Physiology of hearing
- 1. PHYSIOLOGYOF HEARING Dr Seema S 1
- 2. Outline Introduction to sound Ear Function as a transducer Parts and how it functions External ear Middle ear Internal ear Electrical potential Auditory path way 2
- 3. SOUND A form of energy propagates in the form of waves The speed of sound depend on the medium through which the wave pass air - 343m/s water - 1482m/sec Audible frequencies t for humans 20 to 20,000 cycles per second (cps, Hz). It can detect the difference between two sounds occurring 10micro seconds apart in time 3
- 4. EAR AS A TRANSDUCER SOUNDENERGY MECHANICAL ENERGY ELECTRICAL ENERGY 4
- 5. Technical jargons • Strength of the sound • Loudness denotes the appreciation of sound intensity • Expressed in decibel (dB) Amplitude/loudness • Number of cycles per second • Pitch /Tone denotes the appreciation of frequency • Expressed in Hertz(Hz) Frequency/Pitch/Tone • Resistance offered by a medium to sound waves Impedence 5
- 6. • Resonance is the tendency of a system to oscillate with larger amplitude at some frequencies than at others RESONANCE • Attenuation is a general term that refers to any reduction in the strength of a signal ATTENUATION 6
- 7. Values of hearing: 15-25dB —Whisper 35dB —Background noise 40-60dB —Background noise ( home ) 65—70dB –- normal speaking voice 130dB —painful noise 140-180dB —jet air craft engine noise
- 8. Natural resonant frequency EXTERNAL AUDITORY CANAL--------------- 3000Hz TYMPANIC MEMBRANE----------------------- 800-1600Hz MIDDLE EAR--------------------------------------- 800Hz OSSICULAR CHAIN--------------------------- 500-2000Hz 8
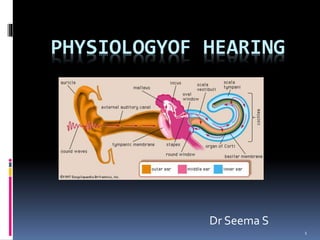
- 9. External ear 9
- 10. Functions of EXTERNAL EAR Sound collection Increasing pressure on the tympanic membrane in a frequency sensitive way Sound localization 10
- 11. Sound collection Pinna- concha system catches sound over large area and concentrate it to smaller area of ext. auditory meatus. This increases the total energy available to the tympanic membrane 11
- 12. Pressure increase by EAC If a tube which is closed at one end and open at other is placed in a sound field then pressure is low at open end and high at closed end. 12
- 13. Sound localization Because of its shape, the pinna shield the sound from rear end,change timbre,and helps to localize sound from infront or back Cues for sound localization from right/left Sound wave reaches the ear closer to sound source before it arise in farthest ear Sound is less intense as it reaches the farthest ear because head act as barrier Auditory cortex integrates these cues to determine location. 13
- 14. Middle ear 14
- 15. FUNCTIONS OF MIDDLE EAR 15
- 16. Impedence mismatch IF THERE WAS NO MIDDLE EAR SYSTEM ,99% OF SOUND WAVES WOULD HAVE REFLECTED BACK FROM OVAL WINDOW MIDDLE EAR BY ITS IMPEDENCE MATCHING PROPERTY ALLOWS 60% OF SOUND ENERGY TO DISSIPATE IN INNER EAR 16
- 17. “Impedance Matching” by the middle ear System (a) Area of tympanic membrane relative to oval window (b)The lever action of middle ear ossicles (c)The shape of tympanic membrane 17
- 18. (a) HYDRAULIC ACTION OFTYMPANIC MEMBRANE Total effective area of tympanic membrane 45mm2 Area of stapes footplate is 3.2mm2 Effective areal ratio is 14:1 Thus by focusing sound pressure from large area of tympanic membrane to small area of oval window the effectiveness of energy transfer between air to fluid of cochlea is increased 18
- 19. (b) Lever action of ossicles Handle of malleus is 1.3 times longer than long process of incus Overall this produces a lever action that converts low pressure with along lever action at malleus handle to high pressure with a short lever action at tip of long process of incus 19
- 20. (c) Action of tympanic membrane Eustachian tube equilibrates the air pressure in middle ear with that of atmospheric pressure, thus permitting tympanic membrane to stay in its most neutral position. A buckling motion of tympanic membrane result in an increased force and decreased velocity to produce a fourfold increase in effectiveness of energy transfer 20
