : 44 An infant with seizures is being investigated. The following are the lab reports. Serum Calcium: 6.6mg% Po4: 9mg% SAP: 500 units Mg: 3mg% 1) What is the probable diagnosis? 2) What will be the levels of PTH & 1, 25(OH2) D3? 3) The same infant is also noted to be dark and having mucocutaneous candidiasis. What is your diagnosis? 4) CT brain is carried out. What finding do you expect?
- 95. Answer for Question No : 44 1) Hypoparathyroidism 2) Both are low 3) Type I polyendocrinopathiy (with Addison’s) 4) Basal ganglia calcification
- 96. Question No : 45 A 16 week infant is examined for developmental assessment. Write what patterns of behaviour will you expect in this age?
- 97. Answer for Question No : 45 Prone : Lifts head and chest, arms extended. Ventral suspension : head above plane of body Supine : TNR and reaches toward and misses objects. Sitting : No head lag on pulling, head steady, tipped forward, enjoys sitting with truncal support. Standing : when held erect, pushes with feet. Adaptive : Sees pellet, makes no move to it Social : Laughs out loud, excited at sight of food, may show displeasure if social contact is broken.
- 98. Question No : 46 A child with meningoenclphalitis is comatose. His serum sodium is 116 and you are contemplating diagnosis of SIADH 1) Which of the following lab values will be present? a) Urine OSM <100 mosm/l b) Plasma volume normal or increased c) Urine Na 200mg/L d) Serum uric acid 10mg% 2) Name 2 drugs which increases the vasopressin levels? 3) The fluid intake should be restricted to 4) Which drug may be given? 5) 2 acute respiratory illnesses, which cause this?
- 99. 6) Anticonvulsant, which decreases ADH production? Answer for Question No : 46 1) a) Urine OSM <100 mosm/l - Negative b) Plasma volume normal or increased - Positive c) Urine Na 200mEq/L - Positive d) Serum uric acid 10mg% - Negative 2) CBZ, Vincristine, TCA 3) 1000ml/ m2 /24hr 4) Demeclocycline 5) Broncholitis, pneumonia 6) Phenytoin
- 100. Question No : 47 1) Identify this. 2) What is the route of entry of this organism? 3) Name 2 conditions that are high risk for this infection? 4) What hematological clue will occur? 5) Drug of choice? 6) 1 complication
- 101. Answer for Question No : 47 1) Strongyloides stercoralis Larvae 2) Skin 3) HIV/ Immunosuppression, PEM, MR, Autoimmune disease 4) Eosinophilia 5) Ivermectin 200mcg/kg OD for 1 – 2 days 6) Hyperinfection syndrome
- 102. Question No : 48 A child with stroke is noted to have Ectopia Lentis, arachinodactyly blue eyes and developmental delay. 1) What is the likely diagnosis? 2) What urine screening test will be positive? 3) Estimation of plasma amino acids will show ↑ cystine ↑ Methionine ↑ Homocystine 4) Which vitamin is indicated? 5) What other drug is needed?
- 103. 6) Mode of inheritance? Answer for Question No : 48 1) Homocystinuria 2) Positive cyanide nitroprusside test 3) ↑ cystine - Negative ↑ Methionine - Positive ↑ Homocystine - Positive 4) B6 200 – 1000mg/24hr 5) Betaine 6) AR
- 104. Question : 49 You are to meet a child with Thalassemia major 1) When do you start transfusion? 2) Optimum Hb 3) Intervals for transfusion 4) What is the risk in keeping Hb > 14? 5) When will HbF be low? 6) How do you reduce non-hemolytic febrile transfusion? 7) What is the level of serum ferritin to be maintained? 8) Indications for splenectomy
- 105. 9) When to give vaccines before splenectomy? 10) Antenatal diagnosis How and When? Answerfor Question No : 49 1) < 7gm 2) 9 – 10gm 3) 2 – 4 weeks 4) Thrombosis 5) After repeated transfusions 6) Leukocyte filter, pheneramine with paracetamol 7) < 1000mg/L 8) > 220ml/kg/yr of PRBCs, hypersplenism, massive spleen with prominent abdominal discomfort. 9) Atleast 4 weeks
- 106. 10) CVS- mutation, 12to 14 weeks (MTP < 20weeks) Question No : 50 Match the disease with the Urine Screening Test 1) Galactosemia Nitroprusside test 2) PKU CN PT 3) MPS DNPH 4) HCU Benedicts test 5) Organic aciduria spot test (Toludene blue test) 6) Cystinuria Fecl2
- 107. Answer for Question No : 50 1) Galactosemia Benedicts test 2) PKU Fecl2 3) MPS MPS spot test (Toludene blue test) 4) HCU (Nitroprusside test) 5) Organic aciduria DNPH 6) Cystinuria CNPT
- 108. Question : 51 DRUG: Vigabatrine 1) Mode of action? 2) Dosage 3) Important side effects 4) Mention important uses
- 109. Answer for Question No : 51 1) Y aminobutyric acid, transaminase inhibitor 2) 30mg/kg/d, od /bd upto 100mg/kg/d 3) Visual field constriction, Optic atrophy, optic neuritis 4) Infantile spasms, Tuberous sclerosis adjuvant for poorly controlled seizures.
