smart home.pptx
•Download as PPTX, PDF•
0 likes•11 views
Bbd
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
AI is revolutionising the transport industry. From safety to speed, AI is redefining the way we commute.
Sensors
Safe transport
data
logistics
feedback
passengers
commuters
driversArtificial Intelligence (AI) in Transportation.pptx

Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Transportation.pptxDr.A.Prabaharan Professor & Research Director, Public Action
Recommended
AI is revolutionising the transport industry. From safety to speed, AI is redefining the way we commute.
Sensors
Safe transport
data
logistics
feedback
passengers
commuters
driversArtificial Intelligence (AI) in Transportation.pptx

Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Transportation.pptxDr.A.Prabaharan Professor & Research Director, Public Action
Saudi Arabia [ Abortion pills) Jeddah/riaydh/dammam/+966572737505☎️] cytotec tablets uses abortion pills 💊💊
How effective is the abortion pill? 💊💊 +966572737505) "Abortion pills in Jeddah" how to get cytotec tablets in Riyadh " Abortion pills in dammam*💊💊
The abortion pill is very effective. If you’re taking mifepristone and misoprostol, it depends on how far along the pregnancy is, and how many doses of medicine you take:💊💊 +966572737505) how to buy cytotec pills
At 8 weeks pregnant or less, it works about 94-98% of the time. +966572737505[ 💊💊💊
At 8-9 weeks pregnant, it works about 94-96% of the time. +966572737505)
At 9-10 weeks pregnant, it works about 91-93% of the time. +966572737505)💊💊
If you take an extra dose of misoprostol, it works about 99% of the time.
At 10-11 weeks pregnant, it works about 87% of the time. +966572737505)
If you take an extra dose of misoprostol, it works about 98% of the time.
In general, taking both mifepristone and+966572737505 misoprostol works a bit better than taking misoprostol only.
+966572737505
Taking misoprostol alone works to end the+966572737505 pregnancy about 85-95% of the time — depending on how far along the+966572737505 pregnancy is and how you take the medicine.
+966572737505
The abortion pill usually works, but if it doesn’t, you can take more medicine or have an in-clinic abortion.
+966572737505
When can I take the abortion pill?+966572737505
In general, you can have a medication abortion up to 77 days (11 weeks)+966572737505 after the first day of your last period. If it’s been 78 days or more since the first day of your last+966572737505 period, you can have an in-clinic abortion to end your pregnancy.+966572737505
Why do people choose the abortion pill?
Which kind of abortion you choose all depends on your personal+966572737505 preference and situation. With+966572737505 medication+966572737505 abortion, some people like that you don’t need to have a procedure in a doctor’s office. You can have your medication abortion on your own+966572737505 schedule, at home or in another comfortable place that you choose.+966572737505 You get to decide who you want to be with during your abortion, or you can go it alone. Because+966572737505 medication abortion is similar to a miscarriage, many people feel like it’s more “natural” and less invasive. And some+966572737505 people may not have an in-clinic abortion provider close by, so abortion pills are more available to+966572737505 them.
+966572737505
Your doctor, nurse, or health center staff can help you decide which kind of abortion is best for you.
+966572737505
More questions from patients:
Saudi Arabia+966572737505
CYTOTEC Misoprostol Tablets. Misoprostol is a medication that can prevent stomach ulcers if you also take NSAID medications. It reduces the amount of acid in your stomach, which protects your stomach lining. The brand name of this medication is Cytotec®.+966573737505)
Unwanted Kit is a combination of two medicinIn Riyadh Saudi Arabia |+966572737505 | Buy Cytotec| Get Abortion pills

In Riyadh Saudi Arabia |+966572737505 | Buy Cytotec| Get Abortion pillsAbortion pills in Riyadh +966572737505 get cytotec
More Related Content
Similar to smart home.pptx
Similar to smart home.pptx (20)
Smart Cities and Communication Infrastructure.pptx

Smart Cities and Communication Infrastructure.pptx
The Role and Impact of Intelligent Transportation Systems | GQ Research

The Role and Impact of Intelligent Transportation Systems | GQ Research
SMART SOLUTION FOR RESOLVING HEAVY TRAFFIC USING IOT

SMART SOLUTION FOR RESOLVING HEAVY TRAFFIC USING IOT
Smart transit payment for university campus transportation using RFID card sy...

