Nucleus .veena (1)
- 1. VEENA P KUMAR 1st YEAR MSC.MICROBIOLOGY SCHOOL OF BIOSCIENCE Veena P Kumar 1
- 2. Eukaryotic membrane based organelle. Comprises of linear DNA molecules. Monitors cellular activity by gene regulation. Enclosed in a double membrane envelope. Comprises of pores to allow transport of molecules. Largest cell organelle in animals. Comprises of viscous fluid throughout the organelle(nucleoplasm). Veena P Kumar 2
- 3. Discovered by A. V. Leeuwenhoek for first time. Franz Bauer in 1802 also described it. Scottish botanist Robert Brown explained it in more detail. Later it was concluded that it is a membrane bounded organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Veena P Kumar 3
- 4. Veena P Kumar 4
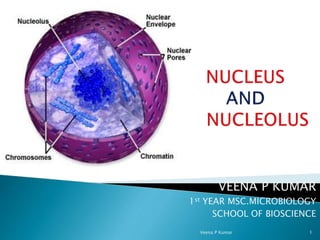
- 5. 1. Nuclear envelope - pore riddle. 2. Nucleoplasm – fluid interior portion. 3. Nucleolus – dense cluster of RNA. 4. Chromatin – all DNA + protein. Veena P Kumar 5
- 6. Existence of nuclear membrane – late 19th century. Phase contrast microscopy – 20th century. Further investigations – double membrane with space between 2 phospholipid bi layers. Veena P Kumar 6
- 7. Inner and outer nuclear membrane with perinuclear space. 7-8nm thick and trimellar appearance. Inner membrane lined with fiber net work- nuclear lamina-10 - 40nm. Nuclear lamina- intermediate filament (protein) called as Lamins. Nuclear lamina support to NE & attachment site for chromatin. Veena P Kumar 7
- 8. Outer membrane continuous with ER. Outer membrane studded with ribosomes- protein synthesis. Perinuclear space-20 to 40nm continuous with cisternae of ER. Filaments of cytoskeleton extend outward cytoplasm-anchored to organelles/plasma membrane- known as nuclear matrix. Veena P Kumar 8
- 9. Veena P Kumar 9
- 10. Most distinctive feature of nuclear envelope. Small cylindrical channels- direct contact b/w cytosol & nucleoplasm. Readily visible- freeze fracture microscopy. Density- cell type & activity. Mammalian nucleus-3000to4000 pores. Density 10-20 pores/sq. micrometer. Structural complexity control transport of key molecules. Veena P Kumar 10
- 11. Veena P Kumar 11
- 12. Nuclear pores are large protein complexes that cross the nuclear envelope, which is the double membrane surrounding the eukaryotic cell nucleus. Diameter 120 nm, over all mass 120 million da, 100 or more different poly peptide sub units. Shape- wheel lying on its side within NE. Two parallel rings –rim of wheel – 8 sub units. Anchor protein - proteins extend from rim into peri nuclear space. Fibers extend from rings to cytosol and nucleoplasm. Veena P Kumar 12
- 13. Veena P Kumar 13
- 14. Veena P Kumar 14
- 15. Enzymes and proteins-replication and transcription must be imported from cytoplasm. RNA and ribosomes for protein synthesis in cytoplasm must be obtained rom nucleus. Natures solution – evolution of eukaryotic Ne with pores. Veena P Kumar 15
- 16. Veena P Kumar 16
- 17. 3000 t0 4000 nuclear pores are usually present in actively growing mammalian cell. Ribosomes are partially assembled in nucleus. In an actively growing mammalian cell- 2000ribosomal unit per minute. Transport rate of ribosomal subunit- 5 to 6 units/minutes/pore. During replication histones needed @3,00,000 molecules/min. Rate of inward movement-100 histones/min. Veena P Kumar 17
- 18. Apart from macromolecules pore allow –small molecules and ions. Aqueous channels-direct contact cytosol and nucleoplasm. Permeable to small molecules and ions Nucleoside triphosphates required for DNA&RNA synthesis-diffuse freely through pores. Small molecules- metabolic pathways. Eight 9nm channels between the spokes + 9nm channel at center of transporter. Veena P Kumar 18
- 19. Veena P Kumar 19
- 20. Eukaryotic chromosomes 2 two broad components. 1.Nucleic acid; DNA + small amount of RNA 2.Proteins; Histones-core histones , linker histones. Non histone proteins. Veena P Kumar 20
- 21. Histones bind to-vely charged DNA –stability to the DNA. E/M examination of inter phase chromatin – ellipsoidal beads joined together by linker DNA known as nucleosomes Veena P Kumar 21