- 110. Question No : 52 A 2 year old child is brought for Toe walking. 1) What is the commonest cause? 2) What is the Differential diagnosis? 3) Upto what age is it normal?
- 111. Answer for Question No: 52 1) Normal children 2) Cerebral palsy, Duchenne muscular dystrophy, tethered cord, congenital tendo-achilles contracture, leg-length discrepancy, CDH and habitual 3) 3 year
- 112. Question No : 53 1) What is premature thelarche? 2) Upto what age is it benign? 3) What is exaggerated or atypical thelarche? 4) What will be the level of FSH, LH, oestradiol in benign premature thelarche? 5) What will be the USG findings?
- 113. Answer for Question No : 53 1) Isolated breast development 2) < 3 yrs 3) Associated with accelerated bone age due to systemic ostrogen effects 4) Low 5) Small Ovanian cysts
- 114. Question No: 54 A child has chronic polyarthritis of 4 joints and is ANA positive. 2) What arthritis is it likely to be? 3) What complication should we anticipate? 4) In which type of JRA is HLA β27 positive ? 5) A child with JRA presents with fever, leuepenia and hepatosplenomegaly and lymphadenopathy. What is the diagnosis? 6) What drug is indicated in treatment of Q4?
- 115. Answer for Question No: 54 1) JIA pauciarticular type I 2) Chronic uveitis 3) Pauciarticular type II 4) MAS 5) Cyclosporin
- 116. Question No :55 Oxygen therapy 1) Below what blood O2 does WHO recommend O2 therapy? 2) What are the clinical indications for O2 therapy? 3) O2 concentration with reference to FiO2 Nasal prongs @1-2 lit/min, Nasopharyngeal catheter
- 117. Answer for Question No : 55 1) <90% 2) Central cyanosis, unable to drink due to respiratory distress. In those with pneumonia, Broncholitis and asthma- severe lower chest in drawing, RR >70, Grunting, Head nodding 3) FiO2 30 – 35 %, 45 – 60 %
- 118. Question No : 56 A child is brought with snakebite. 1) In which of the following is appropriate as first aid. a) Splint the limb b) Apply ice c) Apply tourniquet to occlude venous flow d) Clean the wound e) Transport to hospital 2) 2 specific indication for ASV 3) What is the dose of ASV to a 3 year old? 4) What is the diluent for ASV?
- 119. Answer for Question No : 56 1) a) Splint the limb - b) Clean the wound – c) Transport to hospital – 2) Indications: a) Systemic signs of envenomation b) Local symptoms like severe necrosis, swelling of > half of the limb 3) Same as adult 4) Normal saline (2 to 3 volumes)
- 120. Question No: 59 1) What are the 4 types of lesions? 2) What bacteria cause this? 3) Which drug can induce this? 4) Name 4 drugs used? 5) What Dietary advice will you give?
- 121. Answer for Question No : 59 1) Open Comedones – blackhead Closed comedones – whitehead Papules, pustules and nodulocystic lesions 2) Propionibacterium acnes 3) Corticosteroid, androgens, INH, phenobarbital, Phenytoin, B12 and lithium 4) Benzoyl Peroxide, Tretinoin, Adapalene, Topical – Erythromycin and clindamycin Use for 4 to 8 weeks: Systemic therapy: Tetracycline, Doxy, Minocycline Isotretinoin (nodulocystic) (teratogenic) Intradermal triamcinolone 5) Normal
- 122. Question No : 57 A child presents with muscle cramps. The serum Magnesium is 1mg/dl, K is 1.6mg/dl and Hco3 is 40mg/dl. There is no dehydration. 1) What electrolyte in urine will you estimate? 2) Why? 3) The level of the urinary electrolyte estimated is high – BP is normal. List 3 possible diagnosis? 4) There is no history of drug ingestion or failure to thrive hypertension. What is the diagnosis? 5) 3 drugs for treatment 6) What will be level of renin and aldosterone in serum? 7) What will be the urinary calcium level?
