Molecular Diagnostics 4th Year Notes
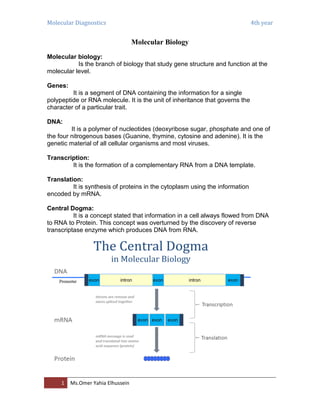
- 1. Molecular Diagnostics 4th year 1 Ms.Omer Yahia Elhussein Molecular Biology Molecular biology: Is the branch of biology that study gene structure and function at the molecular level. Genes: It is a segment of DNA containing the information for a single polypeptide or RNA molecule. It is the unit of inheritance that governs the character of a particular trait. DNA: It is a polymer of nucleotides (deoxyribose sugar, phosphate and one of the four nitrogenous bases (Guanine, thymine, cytosine and adenine). It is the genetic material of all cellular organisms and most viruses. Transcription: It is the formation of a complementary RNA from a DNA template. Translation: It is synthesis of proteins in the cytoplasm using the information encoded by mRNA. Central Dogma: It is a concept stated that information in a cell always flowed from DNA to RNA to Protein. This concept was overturned by the discovery of reverse transcriptase enzyme which produces DNA from RNA.
- 2. Molecular Diagnostics 4th year 2 Ms.Omer Yahia Elhussein Eukaryote Prokaryote
- 3. Molecular Diagnostics 4th year 3 Ms.Omer Yahia Elhussein Bacteria contain only one circular DNA molecule contained in the cytoplasm and Plasmid; small, circular, double stranded DNA separated from bacterial chromosome. Human cells contain two sources of DNA: Nuclear and Mitochondrial DNA. Nuclear DNA arranged in 23 pairs of chromosomes as follows” 22 pairs (autosomes). 1 pair (sex chromosome); XX for female and XY for male Mitochondrial DNA is a circular, protein and intron free DNA and It is inherited maternally. Diploid: Containing both member of each pair of homologous chromosomes e.g. All cells except germinal cells and mature RBCs Haploid: Containing only one member of each pair of homologous chromosomes. Haploid cells are produced during Meiosis. e.g. sperm and ova Features held in common by Eukaryote and Prokaryote: 1. Genetic information encoded in DNA using identical genetic code (G, C, A, T). 2. Similar mechanisms for transcription and translation of genetic information. Features of Eukaryotic cells not found in Prokaryotes: 1. The cell is divided in to nucleus and cytoplasm, separated by a nuclear envelope containing complex pore structure. 2. Complex chromosomes composed of DNA and associated proteins. 3. Cell division using a microtubule – containing mitotic spindle that separate chromosomes. 4. Presence of two copies of genes per cell (Diploid) one from each parent. 5. Presence of three different RNA synthesizing enzymes (RNA Polymerases). Genome: The complement of genetic information unique to each species of organism. It is equivalent the DNA of Haploid set of chromosomes from that species.
- 4. Molecular Diagnostics 4th year 4 Ms.Omer Yahia Elhussein DNA STRUCTURE 3.2 billion Base pair (BP) of DNA in Human genome. The total size of DNA when we consider the two copies is 6.4 billion BP. 640,000,0000 bp Size/length unit isBp (Base Pair). Kb (Kilo base). 1000 bp Mb (Mega base). 1000000 bp
- 5. Molecular Diagnostics 4th year 5 Ms.Omer Yahia Elhussein The complete set of metaphase chromosomes in a eukaryotic cell is called its karyotype. Humans, which are diploid (2N) organisms, have 46 chromosomes (two genomes), with one haploid (N) set of chromosomes (23 chromosomes: one genome) coming from the egg and another haploid set coming from the sperm. Chromatin: is the stainable material in a cell nucleus: DNA and proteins. A complex nucleoprotein material that makes up the chromosomes of eukaryotes. The term is commonly used in descriptions of chromosome structure and function. Chromatin that remains compacted during interphase is called heterochromatin to distinguish it from euchromatin, which returns to a dispersed state. Histones and nonhistones are two major types of proteins associated with DNA in chromatin. Both types of proteins play an important role in determining the physical structure of the chromosome. The histones are the most abundant proteins in chromatin. They are small basic proteins with a net positive charge that facilitates their binding to the negatively charged DNA. Five main types of histones are associated with eukaryotic nuclear DNA: H1, H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. Weight for weight, there is an equal amount of histone and DNA in chromatin. Nonhistones are all the proteins associated with DNA, apart from the histones. Nonhistones include proteins that play a role in the processes of DNA replication, DNA repair, transcription (including gene
- 6. Molecular Diagnostics 4th year 6 Ms.Omer Yahia Elhussein regulation), and recombination. Chemical structure and types of nucleic acids: Organisms contain genetic material that governs an individual’s characteristics and that is transferred from parent to progeny. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is the genetic material of all living organisms and some viruses. Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) is the genetic material only of certain Viruses .In prokaryotes and eukaryotes; the DNA is always double-stranded, whereas in viruses the genetic material may be double- or single-stranded DNA or RNA, depending on the virus. DNA and RNA are macromolecules composed of smaller building blocks called nucleotides. Each nucleotide consists of a five-carbon sugars (deoxyribose in DNA, ribose in RNA) to which are attached a nitrogenous base and a phosphate group. In DNA, the four possible bases are adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine; in RNA, the four possible bases are adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil.
