Schistosoma parasitology kasr el Einy department
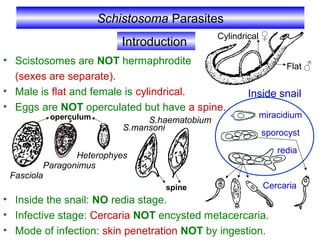
- 1. Schistosoma Parasites • Scistosomes are NOT hermaphrodite (sexes are separate). • Male is flat and female is cylindrical. • Eggs are NOT operculated but have a spine. • Inside the snail: NO redia stage. • Infective stage: Cercaria NOT encysted metacercaria. • Mode of infection: skin penetration NOT by ingestion. Introduction Fasciola Paragonimus Heterophyes S.mansoni S.haematobium miracidium sporocyst redia Inside snail operculum spine Flat ♂ Cylindrical ♀ Cercaria
- 2. Schistosoma causes Schistosomiasis Geographical distribution: Schistosoma mansoni Distribution Schistosoma haematobium Distribution
- 3. Schistosoma japonicum Distribution Present in the Far East
- 4. Definitive Host Man Habitat Superior & Inferior mesenteric plexus of veins Vesical & pelvic plexus of veins Where adult S.mansoni live Where adult S.haematobium live Blood vessels Thus Schistosomes are called Blood flukes Inferior mesenteric plexus of veins Where adult S.japonicum live
- 5. Life Cycle Infected human Egg in urine miracidium B.truncatus B.alexandrina Intermediate host Furcocercous cercaria Egg in stoolCercaria penetrate human skin Fresh water Definitive host S.haematobium S.mansoni Infective stage Mode of infection Diagnostic stage
- 6. Diagnostic Stage S.haematobium egg in urine S.mansoni egg in stool Size: Shape: Colour: Content: 140X60 µ 150X60 µ Oval, thin shell Terminal spine Lateral spine Translucent Miracidium
- 7. Mode of Infection Skin penetration by furcocercous cercaria from contaminated canal water. Aided by: - Surface tension of drying droplets of water. - Proteolytic enzymes secreted by penetration glands. - Strong lashing movement of the tail pressing the body of the cercaria into the skin.
- 8. Development of Schistosoma inside the body of infected human Cercariae penetrates human skin Schisto- somula Venous circulation Systemic circulation Liver Portal circulation Vesical plexus S.haematobium I III IV II Inf. mesenteric plexus S.mansoni Direction of venous blood flow Aorta
- 9. Pathogenesis and Clinical Picture There are 4 progressive stages: Local dermatitis, irritation. Papular rash. I- Stage of invasion
- 10. II- Stage of migration Metabolic products: toxic and allergic manifestations as urticaria, fever, headache, muscle pain. Eosinophilia, leucocytosis. In the lung: verminous pneumonitis, minute haemorrhage, cough, haemoptysis. In the liver: enlarged and tender. By schistosomula
- 11. III- Stage of egg deposition and extrusion The patient may complain of: Generalized malaise, fever, rigors, urticaria, abdominal pain and liver tenderness. A- Eggs are deposited in the venous plexus
- 12. Katayama Syndrome Blood vessel Soluble egg antigens are released in blood stream Occurs mainly in S.japonicum infection 1- ♀ lays large number of eggs 2- greater proximity to the liver immune complex Deposited in the tissues Tissue damageThe patient suffers from: Fever, chills, diarrhoea, generalized lymphadenopathy Eosinophilia Due to: Thus also called acute toxoemic schistosomiasis Circulate in blood
- 13. IV- Stage of egg deposition and extrusion: Terminal haematuria frequency of micturition burning pain Dysentery (blood and mucus in stool) Vesical & pelvic plexus of veins Bladder wall mesenteric plexus of veins Intestinal wall This produces tissue damage & haemorrhage In S.haematobium In S.mansoni & japonicum B- Eggs escape from the veins to the perivascular tissue
- 14. IV- Stage of tissue reaction (chronic stage) around Schistosoma eggs trapped in various tissues. Attract inflammatory cells Deposition of fibrous tissue Damage of affected organ and its fibrosis Loss of its function Egg shell miracidium Inflammatory cells Shell & miracidial antigens Delayed-type hypersensitivity e.g.Granuloma formation in bladder Where? Granuloma develops