Smart transit payment for university campus transportation using RFID card sy...
IoT In Transportation Evolution_ Advancements In Autonomous Vehicles.pdf

IoT In Transportation Evolution_ Advancements In Autonomous Vehicles.pdf
A SHORT SURVEY ON CONSTRUCTING AN IOTBASED INTELLIGENT ROAD SYSTEM

A SHORT SURVEY ON CONSTRUCTING AN IOTBASED INTELLIGENT ROAD SYSTEM
A Short Survey on Constructing an IoT based Intelligent Road System

A Short Survey on Constructing an IoT based Intelligent Road System
A Short Survey on Constructing an IoT based Intelligent Road System

A Short Survey on Constructing an IoT based Intelligent Road System
Intelligent transportation system based on iot service for traffic control

Intelligent transportation system based on iot service for traffic control
Implementing Intelligent Transport Systems in the Creation of Smart Cities

Implementing Intelligent Transport Systems in the Creation of Smart Cities
IRJET- Traffic Congestion at Toll Plaza: A Case Study of Khed-Shivapur, Pune

IRJET- Traffic Congestion at Toll Plaza: A Case Study of Khed-Shivapur, Pune
Recently uploaded
Saudi Arabia [ Abortion pills) Jeddah/riaydh/dammam/+966572737505☎️] cytotec tablets uses abortion pills 💊💊
How effective is the abortion pill? 💊💊 +966572737505) "Abortion pills in Jeddah" how to get cytotec tablets in Riyadh " Abortion pills in dammam*💊💊
The abortion pill is very effective. If you’re taking mifepristone and misoprostol, it depends on how far along the pregnancy is, and how many doses of medicine you take:💊💊 +966572737505) how to buy cytotec pills
At 8 weeks pregnant or less, it works about 94-98% of the time. +966572737505[ 💊💊💊
At 8-9 weeks pregnant, it works about 94-96% of the time. +966572737505)
At 9-10 weeks pregnant, it works about 91-93% of the time. +966572737505)💊💊
If you take an extra dose of misoprostol, it works about 99% of the time.
At 10-11 weeks pregnant, it works about 87% of the time. +966572737505)
If you take an extra dose of misoprostol, it works about 98% of the time.
In general, taking both mifepristone and+966572737505 misoprostol works a bit better than taking misoprostol only.
+966572737505
Taking misoprostol alone works to end the+966572737505 pregnancy about 85-95% of the time — depending on how far along the+966572737505 pregnancy is and how you take the medicine.
+966572737505
The abortion pill usually works, but if it doesn’t, you can take more medicine or have an in-clinic abortion.
+966572737505
When can I take the abortion pill?+966572737505
In general, you can have a medication abortion up to 77 days (11 weeks)+966572737505 after the first day of your last period. If it’s been 78 days or more since the first day of your last+966572737505 period, you can have an in-clinic abortion to end your pregnancy.+966572737505
Why do people choose the abortion pill?
Which kind of abortion you choose all depends on your personal+966572737505 preference and situation. With+966572737505 medication+966572737505 abortion, some people like that you don’t need to have a procedure in a doctor’s office. You can have your medication abortion on your own+966572737505 schedule, at home or in another comfortable place that you choose.+966572737505 You get to decide who you want to be with during your abortion, or you can go it alone. Because+966572737505 medication abortion is similar to a miscarriage, many people feel like it’s more “natural” and less invasive. And some+966572737505 people may not have an in-clinic abortion provider close by, so abortion pills are more available to+966572737505 them.
+966572737505
Your doctor, nurse, or health center staff can help you decide which kind of abortion is best for you.
+966572737505
More questions from patients:
Saudi Arabia+966572737505
CYTOTEC Misoprostol Tablets. Misoprostol is a medication that can prevent stomach ulcers if you also take NSAID medications. It reduces the amount of acid in your stomach, which protects your stomach lining. The brand name of this medication is Cytotec®.+966573737505)
Unwanted Kit is a combination of two medicinIn Riyadh Saudi Arabia |+966572737505 | Buy Cytotec| Get Abortion pills

