3.0 forces and pressure teacher copy
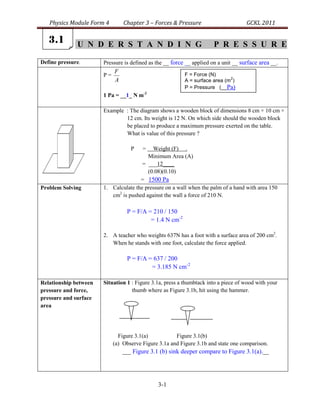
- 1. Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 3 – Forces & Pressure GCKL 2011 3.1 U N D E R S T A N D I N G P R E S S U R E Define pressure. Pressure is defined as the __ force __ applied on a unit __ surface area __. F F = Force (N) P= 2 A A = surface area (m ) P = Pressure (__Pa) 1 Pa = __1_ N m-2 Example : The diagram shows a wooden block of dimensions 8 cm × 10 cm × 12 cm. Its weight is 12 N. On which side should the wooden block be placed to produce a maximum pressure exerted on the table. What is value of this pressure ? P = Weight (F) . Minimum Area (A) = ___12____ (0.08)(0.10) = 1500 Pa Problem Solving 1. Calculate the pressure on a wall when the palm of a hand with area 150 cm2 is pushed against the wall a force of 210 N. P = F/A = 210 / 150 = 1.4 N cm-2 2. A teacher who weights 637N has a foot with a surface area of 200 cm2. When he stands with one foot, calculate the force applied. P = F/A = 637 / 200 = 3.185 N cm-2 Relationship between Situation 1 : Figure 3.1a, press a thumbtack into a piece of wood with your pressure and force, thumb where as Figure 3.1b, hit using the hammer. pressure and surface area Figure 3.1(a) Figure 3.1(b) (a) Observe Figure 3.1a and Figure 3.1b and state one comparison. ___ Figure 3.1 (b) sink deeper compare to Figure 3.1(a).__ 3-1
- 2. Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 3 – Forces & Pressure GCKL 2011 (b) Which one is received a higher force? ____ Figure 3.1(b) received higher force.____ (c) State the relationship between pressure and force. The pressure produce increases with force applied . Situation 2 : A 500 g cardboard box placed on a table in two different orientations. Figure 3.2a Figure 3.2b. (a) Calculate the pressure exerted on the table for i) figure 3.2a ii) figure 3.2b. 5 / 12 x 20 5 / 10 x 20 = 0.028 N cm-2 = 0.025 N cm-2 (b) Which figure shows that the higher pressure is exerted to the table? __ figure 3.2(b)_ (c) State the relationship between pressure and surface area. ____ Pressure is inversely proportional to the surface area.__ Factor that affecting 1. Ways to increase pressure are : pressure. a) __increase _force ; b) __decrease __area of contact. - Force - Surface Area 2. Ways to decrease pressure are : a) ___ decrease __force ; b) __ increase _area of contact. The applications of a) High pressure. pressure in our daily life. Tools like knives, chisels, axes and saws have sharp cutting edges. The surface area of contact is _small_ When a force is applied on the tool, the small area of contact will produce a _ higher__ pressure to cut the material. 3-2
- 3. Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 3 – Forces & Pressure GCKL 2011 b) Low pressure. The flat base of each metal pole of a tent has a __big__ surface area to _reduce_ the pressure exerted on the ground. The poles will not sink into the ground because of the flat bases. Exercise 1. A cylinder has a mass of 12 kg and a 2. Wind blows normally on a wall at a cross-sectional area of 200 cm2. What pressure of 200 kPa. If the wall has is the pressure acting at its base? an area of 5 m2., what is the force acting on the wall? A. 6 kPa B. 9 kPa A. 40kN B. 800kN C. 12 kPa D. 15 kPa C. 1000KN D. 1200kN 3. A 250 N force is applied at an angle 30o to the 4. A balloon is pressed with a force of 2.4 N surface of a block. The surface is a square of using a finger. Find the pressure exerted on sides 10 cm. What is the pressure exerted on the balloon if the area of fingertip is 2.0 x the surface? 10-4 m2 A. 1.25 kPa B. 2.50 kPa C. 25.0 kPa D. 12.5 kPa P = F/A = 2.4 / 2 x 10-4 = 12 000 Pa 5. The diagram below shows a concrete block of dimension 1.5 m x 2.0 m x 3.0 m. Its weight is 60N. Calculate (a)maximum pressure, (b)minimum pressure: a) maximum pressure b) minimum pressure = 60 / 2.0 x 1.5 = 20 Pa =60 / 2.0 x 3.0 = 10 Pa 3-3
