section 3, chapter 9 cross-bridge cycling
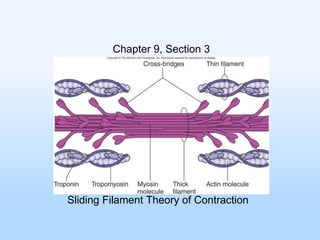
- 1. Chapter 9, Section 3 Sliding Filament Theory of Contraction
- 2. The Sliding Filament Model of Muscle Contraction During a muscle contraction Thick (myosin) filaments and thin (actin) filaments slide across one another The filaments do not change lengths Z-bands move closer together causing the sarcomere to shorten. I bands appear narrow Figure 9.11a. Individual sarcomeres shorten as thick and thin filaments slide past one another.
- 3. Cross Bridge Cycling 1. When a muscle is relaxed, tropmyosin covers the binding sites on actin. A molecule of ADP and Phosphate remains attached to myosin from the previous contraction.
- 4. Cross Bridge Cycling 2. During a contraction, Calcium binds to troponin. Tropomyosin is repositioned, exposing the myosin binding sites on actin filaments
- 5. Cross Bridge Cycling 3. Myosin heads bind to actin filaments. The phosphate is released.
- 6. Cross Bridge Cycling 4. Myosin heads spring forward “Power Stroke” pulling the actin filaments. ADP is released from Myosin
- 7. Cross Bridge Cycling 5. Myosin is released from actin. A new molecule of ATP binds to myosin, causing it to be released from the actin filament. • ATP is not yet broken down, but it is essential to release the crossbridges.
- 8. Cross Bridge Cycling 6. ATP is broken down, providing the energy to “cock” the myosin filaments (recovery stroke). 7. Steps 1-6 are repeated several times.
- 9. Figure 9.10. The cross-bridge cycle. The cycle continues as long as ATP is present, and nerve impulses release Acetylcholoine. Watch the You-Tube video “Sliding Filament” to view cross-bridge cycling in action.
- 10. Relaxation When a nerve impulse ceases, two events relax muscle fibers. 1. Acetylcholinesterase breaks down Ach in the synapse. • Prevents continuous stimulation of a muscle fiber. 2. Calcium Pumps (Ca2+ATPase) remove Ca2+ from the sarcoplasm and returns it to the SR. • Without calcium, tropomyosin covers the binding sites on actin filaments.
- 11. Relaxation Rigor Mortis is a partial contraction of skeletal muscles that occurs a few hours after death. • After death calcium leaks into sarcoplasm, triggering the muscle contractions. • But ATP supplies are diminished after death, so ATP is not available to remove the cross-bridge linkages between actin and myosin. • muscles do not relax*. • Contraction is sustained until muscles begin to decompose. * Notice that ATP is required for muscle relaxation!
- 12. End of Chapter 9, Section 3