In Riyadh Saudi Arabia |+966572737505 | Buy Cytotec| Get Abortion pillsAbortion pills in Riyadh +966572737505 get cytotec
Saudi Arabia [ Abortion pills) Jeddah/riaydh/dammam/+966572737505☎️] cytotec tablets uses abortion pills 💊💊
How effective is the abortion pill? 💊💊 +966572737505) "Abortion pills in Jeddah" how to get cytotec tablets in Riyadh " Abortion pills in dammam*💊💊
The abortion pill is very effective. If you’re taking mifepristone and misoprostol, it depends on how far along the pregnancy is, and how many doses of medicine you take:💊💊 +966572737505) how to buy cytotec pills
At 8 weeks pregnant or less, it works about 94-98% of the time. +966572737505[ 💊💊💊
At 8-9 weeks pregnant, it works about 94-96% of the time. +966572737505)
At 9-10 weeks pregnant, it works about 91-93% of the time. +966572737505)💊💊
If you take an extra dose of misoprostol, it works about 99% of the time.
At 10-11 weeks pregnant, it works about 87% of the time. +966572737505)
If you take an extra dose of misoprostol, it works about 98% of the time.
In general, taking both mifepristone and+966572737505 misoprostol works a bit better than taking misoprostol only.
+966572737505
Taking misoprostol alone works to end the+966572737505 pregnancy about 85-95% of the time — depending on how far along the+966572737505 pregnancy is and how you take the medicine.
+966572737505
The abortion pill usually works, but if it doesn’t, you can take more medicine or have an in-clinic abortion.
+966572737505
When can I take the abortion pill?+966572737505
In general, you can have a medication abortion up to 77 days (11 weeks)+966572737505 after the first day of your last period. If it’s been 78 days or more since the first day of your last+966572737505 period, you can have an in-clinic abortion to end your pregnancy.+966572737505
Why do people choose the abortion pill?
Which kind of abortion you choose all depends on your personal+966572737505 preference and situation. With+966572737505 medication+966572737505 abortion, some people like that you don’t need to have a procedure in a doctor’s office. You can have your medication abortion on your own+966572737505 schedule, at home or in another comfortable place that you choose.+966572737505 You get to decide who you want to be with during your abortion, or you can go it alone. Because+966572737505 medication abortion is similar to a miscarriage, many people feel like it’s more “natural” and less invasive. And some+966572737505 people may not have an in-clinic abortion provider close by, so abortion pills are more available to+966572737505 them.
+966572737505
Your doctor, nurse, or health center staff can help you decide which kind of abortion is best for you.
+966572737505
More questions from patients:
Saudi Arabia+966572737505
CYTOTEC Misoprostol Tablets. Misoprostol is a medication that can prevent stomach ulcers if you also take NSAID medications. It reduces the amount of acid in your stomach, which protects your stomach lining. The brand name of this medication is Cytotec®.+966573737505)
Unwanted Kit is a combination of two mediAbortion pills in Jeddah |+966572737505 | Get Cytotec