- 123. Answer for Question No : 57 1) Calcium 2) To distinguish low and high urine calcium levels 3) Barter’s, giltelman’s and base administration 4) Giltelman syndrome 5) Na, mg and spiranolactone 6) Normal 7) Low
- 124. Question No : 58 A child is admitted with TCA poisoning. 1) What are the 3 ‘C’s in manifestations? 2) What ECG findings do you anticipate? (3) 3) Which of the following is correct? a) Emesis is indicated b) Activated charcoal to be given c) Na Hco3 must d) PH should be 7.45 to 7.55 e) Lidocaine not be used for any time f) Quinidine & procainamide - to be used g) NaHco3 is used to prevent cardiac arrhythmias
- 125. Answer for Question No : 58 1) Coma, convulsion, cardiac toxicity 2) Widening of QRS, Q-T prolongation,-, flat or inverted T , ST depression, RBB, CHB 3) A) No b) Yes c) Yes d) Yes e) No f) No g) Yes
- 126. Question No : 61 1) What is the diagnosis? 2) Name 2 topical agents of use? 3) Duration and frequency? 4) 2 drugs for systemic therapy? 5) Commonest organisms?
- 127. Answer for Question No : 61 1) Tinea corporis 2) Miconazole, ketoconazole, clotrimazole, econazole, terbinafine, niftifine 3) Bd, 2 to 4 week 4) Griseofulvin – several weeks Itraconazole – 1 – 2 week 5) T. Rubrum, T. Mentagrophytes
- 128. Question No : 60 Write the calorie value of Rice – 1 cup Puri – 1 Upma – 1 cup Idli – 1 Dosa – 1 Kichidi - 1 cup Boiled egg - 1 Vada - 1 Pizza – 1 slice Oil – 1 tbsp Ice cream – ½ cup Peanuts – 50 nos Banana – 1 Cashew nuts – 10 Milk chocolate – 25gm
- 129. Answer for Question No : 60 Rice – 1 cup - 170 Puri – 1 - 100 Upma – 1 cup - 270 Idlli – 1 - 75 Dosa – 1 - 125 Kichidi - 1 cup - 200 Boiled egg – 1 - 90 Vada – 1 - 70 Pizza – 1 slice - 200 Oil – 1 tbsp - 60 Ice cream – ½ cup - 200 Peanuts – 50 nos - 90 Banana – 1 - 90 Cashew nuts – 10 - 95 Milk chocolate – 25gm - 140
- 130. Question No : 62 This girl has palpitation, diarrhea, and loss of weight 1) What is the diagnosis? 2) The thyroid swelling is not tender, not nodular. She has exophthalmos. What is the cause? 3) List 4 other causes? 4) Investigations 5) 2 drugs used
- 131. Answer for Question No : 62 1) Hyperthyroidism 2) Graves Disease 3) Toxic adenoma, toxic multinodular , subacute thyroiditis, Lymphocytic thyroiditis, iodine induce, exogenous hormone, pituitary adenoma and ovarian tumor. 4) TSH is decreased, T4 increased. Thyroid uptake increased 5) β blockers, methimazole (propylthiouracil)
- 132. Question No : 63 A spirometry is performed in an asthmatic child 1) What will be abnormalities in the following: FEV1 FEV1 / FVC Improvement in FEV1 Exercise challenge 2) What PEFR variation that is consistent with a diagnosis of asthma?
- 133. Answer for Question No : 63 1) FEV1 – Low FEV1 / FVC ration < 0.8 Improvement in FEV1 with inhaled β2 agonist ≥12% Exercise challenge – worsening in FEV1 ≥ 15% 2) Morning to afternoon variation ≥ 20%
- 134. Question No : 64 The following is the ABG is an infant PH - 7.2, Hco3 – 10, CO2 – 30 1) What is the diagnosis? 2) Why? 3) Give an example of a common clinical setting for this condition? 4) Write the other compensation in acid bone disorder. Which are appropriate?