- 15. Polyps in the colon Barium enema that shows polyps in the colon Tissue fibrosis, nodules, papillomata & sandy patches
- 16. IV- Stage of tissue reaction (chronic stage) Liver: portal hypertension, hepatosplenomegaly, oesophageal varices, ascites. Lung: pulmonary hypertension, bilharzial cor-pulmonale. Eggs swept by blood Eggs trapped in Bladder wall Eggs trapped in Intestinal wall Eggs that fail to fix to venule wall cause Embolic lesions Eggs swept by blood Eggs extruded in urine Eggs extruded in stool
- 17. Diagnosis • Direct parasitological methods: Detection of S.haematobium eggs in urine. Test for viability. Detection of S.mansoni eggs in stool by direct smear method or by concentration method. Kato thick faecal smear: for egg counting to assess the intensity of infection Rectal swab • Blood examination: eosinophilia, leucocytosis, anaemia. I- Laboratory
- 18. Serological Tests: 1- IHAT (Indirect Haemagglutination test) Detection of anti-Schistosoma antibodies or antigen in patient’s serum 2- ELISA (Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) 3- IFAT (Indirect Fluorescent Antibody test) wash wash wash wash wash Ab detected wash wash wash Ag detected Coating with Schisto Ag Coating with anti-Schisto monoclonal Ab Latex particles Sensitized sheep RBCs +ve -ve Schisto Ag Patient serum Ab detected
- 19. Calcified bladder with hydroureter Intestinal affection Stenosed ureters and hydronephrosis II- Radiological imaging S.haematobium infection S.mansoni infection
- 20. المناظيرIII- Endoscopy Cystoscopy S.haematobium Colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy S.mansoni Done in chronic cases to detect lesions and take biopsies
- 21. Treatment Praziquantel Prevention and Control - Mass treatment. - Health Education. - Snail control: Physical methods Biological methods Chemical methods X Balanites aegyptica Copper sulphate
- 22. Cercarial Dermatitis (Bather’s itch( A condition that occurs due to penetration of cercariae of non-human species of schistosomes the skin of man. Cercariae cannot go beyond the germinal layer. Clinical picture: Dermatitis, itching, oedema and secondary bacterial infection. Treatment: Antipruritics, antihistamincs, antibiotics.
- 23. M.C.Q. The major cause of morbidity in schistosomiasis is: a- Migration of adult worms against blood stream. b- Migration of adult worms in the liver. c- Embolic lesions. d- Deposition of eggs in tissues. Kato technique is used to diagnose: a- Paragonimiasis c- Schistosomiasis haematobium Bather’s itch occurs frequently with: a- S.haematobium b- S.japonicum b- Schistosomiasis mansoni d- Fascioliasis b- S.mansoni d- non human schistosomes
- 24. M.C.Q. Katayama syndrome: a- occurs most frequently in S.haematobium infection. b- consists of pulmonary hypertension and right-sided heart failure. c- occurs most frequently in S.japonicum infection. d- occurs in chronic schistosomiasis.
- 25. Give reasons for Terminal haematuria is due to active deposition of eggs by adult female S. haematobium in vesical venous plexuses. Eggs escape to the perivascular tissue and become extruded to the lumen of the urinary bladder. Powerful contraction of the bladder at the end of micturition (to squeeze the last drops of urine( leads to haemorrhage (terminal haematuria(. Occurrence of terminal haematuria in S.haematobium infection Lumen of urinary bladder
- 26. Give reasons for Many eggs that fail to be fixed to walls of venules are swept by blood to reach various organs as the lungs where they form granulomas and fibrosis with obliteration of flow resulting in pulmonary hypertension and right-sided heart failure. Occurrence of Bilharzial cor-pulmonale in schistosomiasis Swept by blood LungHeart