Abortion pills in Jeddah |+966572737505 | Get CytotecAbortion pills in Riyadh +966572737505 get cytotec
Jual Obat Aborsi (088980685493) Obat Aborsi Cytotec Asli.
Klinik _ Apotik Online Solusi Menggugurkan Masalah Kehamilan Anda | Jual Obat Aborsi Asli ( Wa – 088980685493 )
KLINIK ABORSI TERPEECAYA _ Jual Obat Aborsi Cytotec Misoprostol Asli 100% Ampuh Hanya 3 Jam Langsung Gugur || OBAT PENGGUGUR JANIN KANDUNGAN AMPUH |
Jual Obat Aborsi Asli, Ampuh, Manjur, Tuntas | OBAT ABORSI OLINE “APOTIK Jual Obat Cytotec, Gastrul, Gynacoside Asli Ampuh. JUAL ” Obat Aborsi Tuntas | Obat Aborsi Manjur | Obat Aborsi Ampuh | Obat Penggugur Janin | Obat Pencegah Kehamilan | Obat Pelancar Haid | Obat terlambat Bulan | Ciri Obat Aborsi Asli | Obat Telat Bulan | GDP Aborsi Asli |
Obat Penggugur Kandungan, Obat Aborsi Batam, Obat Aborsi Banjarmasin, Obat Aborsi Banjarbaru, Obat Aborsi Banjar, Obat Aborsi Bandung, Obat Aborsi Bandar Lampung, Obat Aborsi Banda Aceh, Obat Aborsi Balikpapan, Obat Aborsi Ambon, Obat Aborsi Batu, Obat Aborsi Baubau, Obat Aborsi Bekasi, Obat Aborsi Bengkulu, Obat Aborsi Bima, Obat Aborsi Binjai, Obat Aborsi Bitung, Obat Aborsi Blitar, Obat Aborsi Bogor, Obat Aborsi Bontang, Obat Aborsi Bukittinggi, Obat Aborsi Cilegon, Obat Aborsi Cimahi, Obat Aborsi Cirebon, Obat Aborsi Denpasar Bali, Obat Aborsi Depok, Obat Aborsi Dumai, Obat Aborsi Gorontalo, Obat Aborsi Jambi, Obat Aborsi Jakarta, Obat Aborsi Sawahlunto, Obat Aborsi Kendari, Obat Aborsi Kediri, Obat Aborsi Jayapura, Obat Aborsi Langsa, Obat Aborsi Kupang, Obat Aborsi Surabaya , Obat Aborsi Kotamobagu, Obat Aborsi Medan, Obat Aborsi Madiun,Obat Aborsi Lubuklinggau, Obat Aborsi Lhokseumawe, Obat Aborsi Magelang, Obat Aborsi Makassar, Obat Aborsi Malang, Obat Aborsi Manado, Obat Aborsi Mataram, Obat Aborsi Metro, Obat Aborsi Mojokerto, Obat Aborsi Meulaboh, Obat Aborsi Padang, Obat Aborsi Padang Panjang, Obat Aborsi Padang Sidempuan, Obat Aborsi Pagaralam, Obat Aborsi Palangkaraya, Obat Aborsi Pangkal Pinang, Obat Aborsi Palu, Obat Aborsi Palopo, Obat Aborsi Palembang, Obat Aborsi Parepare, Obat Aborsi Pariaman, Obat Aborsi Pasuruan, Obat Aborsi Payakumbuh, Obat Aborsi Pontianak, Obat Aborsi Pematang Siantar, Obat Aborsi Pekanbaru, Obat Aborsi Pekalongan, Obat Aborsi Salatiga, Obat Aborsi Sabang, Obat Aborsi Purwokerto, Obat Aborsi Probolinggo, Obat Aborsi PRABUMULIH, Obat Aborsi Samarinda, Obat Aborsi Semarang, Obat Aborsi Serang, Obat Aborsi Sibolga, Obat Aborsi singkawang,Obat Aborsi Solok, Obat Aborsi Sorong, Obat Aborsi Subulussalam, Obat Aborsi Sukabumi, Obat Aborsi Sungai Penuh, Obat Aborsi Surakarta, Obat Aborsi Tangerang, Obat Aborsi Tangerang Selatan, Obat Aborsi Tanjung Pinang, Obat Aborsi Tarakan, Obat Aborsi Tasikmalaya, Obat Aborsi Tegal , Obat Abersi Ternate, Obat Abersi Tidore Kepulauan, Obat Abersi Tomohon, Obat Abersi Tual, Obat Abersi Tanjung Balai, Obat Abersi Tebing Tinggi, Obat ABORSI YOGYAKARTA.OBAT ABORSI TEBING TINGGI, OBAT ABORSI YOGYAKARTA.OBAT Ogyakarta.Obat Aborsi Tidore Kepulauan, Obat Aborsi Tomohon, Obat Aborsi Tual, Obat Aborsi Tanjung Balai, Obat AborsiJual Obat Aborsi Samarinda ( No.1 ) 088980685493 Obat Penggugur Kandungan Cy...