- 21. Total gain Total transformer ratio=14x1.3x4=73:1 21
- 22. Attenuation reflex When loud sounds are transmitted through the ossicular system and from there into the central nervous system, a reflex occurs after a latent period of only 40 to 80 ms to cause contraction of the stapedius muscle and the tensor tympani muscle The tensor tympani muscle pulls the handle of the malleus inward while the stapedius muscle pulls the stapes outward. These two forces oppose each other and thereby cause the entire ossicular system to develop increased rigidity, thus greatly reducing the ossicular conduction of low frequency sound 22
- 23. Function of attenuation reflex To protect the cochlea from damaging vibrations caused by excessively loud sound. To mask low-frequency sounds in loud environments. This usually removes a major share of the background noise To decrease a person’s hearing sensitivity to his or her own speech 23
- 24. PHASE DIFFERENTIAL EFFECT Sound waves striking the tympanic membrane do not reach the oval and round window simultaneously. There is preferential pathway to oval window due to ossicular chain. This acoustic separation of windows is achieved by intact tympanic membrane and a cushion of air around round window This contributes 4dB when tympanic membrane is intact 24
- 25. INNER EAR 25
- 26. COCHLEA ---TWO FUNCTIONS…. A TRANSDUCER that translates sound energy into a form suitable for stimulating the dendrites of auditory nerve. AN ENCODER that programs the features of an acoustic stimulus so that the brain can process the information contained instimulating sound. 26
- 27. Electrical potential of cochlea and CN VIII 27
- 28. Endocochlear potential An electrical potential of about +80 millivolts exists all the time between endolymph and perilymph, with positivity inside the scala media and negativity outside. This is called the endocochlear potential, and it is generated by continual secretion of positive potassium ions into the scala media by the stria vascularis 28
- 29. Cochlear microphonic When basilar membrane move in response to sound stimulus electrical resistance at the tip of hair cells change allowing flow of K+ through hair cells and produce voltage fluctuations called cochlear micro phonic. This is AC potential 29
- 30. Summating potential Produced by hair cells DC potential superimposed on VIII nerve action potential 30
- 31. Compound action potential All or none response of auditory nerve fibres 31
- 32. Central auditory pathway • nerve fibers from the spiral ganglion of Corti enter the dorsal and ventral cochlear nuclei • second-order neurons pass mainly to the opposite side of the brain stem to terminate in the superior olivary nucleus • the superior olivary nucleus,the auditory pathway passes upward through the lateral lemniscus. 32
- 33. Some of the fibers terminate in the nucleus of the lateral lemniscus, but many bypass this nucleus and travel on to the inferior colliculus, where all or almost all the auditory fibers synapse From there, the pathway passes to the medial geniculate nucleus, where all the fibers do synapse Finally, the pathway proceeds by way of the auditory radiation to the auditory cortex, located mainly in the superior gyrus of the temporal lobe. 33
- 34. Pecularities of auditory pathway First,signals from both ears are transmitted through the pathways of both sides of the brain, with a preponderance of transmission in the contralateral pathway Second, many collateral fibers from the auditory tracts pass directly into the reticular activating system of the brain stem Third, a high degree of spatial orientation is maintained in the fiber tracts from the cochlea all the way to the cortex 34
- 35. Function of auditory cortex Perception of sound Judging the intensity of the sound Analysis of different property of sound 35
- 36. 36