2011 survey islam_i
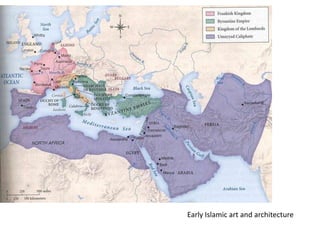
- 1. Early Islamic art and architecture
- 2. Islam Religion founded by Muhammad (570-630), who is revered as Islam’s Final Prophet Ca. 570: birth of Muhammad at Mecca 610: Muhammad begins preaching a religion of one God after receiving revelations from God (“Allah” in Arabic) 622: The Hijra = Flight of Muhammad from Mecca to Medina 630: Muhammad captures Mecca with an army of 10,000 believers, destroys pre-Islamic idols, preserves the Kaaba as the Islamic world’s symbolic center 632: Death of Muhammad at Medina • Islam means “submission (to Allah’s will)”. • Believers are called Muslims (“those who submit”). • Sacred book of Islam is the Koran (“recitations”) – references the archangel Gabriel’s instructions to Muhammad in 610 to recite the verses in the name of Allah. Kaaba at Mecca
- 3. Islam Religion founded by Muhammad (570-630), who is revered as Islam’s Final Prophet Ca. 570: birth of Muhammad at Mecca 610: Muhammad begins preaching a religion of one God after receiving revelations from God (“Allah” in Arabic) 622: The Hijra = Flight of Muhammad from Mecca to Medina 630: Muhammad captures Mecca with an army of 10,000 believers, destroys pre-Islamic idols, preserves the Kaaba as the Islamic world’s symbolic center 632: Death of Muhammad at Medina • Islam means “submission (to Allah’s will)”. • Believers are called Muslims (“those who submit”). • Sacred book of Islam is the Koran (“recitations”) – references the archangel Gabriel’s instructions to Muhammad in 610 to recite the verses in the name of Allah. Five pillars of Islam:1. Profession of faith in one God, Allah, and that Muhammad was His final Prophet 2. Recitation of prayers five times a day while facing in the direction of Mecca 3. Fasting during the month of Ramadan 4. Charitable giving of alms to the poor 5. Making a pilgrimage (“hajj”) at least once in one’s lifetime to Mecca
- 4. Jerusalem, Dome of the Rock, 687-692. Built by Umayyad caliph Abd al-Malik
- 5. Jerusalem, Dome of the Rock, 687-692
- 6. Dome of the Rock, view of interior, and plan of the building
- 7. Ravenna, Italy, Church of San Vitale, 526-547 Jerusalem, Dome of the Rock, 687-692
- 8. Rome, Santa Costanza, 337-351 Jerusalem, Dome of the Rock, 687-692
- 9. Rome, Santa Costanza, 337-351. Detail of mosaic ceiling Jerusalem, Dome of the Rock, 687-692. Detail of wall mosaics
- 10. Ravenna, San Vitale, Detail of mosaics in the apse of the church, 6th century Jerusalem, Dome of the Rock, 687-692. Detail of wall mosaics
- 12. Damascus, Syria. Great Mosque, 706-715 Built by Umayyad caliph al-Walid
- 13. Damascus, Syria. Great Mosque, 706-715
- 14. Damascus, Syria. Great Mosque, detail of mihrab and minbar. Both are placed along the qibla wall.
- 15. Damascus, Syria. Great Mosque, 706-715 Detail of mosaic
- 16. Mshatta palace, Jordan, 740-750. Now removed to a museum in Berlin, Germany
- 18. Mausoleum of the Samanids, Bukhara, Uzbekistan, early 10th century
- 20. Great Mosque, Cordoba, Spain. 8th – 10th centuries Built by the Umayyad caliph Abd al-Rahman I
- 21. Cordoba, Spain, Great Mosque. Prayer hall begun 784.
- 22. Cordoba, Spain. Maqsura of the Great Mosque, 961-965
- 23. Cordoba, Spain. Dome in front of mihrab of the Great Mosque, 961-965.
- 24. Koran page, beginning of surah (verse) 18, “Al-Kahf”, (The Cave), 9th cent. Now in the Chester Beatty Library and Oriental Art Gallery, Dublin, Ireland
Notas del editor
- Muhammed was born into an area that was influenced by Jewish and Christian religion. Also, an area of Arabs, nomadic tribes. Mohammed began to have visions from God at the year 610 – a monotheistic God. There was great resistance to his preachings about this God – so he had to flee from his home. He was able to gain a following in Medina where he was able to convince those there of his conviction. The word for God in Arabic is Allah. By 630 he was after to return to Mecca with an army of believers, and was able to conquer the city. The city was the center of Arabic belief. Here, a shrine was located that kept the idols related to the religion. The word Islam means submission.