- 135. Answer for Question No : 64 1) Metabolic acidosis – respiratory acidosis 2) Expected Co2 = 1.5 X (10) + 8 ± 2 = 21 to 25 Co2 >25 3) Pneumonia with sepsis (lactic acidosis and respiratory acidosis) 4) Metabolic alkalosis Pco2 ↑ 7mm for 10meq/L of Hco3 Respiratory acidosis – Acute: Hco3 ↑ 1 for 10mm ↑ in Pco2 Chronic: Hco3 ↑ 3.5 for 10mm ↑ in Pco2 Respiratory alkalosis Acute: Hco3 ↓ 2 for 10mm ↓ in Pco2 Chronic: Hco3 ↓ 4 for 10mm↓ in Pco2
- 136. Question No : 65 Serum Na - 136, Cl - 102 and Hco3 - 10 1) What is the anion gap? 2) What is the normal anion gap? 3) In which of the following is anion gap normal or increased? Diarrhea Lactic acidosis DKA ARF RTA Salicylate poisoning Urinary tract diversion IEM Septic shock Post hypocapnea
- 137. Answer for Question No : 65 1) (136) – (102 + 10) = 24 2) 8 – 16 3) Diarrhea - Normal Lactic acidosis - increased DKA - increased ARF - increased RTA - Normal Salicylate - increased Urinary tract diversion - Normal IEM - increased Septic shock - increased Post hypocapnea - Normal
- 138. Question No : 66 1) What is the mode of inheritance? 2) 2 examples 3) Characteristics of the inheritance 4) Plasma ammonia in this child is normal. What is the likely diagnosis? 5) There is no odor or skin lesion, but there is ketosis. What is the likely diagnosis?
- 139. Answer for Question No : 66 1) XLD 2) VDRR (Hypophosphotemia), incontinentia pigmenti 3) Affected men all affected All normal All + of affected have 50% inheritance Rare XLD - milder disease Thrice as common as male 4) Organic acidemia Urea cycle – NH3 , anion gap – normal Amino acid defects or Galactosemia NH3 – normal, anion gap – normal
- 140. 5) MMA, Propionic acidemia, Ketothiolase deficiency Odor + - MSUD / isovaleric Skin + - Multiple carboxylase deficiency Ketosis - Acyl CoA, 3Hydroxy 3HGA, HMG co - synthetase deficiency
- 141. Question No : 67 1) What is the clinical classification of leprosy in India? 2) What are the differences in leprosy constitution? 3) What is the WHO recommended standard treatment regime for children aged 10 – 14 yrs?
- 142. Answer for Question No : 67 1) Indeterminate Tuberculoid Paucibacillary 1 to 5 lesions Borderline in skin Lepromatous Multi bacillary > 5 lesions Pure neuritis 2) Case of leprosy – clinical sign + Bacilli in smear + Not completed treatment Paucibacillary – 1 to 5 lesions Multibacillary Adequate treatment Repeated treatment
- 143. Newly diagnosed case Defaulter Relapsed case 3) Multi Bacillary (completed in 12 months) RMP 450mg once a month Clofazamine 150mg once a month (supervised) Clofazamine 50mgEod (self administered) Dapsone 5omg once a month (supervised) Dapsone 50mg daily dose ( domiciliary) Pauci Bacillary (completed in 6 months) Rifampicin 450mg once a month Dapsone 50mg OD daily (domiciliary)
- 144. Question No : 68 Midday meal program 1) What are the principles? 2) Write a model menu?
- 145. Answer for Question No : 68 1) Meal – a supplement, not a substitute to home diet Should supply 1/3 of total energy, ½ of protein Cost low Easily cookable in school Use locally available foods Change menu frequently 2) Cereals & and millets – 75gms Pulses - 30 Oil & fat - 8 Leafy vegetable –30 Non-leafy - 30
- 146. Question No : 69 Answer the following questions with regard to cold chain equipment: 1) Which vaccines are stored in deep freezers? 2) Which vaccines are stored in ILR? 3) Which vaccines are kept in the basket of ILR? 4) What is the function of cold boxes? 5) What are Day carriers used for? 6) What are vaccine carriers used for? 7) Which vaccines should not be frozen?
- 147. Answer for Question No : 69 1) Measles & OPV 2) All 3) TT, DPT, DT and diluents (not in the floor – may be frozen) 4) Transportation of vaccines 5) Carry small quantities of vaccines to a nearly session. 6) Carry small quantities of vaccines to out of reach session 7) DPT, DT, TT, Typhoid, BCG, HBV, diluent
- 148. Question No : A 11 year old boy is brought with a penetrating crush injury with a compound fracture. His immunity and immunization status for tetanus is unknown. Which of the following action is correct with regard to tetanus prevention? a) Nothing is required b) Toxoid 1 dose c) Toxoid 1 dose + TIG d) Toxoid complete course + TIG His 8 year old sister has multiple clean abrasions. She has earlier received 3 doses of DPT in the first year and 1 booster at 1 ½ year and no other vaccines after that What prevention will you carry out?
