Magnetic circuits
•Download as PPT, PDF•
23 likes•13,987 views
Electro-Magnetic Field
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENT & MEASURING INSTRUMENTS [Emmi- (NEE-302) -unit-1]![ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENT & MEASURING INSTRUMENTS [Emmi- (NEE-302) -unit-1]](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
![ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENT & MEASURING INSTRUMENTS [Emmi- (NEE-302) -unit-1]](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENT & MEASURING INSTRUMENTS [Emmi- (NEE-302) -unit-1]
Power Electronics - Power Semi – Conductor Devices

Power Electronics - Power Semi – Conductor Devices
Similar to Magnetic circuits
Similar to Magnetic circuits (20)
More from Abhinay Potlabathini
More from Abhinay Potlabathini (20)
A11 microprocessors & microcontrollers (common to eee, ece and ecm)

A11 microprocessors & microcontrollers (common to eee, ece and ecm)
A10 microprocessor & microcontrollers ( eee, ece & ecm )

A10 microprocessor & microcontrollers ( eee, ece & ecm )
A12 microprocessors & microcontrollers (common to eee & ecm)

A12 microprocessors & microcontrollers (common to eee & ecm)
A10 a11-microprocessor & microcontrollers (common to eee, ece & ecm)

A10 a11-microprocessor & microcontrollers (common to eee, ece & ecm)
Recently uploaded
God is a creative God Gen 1:1. All that He created was “good”, could also be translated “beautiful”. God created man in His own image Gen 1:27. Maths helps us discover the beauty that God has created in His world and, in turn, create beautiful designs to serve and enrich the lives of others.
Explore beautiful and ugly buildings. Mathematics helps us create beautiful d...

Explore beautiful and ugly buildings. Mathematics helps us create beautiful d...christianmathematics
Mehran University Newsletter is a Quarterly Publication from Public Relations OfficeMehran University Newsletter Vol-X, Issue-I, 2024

Mehran University Newsletter Vol-X, Issue-I, 2024Mehran University of Engineering & Technology, Jamshoro
Recently uploaded (20)
Salient Features of India constitution especially power and functions

Salient Features of India constitution especially power and functions
Basic Civil Engineering first year Notes- Chapter 4 Building.pptx

Basic Civil Engineering first year Notes- Chapter 4 Building.pptx
Mixin Classes in Odoo 17 How to Extend Models Using Mixin Classes

Mixin Classes in Odoo 17 How to Extend Models Using Mixin Classes
Explore beautiful and ugly buildings. Mathematics helps us create beautiful d...

Explore beautiful and ugly buildings. Mathematics helps us create beautiful d...
Kodo Millet PPT made by Ghanshyam bairwa college of Agriculture kumher bhara...

Kodo Millet PPT made by Ghanshyam bairwa college of Agriculture kumher bhara...
Vishram Singh - Textbook of Anatomy Upper Limb and Thorax.. Volume 1 (1).pdf

Vishram Singh - Textbook of Anatomy Upper Limb and Thorax.. Volume 1 (1).pdf
UGC NET Paper 1 Mathematical Reasoning & Aptitude.pdf

UGC NET Paper 1 Mathematical Reasoning & Aptitude.pdf
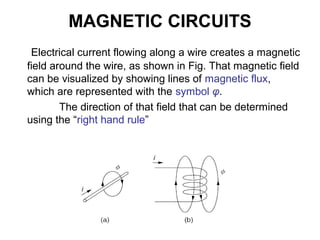
Magnetic circuits
- 1. MAGNETIC CIRCUITS Electrical current flowing along a wire creates a magnetic field around the wire, as shown in Fig. That magnetic field can be visualized by showing lines of magnetic flux, which are represented with the symbol φ. The direction of that field that can be determined using the “right hand rule”
- 2. • Faraday discovered is that current flowing through the coil not only creates a magnetic field in the iron, it also creates a voltage across the coil that is proportional to the rate of change of magnetic flux φ in the iron. • That voltage is called an electromotive force, or emf, and is designated by the symbol e. Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction: •The sign of the induced emf is always in a direction that opposes the current that created it, a phenomenon referred to as Lenz’s law.
- 3. • In the magnetic circuit of Fig, the driving force, analogous to voltage, is called the magneto motive force (mmf), designated by F. The magneto motive force is created by wrapping N turns of wire, carrying current i Magneto motive force (mmf )F = Ni (ampere − turns)
- 4. • The magnetic flux is proportional to the mmf driving force and inversely proportional to a quantity called reluctance R, which is analogous to electrical resistance, • resulting in the “Ohm’s law” of magnetic circuits given by
- 5. Magnetic field intensity (H): With N turns of wire carrying current i, the mmf created in the circuit is Ni ampere-turns. With l representing the mean path length for the magnetic flux, the magnetic field intensity is
- 10. • Faraday’s Laws: First law: EMF is induced in a coil whenever magnetic field linking that coil is changed. Second law: The magnitude of the induced EMF is proportional to the rate of change of flux linkage. Lenz’s law: This law states that the induced EMF due to change of flux linkage by a coil will produce a current in the coil in such a direction that it will produce a magnetic field which will oppose the cause, that is the change in flux linkage.
- 11. Self-induced EMF and Mutually induced EMF The EMF induced in a coil due to change in flux linkage when a changing current flows through the coil is called self-induced EMF. when a second coil is brought near a coil producing changing flux, EMF will be induced in the second coil due to change in current in the first coil. This is called mutually induced EMF.
- 12. Self-Inductance of a Coil L is called the coefficient of self inductance or simply self inductance of the coil.
- 14. Mutual Inductance Consider two coils having N1 and N2 number of turns placed near each other as shown in Fig
- 15. Similarly, if we calculate the induced EMF in coil 1, due to change in current in coil 2, we can find the induced EMF e1 in coil 1 as Now, multiplying the expression for M as in (iii) and (iv) above,
- 16. Inductance of Coils connected in series having a common core Coils connected in series in (a) cumulatively (b) differentially Since the two coils are connected in series, the same current flows through them.
- 17. Due to mutual inductance, the EMF induced in coil 1 due to change in current in coil 2 and vice versa are expressed as EMF induced in coil 1 due to change in current in coil 2 is Now let the total equivalent inductance of the single circuit coil 1 and coil 2 as they are connected as in be ‘Le’ The EMF induced in the whole circuit will, therefore, be
- 18. Thus, equating the expression for ‘e’ ,the total EMFs as When the coils are differentially connected, Dot convention is used to determine the sign of induced voltage Note: If we use dot convention, it will not be required to know the way the coils have been actually wound.
- 19. Example :The total inductance of two coils connected in series cumulatatively is 1.6 H and connected differentially is 0.0.4 H. The self inductance of one coil is 0.6 H. Calculate (a) the mutual inductance and (b) the coupling coefficient. Sol: Given, or,
