Abducens Nerve - Course and relation.
- 1. ABDUCENS NERVE IZMAL UROOJ M.PHIL (OPTOMETRY) 1ST Semester
- 3. INTRODUCTION 6TH CRANIAL NERVE ABDUCENS = TO MOVE AWAY General SOMATIC EFFERENT fibers SUPPLIES LATERAL RECTUS MUSCLE abducens NERVE
- 4. CRANIAL NERVE VI OR ABDUCENS NERVE. • abducens nucleus → only a somatic motor (general somatic efferent) component • Motor neurones supplying the ipsilateral lateral rectus, and interneurones that pass through the medial longitudinal fasciculus to the contralateral medial rectus. • The abducens nucleus is located in the between the pons and medulla oblongata. • The sixth cranial nerve has a long subarachnoid course • Innervates only one extra ocular muscle → Lateral rectus muscle.
- 6. Embryology: • The human abducens nerve is derived from the basal plate of the embryonic pons.
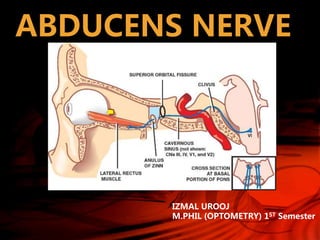
- 7. COURSE • Passes upwards & anterolaterally in subarachnoid space of posterior cranial fossa • Pierces the arachnoid & dura lateral to the dorsum sellae(part of the sphenoid bone)
- 8. • Arises between the layers of dura on the posterior surface of the petrous bone near its apex. • Turns anteriorly to traverse the cavernous sinus
- 9. • Enters the orbit through the superior orbital fissure within the annular tendon to supply the lateral rectus muscle
- 12. NUCLEUS • Situated near the midline in the tegmentum of the pons ventral to the colliculus facialis • Colliculus facialis is an elevation in the floor of the 4th ventricle , produced by the genu of facial nerve.
- 15. INTERNUCLEAR NEURON • About 40% of its neurons project into the ipsilateral MLF only to cross over to the contralateral side and ascend to innervate that contralateral medial rectus subnucleus to participate in contralateral eye adduction.
- 16. ANATOMICAL LANDMARKS SUPERFICIAL EMERGENCE POSTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA MIDDLE CRANIAL FOSSA CAVERNOUS SINUS SUPERIOR ORBITAL FISSURE ORBIT
- 17. SUPERFICIAL EMERGENCE • Emerges between lower border of the pons & lateral part of the pyramid • Emerge as seven or eight rootlets
- 18. • abducens nerves are about 1 cm apart • Between them is the Basilary Artery at its formation from the two vertebral Artery • Lateral to each abducens is the emergence of the facial Nerve at the lateral side of the olive
- 19. 2.POSTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA Just after its emergence , the nerve is crossed by the ANTERIOR INFERIOR CEREBELLAR Artery • Usually the artery is ventral , but it may be dorsal or pass between the abducens rootlets.
- 20. • Sleeved by the piamater , it ascends anterolaterally in the cisterna pontis of the subarachnoid space between pons & occipital bone
- 21. • At the upper border of the bone, it turns forward at a right – angle under the Petro sphenoidal ligament ( Gruber’s ligament ) • Thus passing through a canal called the Dorello’s canal, to enter the cavernous sinus with the inferior petrosal sinus • Often the nerve pierces the inferior sinus, entering the cavernous sinus within the inferior petrosal sinus
- 24. 3.CAVERNOUS SINUS • Here the nerve lies within the cavernous sinus
- 26. Nerve is inferolateral to the horizontal portion of the internal carotid artery with its sympathetic plexus , which may communicate with the nerve
- 27. • In the lateral wall of the sinus , in descending order are • Oculomotor Nerve • Trochlear Nerve • Ophthalmic Nerve • Maxillary Nerve abducens nerve is usually in the sinus, with a separate sheath
- 28. 4.SUPERIOR ORBITAL FISSURE • Traverses the fissure within the annulus of Zinn • At 1st below the division of oculomotor Nerve • Then between them & lateral to nasociliary nerve
- 30. 5.IN THE ORBIT • Nerve divides into 3 or 4 filaments which enter the ocular surface of lateral rectus muscle behind its midpoint
- 32. Coordination of Lateral Rectus and Medial Rectus Muscles • For eye movements in the horizontal plane, the lateral rectus muscle of one eye and the medial rectus muscle of the other eye must work precisely together. • The actions of these muscles is coordinated by the lateral gaze center located in the pontine reticular formation. • Inputs from higher centers of the brain synapse in the lateral gaze center, which then sends simultaneous signals to the ipsilateral abducens nucleus and to the contralateral occulomotor nucleus via the medial longitudinal fasciculus. • The abducens nucleus sends signals via CN VI to the lateral rectus muscle of the ipsilateral orbit to command that eye to be abducted. • Simultaneously, the occulomotor nucleus generates a command via CN III to contract the medial rectus muscle of the contralateral orbit resulting in adduction of that eye.