- 149. Answer for Question No : All wounds – surgical t------ < 6hr, clean, non penetrating with negligible tissue damage a) Nothing b) TT 1 c) TT 1 d) TT complete course All wounds – surgical t------ other wounds immunity category. a) Nothing b) TT 1 c) TT 1 + TIG d) TT complete course + TIG a) Complete course + Bon----- < 5 yrs b) Complete course + 5 to 10 yrs c) Complete course + > 10 yrs d) Immunity unknown + has not heel a complete course of toxoid.
- 150. Question No : 70 The peak flow rates of 10 children of same age are as follows: 250, 260, 290, 200, 240, 240, 260, 270, 270, 290 1) What is the range? 2) What is the mean deviation and Mean? 3) What is the standard deviation?
- 151. Answer for Question No : 70 1) 90 (200 to 290) 2) Mean Deviation =∑ (x – x) N Mean – 257, Mean Deviation – 19.8 3) Standard deviation = ∑ ( x – x ) 2 (>30) n Standard Deviation = ∑ ( x – x ) 2 (<30) n-1 in this case (10-1) Take the deviation of each value from Mean (x-x) Square each (x – x )2 Add and squared deviation ∑ ( x – x ) 2 Divide by no. of observation or n-1 if <30 Then take square root
- 152. Answer No for Question No : 71 Resected tissue from OT Chemical disinfect ion and discharge into drain Waste from laboratory Chemical disinfect ion culture / autoclave / microwave and mutilation shredding Needles and syringes Disinfect ion / shredding Discarded medicines Autoclaving / microwaving / incineration Linen contaminated Incineration autoclaving with Blood / Microwaving Used IV set Incineration and drug disposal in secured land fills Liquid waste from house Incineration / deep burial keeping
- 153. Question No : 71 Write the correct method of treatment and disposable of the following categories of biomedical work? Resected tissue from OT Incineration / deep burial Waste from laboratory Autoclaving / microwaving culture / incineration Needles and syringes Disinfect ion / shredding Discarded medicines Incineration and drug disposal in secured land fills Linen contaminated Incineration, autoclaving with Blood / Microwaving Used IV set Chemical disinfect ion / Autoclaving / microwaving/ Multilation/ shredding Liquid wask from house Chemical disinfect ion keeping and discharge into drain
- 154. Question No : 72 This child also has joint hypermobility 1) What is the diagnosis? 2) What is the usual mode of inheritance? 3) What is the defect? 4) How many clinical forms? 5) What cardiac among can occur? 6) What surgical emergencies? 7) Difference with Cutis Laxa
- 155. Answer for Question No: 72 1) Ehlers Danlos 2) AD 3) Defect of fibrillar collagen – quantitative 4) 10 5) MVP, AR 6) Rupture of great vessels, dissecting aneurysm, stroke, rupture of uterus in pregnancy, echymoses, periodantitis. 7) Cutis Laxa – skin hangs in redundant folds – AR EDS – hyperextensible snaps back into place when stretched - AD Cutis Laxa – Bloodhound appearance, aged appearance Hyperelasticity and hypermobility of joints, hoarse cry, lax vocal cords
- 156. Question No : 73 A child is brought with a history of accidental ingestion of Iron tablets. 1) Which one of the following would be of benefit? Gastric Lavage Activated charcoal Whole bowel irrigation 2) When would you measure serum Iron? 3) What is the level of serum Iron which indicate significant toxicity? 4) If serum iron level reports were delayed, how would you confirm iron ingestion? 5) What are the 2 indications for giving desferioxime? 6) What system exhibits symptom first? When?
- 157. Answer for Question No : 73 1) Whole bowel irrigation 2) 4 – 8 hrs after ingestion 3) >500µg/dl 4) X – ray abdomen 5) Level >500µg/dl Moderate to severe symptoms 6) GI, 30 minutes to 6 hr
- 158. Question No : 74 1) What is the diagnosis? 2) What 2 findings are characteristics? 3) What is the effect of treatment? 4) List 4 drugs useful 5) What physical therapy will help?