- 22. Simplest packing structure of DNA . 146bp DNA wrapped around histone octamer. Octamer-2copies of four histones. DNA length varies between species. Core DNA –DNA associated with histone octamer. Linker DNA –DNA b/w histone octamer- 8-114 bp Veena P Kumar 22
- 23. Veena P Kumar 23
- 24. • Chromatin can be differentiated into two regions . • Euchromatin - • slightly stained. • Hetero chromatin- • densely stained Veena P Kumar 24
- 25. Heterochromatin appears as small, darkly staining, irregular particles scattered throughout the nucleus or accumulated adjacent to the nuclear envelope. Euchromatin is dispersed and not readily stainable. Euchromatin is prevalent in cells that are active in the transcription of many of their genes while heterochromatin is most abundant in cells that are less active or not active. Veena P Kumar 25
- 26. DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, contains the information needed for the creation of proteins (which include enzymes and hormones) and is stored in the nucleus. The nucleus is the site of DNA duplication, which is needed for cell division (mitosis) and organism reproduction and growth. Veena P Kumar 26
- 27. Polymeric molecules made of 4 different monomeric units called nucleotides. Nucleotide : 1. A pentose(5 carbon)sugar. 2. A nitrogen base 3. A phosphate group Veena P Kumar 27
- 28. For DNA pentose sugar is ribose. Nitrogenous bases ; 2 classes 1. Purines – adenine(A)&guanine(G) 2. Pyrimidines – Thymine(T)&Cytosine(C) IN RNA thymine is replaced by uracil Nucleoside =base + sugars. Veena P Kumar 28
- 29. Veena P Kumar 29
- 30. In 1953 James.D.Watson and Francis.H.C. Crick published paper –model for physical and chemical structure of DNA molecule. Its was based on earlier findings by different scientists. 1. Erwin charqoff 1. Rosalind Franklin & Maurice H F Wilkins Watson & crick considered all evidence & began to build three dimentional model of structure of DNA Veena P Kumar 30
- 31. Veena P Kumar 31
- 32. Estable and Sotelo (1951) described the structure of a nucleolus under the light microscope. According to them, nucleolus consists of a continuous coiled filament called the nucleolonema embedded in a homogenous matrix. The first description of nucleolar ultra structure was given by Borysko and Bang (1951) and Bernhard (1952). They described two main nucleolar components, a filamentous one corresponding to the nucleolonema and a homogenous one corresponding to the pars amorpha (matrix). Veena P Kumar 32
- 33. Veena P Kumar 33
- 34. The nucleolus is a non-membrane bound structure composed of proteins and nucleic acids found within the nucleus. The ribosomal RNA is transcribed in the nucleolus. There are three main parts that are recognized: the fibrillar centers, the dense fibrillar component, and the granular components. The nucleolus is the main part of the cell that produces the ribosomes that make the proteins. Veena P Kumar 34
- 35. FC ; Fibrillar centres DFC; Dense fibrillar centres GC; Granular centres Veena P Kumar 35
- 36. As the nucleus is the "brain" of the cell, the nucleolus could loosely be thought of as the brain of the nucleus. The nucleolus takes up around 25% of the volume of the nucleus. This structure is made up of proteins and ribonucleic acids (RNA). Its main function is to rewrite ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and combine it with proteins. This results in the formation of incomplete ribosomes. Veena P Kumar 36
- 37. There is an uninterrupted chain between the nucleoplasm and the interior parts of the nucleolus, which occurs through a system of nucleolar passages. These passages allow macromolecules with a molecular weight up to 2,000 kDa to be easily circulated throughout the nucleolus. Because of its close relationship to the chromosomal matter of the cell and its important role in producing ribosomes, the nucleolus is thought to be the cause of a variety of different human diseases. Veena P Kumar 37
- 38. SYNTHESIS OF RIBOSOME IN NUCLEOLUS Veena P Kumar 38
- 39. Mutations in lamin genes leads to Laminopathies. Eg: Progeria Progeria leads to premature aging. Veena P Kumar 39
- 40. IQGAP1 protein helps in amplification of cancer cells. Veena P Kumar 40
- 41. Dicer is a protein forms RISC( RNA Induced silencing complex) and plays a vital role in RNAi. Veena P Kumar 41