- 7. Molecular Diagnostics 4th year 7 Ms.Omer Yahia Elhussein Nitrogenous bases: Ribonucleic acid (RNA) and deoxy Ribonucleic acid (DNA): Sugar + Phosphate + Nitrogenous base = Nucleic Acid 2’-deoxy ribose + Phosphate + adenine, guanine, = DNA Cytosine or Thymine Ribose + Phosphate + adenine, guanine, = RNA Cytosine or Uracil
- 8. Molecular Diagnostics 4th year 8 Ms.Omer Yahia Elhussein
- 9. Molecular Diagnostics 4th year 9 Ms.Omer Yahia Elhussein According to Watson and Crick’s model, the DNA molecule consists of two polynucleotide (polymers of nucleotides) chains joined by hydrogen bonds between pairs of bases—adenine (A) and thymine (T); and guanine (G) and cytosine (C)—in a double helix. The genetic material of viruses may be linear or circular Double-stranded DNA, single-stranded DNA, double-stranded RNA, or single-stranded RNA, depending on the virus. The genomes of some viruses are organized into a single chromosome, whereas others have a segmented genome. The genetic material of prokaryotes is double-stranded DNA localized into one or a few chromosomes. Typically prokaryotic chromosomes are circular, but linear Chromosomes are found in a number of species. A bacterial chromosome is compacted into the nucleoid region by the supercoiling of the DNA helix and the formation of looped domains of supercoiled DNA.
- 10. Molecular Diagnostics 4th year 10 Ms.Omer Yahia Elhussein The eukaryotic genome is distributed among several linear chromosomes. The complete set of metaphase chromosomes in a eukaryotic cell is called its karyotype. The nuclear chromosomes of eukaryotes are complexes of DNA and histone and nonhistone chromosomal proteins. Each unduplicated chromosome consists of one linear, unbroken, double-stranded DNA molecule running throughout its length; the DNA is variously coiled and folded. The histones are constant from cell to cell within an organism, whereas the Nonhistones vary significantly between cell types. The large amount of DNA present in the eukaryotic chromosome is compacted by its association with histones in nucleosomes and by higher levels of folding of the nucleosomes into chromatin fibers. Properties of DNA: 1. The two chains are antiparallel (show opposite polarity); that is, the two strands are oriented in opposite directions, with one strand oriented in the 5’–to–3’way and the other strand oriented 3’–to–5’. 2. The sugar–phosphate backbones are on the outsides of the double helix, with the bases oriented toward the central axis. 3. The bases in each of the two polynucleotide chains are bonded together by hydrogen bonds, which are relatively weak chemical bonds. The specific pairings observed are A bonded with T (two hydrogen bond) and G bonded with C (three hydrogen bond). The hydrogen bonds make it relatively easy to separate the two strands of the DNA. The specific A–T and G–C pairs are called complementary base pairs, so the nucleotide sequence in one strand dictates the nucleotide sequence of the other. For instance, if one chain has the sequence 5’-TATTCCGA-3’, the opposite, antiparallel chain must bear the sequence 3’-ATAAGGCT-5’.
- 11. Molecular Diagnostics 4th year 11 Ms.Omer Yahia Elhussein 4. The DNA molecule consists of two polynucleotide chains wound around each other in a right- handed double helix. 5. Because of the way the bases bond with each other, the two sugar–phosphate backbones of the double helix are not equally spaced from one another along the helical axis. This unequal spacing results in grooves of unequal size between the backbones; one groove is called the major (wider) groove, the other the minor (narrower) groove. 6. Coiling of DNA: that is, the double helix is twisted in space about its own axis. Types of hydrogen bonding
- 12. Molecular Diagnostics 4th year 12 Ms.Omer Yahia Elhussein Properties of RNA: 1. In the cell, the functional forms of RNA such as messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), ribosomal RNA (rRNA), small nuclear RNA(snRNA), and micro RNA (miRNA) are single-stranded molecules. 2. A single-stranded RNA molecule may fold up on itself to produce regions of antiparallel double-stranded RNA separated by segments of unpaired RNA. This configuration is called the secondary structure of the molecule 3. Single-stranded RNA and double-stranded RNA molecules are the genomes of certain viruses. RNA: is a single stranded; the pyrimidine base uracil (U) replaces thymine and ribose sugar replaces deoxyribose. Messenger RNA/ mRNA Transcripts of structural genes. Encode all the information necessary for the synthesis of a polypeptide of protein. The 5' terminus is capped by 7 methylguanosine triphosphate. Synthesis of the poly (A) tail involves cleavage of its 3' end and then the addition of about 200 adenine residues. Intermediate carrier of genetic information; deliver genetic information to the cytoplasm.
- 13. Molecular Diagnostics 4th year 13 Ms.Omer Yahia Elhussein Transfer RNA/ tRNA: All the tRNAs share a common secondary structure resembles a cloverleaf: They have four base- paired stems defining three stem-loops (the D loop, anticodon loop, and T loop) and the acceptor stem. tRNA carry correct amino acids to their position along the mRNA template to be added to the growing polypeptide chain.
- 14. Molecular Diagnostics 4th year 14 Ms.Omer Yahia Elhussein Ribosomal RNA/ rRNA The central component of the ribosome. Ribosome; factory for protein synthesis; composed of ribosomal RNA and ribosomal proteins (known as a Ribonucleoprotein or RNP). rRNA provides a mechanism for decoding mRNA into amino acids. Questions: 1. Extra chromosomal double stranded, circular DNA molecule present in bacteria which is widely used as vector is ……………………………. 2. What are the differences between bacterial and Human DNA? 3. What are the constituents of Human Genome and Bacterial Genome? 4. What do we mean by CENTRAL DOGMA? 5. What are the constituents of Gene? 6. What do we mean by : Nucleotide? Nucleoside? Deoxyribose? Antiparallel? 7. G ? 8. A ? References: Peter J. Russell, i Genetics: Copyright © Pearson Education. Cell and Molecular Biology concepts and experiments 6 edition.