- 4. Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 3 – Forces & Pressure GCKL 2011 6. A Perodua Myvi with a mass of 900 kg. Air pressure for each tyre is 2 x 105 Pa. (a) What is the meaning of pressure ? ___ force exerted per unit area.___ (b) Calculate the area in contact with the ground for each tyre. A = (9000 / 4) / 2 x 105 = 0.01125 m 2 c) Zamani drives his car to his school with a distance of 10 km and find his car tyre become harder than usual. Explain why this is happen? ________ pressure increase with temperature____ ________________________________________________________________________ 7. Experiment : Based on the diagram below, complete the suitable planning experiment. a) Inference :… Pressure produce depends on surface area.… b) Hypothesis :… The bigger the surface area, the lesser the pressure produced…… c.i) Aim :… To investigate the relationship between surface area and pressure. …… ii) Variables i) Manipulated : … surface area , A ………………………… ii) Responding : … the depth of wood sink in plasticine, P (pressure) iii) Constant : … Force applied ( mass of weights )……… iii) Apparatus …… placticine, 100 g metal weights, wooden support , wooden disc (different & material sizes ) and ruler……. 3-4
- 5. Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 3 – Forces & Pressure GCKL 2011 iv) Diagram ~~ same as diagram in the question ~~ v) Procedure …1. The wooden disc with surface area 2 cm2 is put under the wooden support. 2. Placed 100 g metal weight on the top of wooden rod as shown in diagram above. 3. Measured the depth of wooden sinks in the plasticine using the ruler 4. The experiment is repeated using different sizes of wooden disc, 4 cm2 , 6 cm2 , 8 cm2 and 10 cm2. vii) Result A / cm2 2 4 6 8 10 P / cm viii Analyse data P/ cm A/ cm2 3-5
- 6. Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 3 – Forces & Pressure GCKL 2011 UNDERSTANDING PRESSURE IN LIQUIDS 3.2 Characteristics 1. Pressure in liquids acts in _ all _ directions. of pressure in liquid 2. Draw the jet of water. Pressure in liquids _ increase __ with depth. 3. Draw the water level in the container. Shape and size _ does not___ influence the pressure diagram ( All water level are same.) 4. The hole in both containers are at the same height. Draw the jet of water and oil. water oil - The higher the density the _ higher __ the pressure. - 3-6
- 7. Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 3 – Forces & Pressure GCKL 2011 Formula for The pressure in a liquid is the product of depth, density and gravitational acceleration. pressure in liquid P= x x P = Pressure ( Pascal) -3 ρ = density ( _ kg m _) P=hxρxg -1 g =__ N kg ____ h = height (m) Example :1. An air bubble is at a depth of 5 m below the surface of a lake . What is the pressure of water on the bubble if the density of the water is 1000 kg m-3? P=hρg = 5 x 1000 x 10 = _50 000_ Pa 2. The figure shows a high tin with a length of 100 cm is filled to the full with water. If the pressure caused by the water at point P is 8000 Pa, What is the value of L?(Density of water = 1000 kg m - 3 ) h = 8 000 / ( 1000 x 10 ) = 0.8 m = 80 cm l = 100 – h = 20 cm Experiment : Pressure and density in liquids a. Inference :………………………………………………………………………………………… b. Hypothesis :………………………………………………………………………………………… c. Aim :………………………………………………………………………………………… d. Variables i) Manipulated : …………………………… ii) Responding : …………………………… iii) Constant : …………………………… 3-7
- 8. Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 3 – Forces & Pressure GCKL 2011 e. Apparatus ………………………………………………………………………………………… & material ………………………………………………………………………………………… f. Procedure ………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………. g. Result h. Analyse : Graph of …………………………………………………………………………….. data ………………………………………………………………(draw on graph paper ) i. Conclution :………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………. j. Precaution :………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………. Applications of 1. 2. pressure in liquid 3-8
