Report
Share
Recommended
Recommended
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
Similar to Behaviour of liquids and gases
Similar to Behaviour of liquids and gases (20)
Particulate nature of matter -diffusion & heating curves

Particulate nature of matter -diffusion & heating curves
Physics 2.2 - Simple kinetic molecular model of matter - 2.pptx

Physics 2.2 - Simple kinetic molecular model of matter - 2.pptx
More from amandayoung313
More from amandayoung313 (20)
Behaviour of liquids and gases
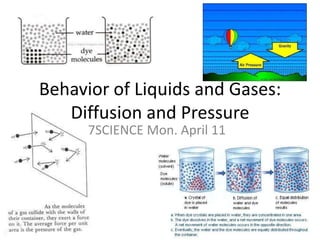
- 1. Behavior of Liquids and Gases: Diffusion and Pressure 7SCIENCE Mon. April 11
- 2. Review: How do substances change state? How does a liquid change to a solid? Freezing (freezing point temperature) How does a solid change to a liquid? Melting (melting point temperature) How does a liquid change to a gas? (2) Boiling (boiling point temperature) Evaporation How does a gas change to a liquid? Condensation What is the name for the process in which a solid changes to a gas or gases change to a solid? Sublimation
- 3. How do liquids and gases behave? Diffusion Pascal’s principle Archimedes’ principle
- 4. Diffusion Diffusion is the mixing of particles Movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration Why can we smell a fire even though we are far away? Particles in the gas state are far apart and move freely to mix with the air Many toxic gases are mixed with chemicals so you can smell them and move to safety!
- 6. Gas Pressure andPascal’s principle You may increase the pressure of a gas in a confined space by forcing more particles into the same amount of space Ex: inflating a balloon or a ball Increasing the pressure by adding more air particles to the space What do you think would happen to the pressure inside the ball if you inflated it inside a warm building then took it outside to a cold temperature?