- 33. BLOOD SUPPLY: • Anterior inferior cerebellar artery, the posterior inferior cerebellar artery, the internal auditory artery, the anterolateral artery, the pontomedullary artery, the inferolateral pontine artery, the anterolateral artery • The majority of the of the abducens nerves were supplied by the anterolateral arteries, and only some of them by the AICA, or the pontomedullary artery.
- 35. 1. At the level of nucleus • Ipsilateral weakness of abduction • Failure of horizontal gaze towards the side of lesion. • Ipsilateral facial nerve palsy (lower motor neurone)→involvement of facial fasciculus.
- 36. AN ISOLATED 6TH NERVE PALSY IS THEREFORE NEVER NUCLEAR IN ORIGIN. In adults, the most likely etiology of isolated sixth nerve palsy is ischemic mononeuropathy that may be due to diabetes mellitus, arteriosclerosis, hypertension, temporal arteritis or anemia
- 37. 2.PONTINE SYNDROMES – AT THE LEVEL OF FASCICULUS • MILLARD GUBLER SYNDROMEM • RAYMOND CESTON SYNDROMER • FOVILLE SYNDROME F
- 38. A. Foville syndrome Involves fasciculus as it passes through PPRF 5th nerve – facial anaesthesia 6th nerve + gaze palsy 7th nerve – facial weakness 8th nerve – deafness Central horner syndrome
- 41. B. Millard – Gubler syndrome Involves fasciculus as it passes through the pyramidal tract Ipsilateral 6th nerve palsy Contralateral hemiplegia (paralysis)
- 42. C. Raymond – Ceston syndrome Due to tumor of cerebral peduncles Red nucleus – speech & gait disorder Paralysis of lateral conjugate gaze Ipsilateral 6th Nerve palsy 5th nerve – facial anaesthesia Contralateral hemiparesis
- 44. 3. At the pontomedullary junction: ACOUSTIC NEUROMA: • May damage the 6th nerve → pontomedullary junction. • 1ST symptom – hearing loss • 1st sign - ↓ corneal sensitivity
- 45. It is very important to test hearing & corneal sensation in all patients with 6th nerve palsy
- 46. 4. In the basilar course A. Raised intracranial tension: • Downward displacement of brainstem • Stretching of 6th nerve over petrous tip • Bilateral 6th nerve palsy – false localizing sign
- 47. B. Nasopharyngeal tumors→ invade skull and its foreman C. Base of skull fractures: → both unilateral and bilateral palsy
- 48. D. GRADENIGO’S SYNDROME: • Mastoiditis/acute Petrositis • - damage to 6th nerve at the petrous tip. • Facial weakness • Pain • Hearing difficulties
- 49. 5. INTRACAVERNOUS PART • Situated close to the internal carotid Artery • More likely to damage than other cranial nerves Intra cavernous 6th nerve palsy is accompanied by a postganglionic Horner’s syndrome
- 50. CLINICAL PRESENTATION • HISTORY: – Esotropia – Head-turn – Binocular diplopia (worse at distance) – Vision loss – Pain – Hearing loss – Symptoms of vasculitis, particularly giant cell arteritis – Trauma
- 53. BCQ’S: 1. True statements of the abducens nerve except: a) Arises from the medulla b) Passes under the petrosphenoidal ligament c) May cross two venous sinuses in its course d) Enters the orbit between the two divisions of III e) May be damaged by raised intracranial pressure
- 54. • The abducens nerve nucleus: a) Lies ventral to the genu of VII b) Communicates indirectly with the nucleus of III c) Sends fibres through Dorello's canal d) Innervates lateral rectus on its extraconal surface
- 55. THANK YOU