- 159. Answer for Question No : 74 1) Psoriasis 2) A) Plaques with yellowish white scale like mica b) Auspitz sign – pinpoint bleed or removal 3) Koebner phenomenon lesions appear 4) Coal tar, topical steroid, salicylic acid, calcipotriene (Vit.D analog), Methotrexate & cyclosporine and retinoid 5) UV light
- 160. Question No : 75 Assess the development of this 3 year old
- 161. Answer for Question No : 75 Motor : Rides tricycle, stands on the foot momentarily Adaptive : Tower of 10 cubes, imitates bridge construction of 3 cubes, copies a circle, imitates a cross Language : Knows age and sex, counts 3 objects correctly, repeats 3 numbers or a sentence of 6 syllables Social : Plays simple games with other children in parallel, helps in dressing – put on shoes, unbuttons, washes hands.
- 162. Question No : 76 1) What is the diagnosis? 2) Commonest organism? 3) Treatment
- 163. Answer for Question No : 76 1) Cutaneous larva migrans 2) A. Braziliense (Hook worm of dogs and cats) (other anky + & Strongyloides) 3) Ivermectin – 200mg/kg/one 1 to 2 days Albendazole – 1 OD X 3 days Topical thiabendazole
- 164. Question No : A mother says she has the following problems in breast- feeding 1) A not enough milk 2) The baby is reluctant to breast feed
- 165. Answer for Question No : If not enough milk – poor weight ----- <500/--- <125gm/--- < birth weight after 2 weeks <6 times / day urine strong / smelling concentrated urine Common reasons : Poor breast feed p------- : Poor attachment, no night feeds, delayed start, short feeds, rigid schedule, broke, other feeds Psychological – strem, tired Physical causes Baby is illness / con---- among Advice : Refusal or reluctance to breast feed : Baby is in pain, ill, sedation Encourage to ---- and feed more often Use EBM Rooming in Correct positioning Clear ------ nose Treat oral ↓ sedation to mother
- 166. Question No : 77 Amniocentesis is brief contemplated for pregnant woman for genetic counseling 1) What is the ideal time? 2) What is the most common indication? 3) Name 4 other indications?
- 167. Answer for Question No : 77 1) 15 to 16 weeks 2) Advanced maternal age > 35 yrs 3) a) Previous child: chromosomal anmaly b) Either parent - a translocation cause c) History of genetic disorder diagnosed by DNA analysis / biochemistry d) Sex detection in XLD / XLR diseases e) Maternal blood testing (triple screening) indication risk f) Work up for fetal anomalies suggested by USG
- 168. Question No : 79 1) Identify the abnormality in RBC? 2) This child has chronic diarrhea. What is the diagnosis? 3) Which vitamin deficiency in these children is associated with neurological symptom? 4) Which lipid abnormalities are characteristics? 5) What is the fundus finding? 6) What is the mode of inheritance? Answer for Question No : 79
- 169. 1) Acanthocytosis 2) A Betalipoprotenemia 3) Vit. E 4) Cholesterol TGL Absent B Liproteins 5) Retinitis pigmentosa 6) Autosomal recessive Question No : 78
- 170. An infant has cough and difficult breathing The respiratory rate 70 / min The infant has severe respiratory distress (head nodding) 1) What does the infant have as per ARI programme? 2) What are other criteria for this status? 3) Will you treat this infant as OP or IP? 4) What is the antibiotic therapy regimen? Answer for Question No : 78 1) Very severe pneumonia
- 171. 2) Central cyanosis -------- to feed / drunk or vomited everything --------- / lethargy / ----------- 3) IP 4) Ampi + Gent—for 5 days Oral ------- for 5 days Or CM for 10 days Or Ceftriaxone Question No: 80
- 172. 1) Identify the organism? 2) What 4 stains are used? 3) What is the treatment?
- 173. Answer for Question No : 80 1) Pneumocystis carinii 2) Grocott- Gomori cyst Toluidine blue Polychrome – Giemsa Trophozoites and sporozoites Fluorescent labeled MAB 3) 5mg/kg once daily 3 day a week Cotrimoxazole 15 – 20mg in 4 3 weeks for AIDS 2 weeks for others Pentamidine
- 174. Atovaquone, trimextrate + steroids Answer for Question No . 82 1) Giandia Lambia 2) Acute Explosive fowl smelling watering diarrhoea Abd distusion / flatuluce / nansea anorara and epigastic cramps 3) FTT / Lactose Mal Absorbtion / Persistant Steattorrhoea, E hystlylica diarrhoea injection 4) Metronidayole 15 kg