Jual Obat Aborsi Samarinda ( No.1 ) 088980685493 Obat Penggugur Kandungan Cy...Obat Aborsi 088980685493 Jual Obat Aborsi
Recently uploaded (20)
In Riyadh Saudi Arabia |+966572737505 | Buy Cytotec| Get Abortion pills

In Riyadh Saudi Arabia |+966572737505 | Buy Cytotec| Get Abortion pills
Top profile Call Girls In Udgir [ 7014168258 ] Call Me For Genuine Models We ...![Top profile Call Girls In Udgir [ 7014168258 ] Call Me For Genuine Models We ...](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
![Top profile Call Girls In Udgir [ 7014168258 ] Call Me For Genuine Models We ...](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
Top profile Call Girls In Udgir [ 7014168258 ] Call Me For Genuine Models We ...
LANDSLIDE MONITORING AND ALERT SYSTEM FINAL YEAR PROJECT BROCHURE

LANDSLIDE MONITORING AND ALERT SYSTEM FINAL YEAR PROJECT BROCHURE
Abort pregnancy in research centre+966_505195917 abortion pills in Kuwait cyt...

Abort pregnancy in research centre+966_505195917 abortion pills in Kuwait cyt...
Abortion pills in Jeddah |+966572737505 | Get Cytotec

Abortion pills in Jeddah |+966572737505 | Get Cytotec
Jual Obat Aborsi Samarinda ( No.1 ) 088980685493 Obat Penggugur Kandungan Cy...

Jual Obat Aborsi Samarinda ( No.1 ) 088980685493 Obat Penggugur Kandungan Cy...
Abortion pills in Jeddah +966572737505 <> buy cytotec <> unwanted kit Saudi A...

Abortion pills in Jeddah +966572737505 <> buy cytotec <> unwanted kit Saudi A...
Guwahati Escorts Service Girl ^ 9332606886, WhatsApp Anytime Guwahati

Guwahati Escorts Service Girl ^ 9332606886, WhatsApp Anytime Guwahati
Vashi Affordable Call Girls ,07506202331,Vasai Virar Charming Call Girl

Vashi Affordable Call Girls ,07506202331,Vasai Virar Charming Call Girl
Abortion Pill for sale in Riyadh ((+918761049707) Get Cytotec in Dammam