- Muhammad was the final prophet to receive the word of God. Within fifty years, Islam spread vastly. Large Arab territory, so they were able to relate to a local preaching figure. Issues that existed with other religions did not exist within Islam. There were five basic pillars preached. The ruling dynasty of this period considered themselves to be direct decendents of Muhammad – so there is a clear relationship between religion and the secular state. With the spread of Islam, initiated a great change in art and architecture of the time.
- Jerusalem plays an important role in Islamic faith – the site where Muhammad died. It is said that before his death he traveled from Mecca to Jerusalem in the middle of the night – and he arrived at the site of the Jewish temple at Solomon, and died there. This is called the Dome of the Rock – the first example of Jerusalem architecture. Built by the Umayyad tribe – those that took over after Muhammad’s death.
- The form of the building is simplistic and clearly read – a domed building, with the base being octagonal. Product of the 16th century – the exterior is covered with mosaic but replaced with tile in the 16th century due to over exposure to the element.
- The interior is an open exposed area of rock – this site is associated with the location of where Muhammad died – related and sacred to Judaism because it was thought to be where Abraham nearly sacrificed Isaac. It was also holy to Christians because it was thought to be the burial place of Adam.
- Similar to Ravenna church due to it’s shape plan. Octagon with a dome on top. This is not a coincidence, but has a direct relationship. The Islamic architects were looking for a particular type of architecture to make this site a monument. They looked to local models of commemorative architecture – the use of the centralized plan to mark commemorative space.
- Adopt even Roman traditions in architecture also Roman and Byzantine types of decoration.
- Vegetable type of decoration to symbol the afterlife – also vine like decorative ornaments to represent the idea of paradise. The Mosaic decoration is take from Roman traditions of representing paradise.
- Symbolic images of paradise. The artists were Byzantine Christians – the art reflects that. The dome of the rock is not a mosque or place of worship, but it is a commemorative architecture, explaining why it is centrally planned. The first model was probably set up in Mecca, modeled after Muhammad’s house.
- The earliest mosque that survived today is found in Damascus in Syria.
- The mosque was a site of an early Byzantine Christian church – before that a Pagan temple. The Umayyad son Caliph al-Walid build the church resusing elements of the church and the pagan temple that once stood before on this site. There are basic qualities of early Islamic mosques – simple types of halls, a hall with several aisle – called a hypostyle hall. In front of the hall is an open courtyard – similar to Christian churches’ atriums and Roman temples that have an open courtyard. There are three towers – called Minarets. Atleast one is attached to each mosque – the tower where the prayer is announced.
- The interior incorporates the elements from the previous architectures used. Corinthian columns used to create the hypostyle hall. Open hallway that is aligned in a way that enables prayer.
- There is a positioning on one end of the building called a mihrab indicating one direction of prayer – called the quibla wall. In a mosque, these are always present to mark the direction in which to pray. The mihrab is simply a niche in the wall.
- Symbols for paradise – colorful architectural landscapes. Brought in from Byzantium and Constantinople. The main different is that that there is a prohibition against human and animals – goes back to old Jewish traditions. Shows simply the paradisiacal landscape.
- There is a clear relationship between ruler ship and religion. The palaces that were build referenced palace architecture in the Roman period. Rectangular buildings that have a lot of open space and they are symmetric. The tradition of clear symmetry is derived from Roman palaces and bath complexes. Resemble the idea of a defensive complex as well. Not mosaics, but sculpture. The palace decorations have human figures in them. The palace contains a mosque – which does not have figure décor.
- The islamic dynasties became in conflict as some points
- Almost 200-300 years after Islamic was established. There is a great deal of abstract patterning of the exterior of the building – adopting Roman architecture styles of columns, but applied in a more abstract way.
- Has an atrium with a largeminorette.
- Fantasical decoration – applied in a unique way, not in a Roman or Byzantium style. Their traditions are adopted but transformed into differing qualities, mainly that of color.
- In the 10th century, an addition was made to the mosque – a small enclosed area used for where the ruler could worship – called the Maqsura
- Composed of interlocking arches that transform the square space into an octagon. References earlier Islamic traditions.