Abortion Pill for sale in Riyadh ((+918761049707) Get Cytotec in Dammam
smart home.pptx
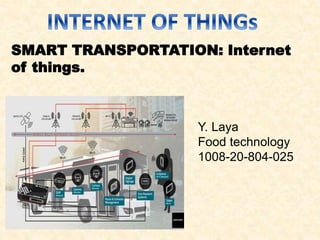
- 1. SMART TRANSPORTATION: Internet of things. Y. Laya Food technology 1008-20-804-025
- 2. IoT in transportation incorporates a wide network of embedded sensors, actuators, smart objects and other intelligent devices. This network collects data about the real-world scenario and transmits it over the specialized software to transform that data into useful information. The operations of the transport sector have been revolutionized with the help of IoT enabled technologies and smart solutions. Furthermore, the transportation system in the urban areas is becoming more complex day by day as the vehicle population on the road is increasing. This highlights the need of the municipalities to integrate IoT in transportation to have access to greater and secure transportation benefits.
- 3. 1. Efficient Traffic Management Traffic management is the biggest segment within the transportation industry where the adoption of IoT technologies is observed to be the most prominent. Million and Billions of Gigabytes of traffic and vehicle-related data are being generated through CCTV cameras. This data is transferred to traffic management centers for keeping a closer look at the vehicles and punishing the car owners who are violating the traffic rules and regulations. Smart parking, automatic traffic light system and smart accident assistance are the few applications of IoT that help the traffic and patrolling officers in managing the traffic efficiently and reducing the risk of accidents.
- 5. 2. Automated Toll and Ticketing Compared to traditional tolling and ticketing systems, IoT in transportation offers automated tolls. With the help of RFID tags and other smart sensors, managing toll and ticketing have become much easier for traffic police officers. Any vehicle which might be a kilometer away from the tolling station can easily be detected with the help of IoT technologies. This enables the lifting of the traffic barriers for the vehicles to pass through. However, the older vehicles do not have IoT connectivity, but the smartphones of the car owners can serve the same purpose as well, that is, taking automatic payments through phones linked to the digital wallet. This indicates that IoT in transportation is much more flexible and is compatible with new vehicles and demonstrate easy integration with older vehicles as well, for automated toll and ticketing procedures.
- 6. 3. Self-driving Cars Self-driving cars or autonomous vehicles are the coolest things that have been introduced in the transportation industry. Self-driving cars are capable of moving safely by sensing the environment, with little or no human interaction. However, to gather data about the surrounding, self-driving cars use a wide range of sensors. For instance, the self-driving car uses acoustic sensors, ultrasonic sensors, radar, LiDAR (Light detection and ranging), camera and GPS sensors to have information about the surroundings and take the data-driven decision about mobility accordingly. This indicates that the functioning of self-driving cars is dependent on IoT sensors. With the help of IoT, sensors equipped in the self-driving cars continuously gather the data about the surrounding in real-time and transfer this data either to a central unit or cloud.
- 7. According to the Intelligent Transportation Society of America, ITS technology makes it possible to: • Use a navigation system to find the best route based on real- time conditions. • Alert drivers of potentially hazardous situations in time to avoid crashes. • Be guided to an empty parking space by a smart sign. • Ride a bus that turns traffic lights green on approach. • Detect and respond promptly to traffic incidents. • Reroute traffic in response to road conditions or weather emergencies. • Allow drivers to manage their fuel consumption. • Adjust speed limits and signal timing based on real-world conditions. • Improve freight tracking, inspection, safety and efficiency. • Make public transportation more convenient and reliable.
- 8. Smart City Ahmedabad gets IoT-driven buses As one of India's fastest growing scientific and industrial hubs, the city of Ahmedabad was among the first 20 candidates selected for the government's Smart City Mission. Recognizing the vital importance of efficient public transport, Smart City Ahmedabad Development Limited (SCADL) partnered with NEC to upgrade the city's manually operated, often erratic bus transit infrastructure with a seamless, safe and reliable intelligent transport management system. Intelligently applied IoT and big data analysis technologies are enabling the city to build a smart bus system that is easy to plan, merge and grow along with its expanding footfall.
- 9. Improving public transport is integral to smart city success. It is costly, but transferring passengers at attractive prices enables education, employment, and ultimately safe movement," advocates SCADL CEO, Rakesh Shankar. Ahmedabad's two major bus services Bus Rapid Transit (BRT) and city bus AMTS operate 1,000 buses transporting 0.8 million passengers daily across the city. Despite attractive ticket prices, the bus services were underutilized due to customer concerns over quality. The previous manually operated system suffered from poor route planning, a lack of advertised bus schedules, bus- bunching, excessive waiting time, rough driving, stop skipping, and inconvenient or inconsistent cash collection. A lack of transparency also resulted in higher operating costs and customer complaint handling. The city authorities were keen to upgrade to a cashless, software-based bus service system backed by advanced ICT to help reduce expenses and problem- response time. "Smart transportation must offer ease of use for the traveler, transparency of services, and the ability to plan. We needed to understand entire routes and behavior, so we could deploy the right resources, add new vehicles and develop seamless transport services."
- 10. Automated Fare Collection Service(AFCS): Quick and secure cashless payment via prepaid RuPay card or smartphone ensures greater convenience, passenger safety and ridership visibility. Automated Vehicle Location Service(AVLS): Real-time visualization of vehicle location via fitted GPS enables the city to calculate estimated time of arrival and support bus operations from a central command center to adhere to a planned schedule. Passenger Information System: Provide real-time bus information via mobile app, website and in-station boards to enable passengers to plan their route and estimate waiting and arrival times. Route and bus stop information is also provided via on-board displays and announcements. Vehicle Planning Schedule and Dispatch System (VPSD): Bus routes and schedules optimized by analysis of bus travel performance and traffic volume. Depot Management System (DMS): Allocate and optimize crew and overall bus operations by automating the management of vehicles, fuel, inventory, personnel, and vehicle maintenance.