- 9. Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 3 – Forces & Pressure GCKL 2011 Exercise 1. Which of the following factor does The density of water is 1000 kg m-3. not influence the pressure of a liquid? A. Depth B. Acceleration due to gravity C. Density D. Volume 4. Mercury has density of 13600 kg m-3. 2. If the pressure of mercury is 650 kPa, Find the density of liquid X in kg m-3? what is the depth from its surface? Px = Pwater A. 4.0 m B. 4.8 m hx x ρx = hwater x ρwater C. 5.8 m D. 6.4m 6 ρx = 2 x 1000 ρx = 333.33 kg m-3 3. Water has density equals to 1 g cm-3. What is its pressure at a depth of 12 m from the surface? A. 80 kPa B. 100 kPa C. 120kPa D. 140kPa 5. A container contains two layers of liquids. An oil layer 45cm thick floats on 60 cm of water. The densityof oil is 750 kg m-3 and water is 1000 kg m-3. ( g = 10 m s-2 ) a) What is the pressure exerted on water by the oil layer? Poil = h x ρ x g = 3375 Pa b) what is the total pressure exerted on the bottom of the container? PT = Poil + Pwater = 9375 Pa 6. The pressure at the bottom of the dam is 2.4 x 106 Pa. What is the depth of water if the density of water is 1 000 kg m-3. h = 2.4 x 106 / ( 1000 x 10 ) = 240 m 3-9
- 10. Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 3 – Forces & Pressure GCKL 2011 7. Figure below shows a cross-sectional area of the structure of a dam. Wall Water Observe the thickness of the wall at the top and bottom part of the dam in the figure above. Based on the observations: (a) State one suitable inference that can be made. [ 1 mark ] (b) State one appropriate hypothesis for an investigation. [ 1 mark ] (c) With the use of apparatus such as a thistle funnel, beaker and other apparatus, describe an experimental framework to test your hypothesis. In your description, state clearly the following: (i) aim of the experiment, (ii) variables in the experiment, (iii) list of apparatus, (iv) arrangement of the apparatus, (v) the procedure of the experiment which include the method of controlling the manipulated variable and the method of measuring the responding variable, (vi) the way you would tabulate the data, (vii) the way you would analysis the data. [ 10 marks ] ( Experiment thistle funnel – density & depth ) 3-10
- 11. Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 3 – Forces & Pressure GCKL 2011 3.3 UNDERSTANDING GAS PRESSURE AND A T M O S P H E R I C P R E S S U R E Kinetic molecular Gases are : theory Made of … tiny particles ……………………………….. Move … at random ………………………………….. Far apart with a very … weak / low force of….. attraction Collide each other and collide with the wall of container with …high energy/speed… The average kinetic energy ……… increases …when the temperature …increases……………. Gas Pressure The gas pressure in a container is caused by the … collision ... of gas molecules with the …wall… of the container. Gas pressure can be measured by using 2 types of instrument known as : (a) . bourdon gauge . gauge (consists of a semi-circular or C-shaped copper tube that tends to straighten if more and more gas is pumped (compressed) into it). (b) … manometer…. (consists of a U-tube about 1 m in height. About 50% of the volume of the U-tube is filled with liquid such as mercury or water). Atmospheric The atmospheric pressure is caused by the downward … force .. exerted by the pressure air ( the weight of the atmosphere) on the Earth’s surface. The greater … the distance … from the sea level, the …lower .. will the atmospheric pressure. The atmospheric pressure at sea level is 1 atmosphere ( 1 atm) 1 atmosphere(atm) = …760.. mm Hg = …105…..Pa = 1000 milibar Find this: If density,ρ of mercury (Hg) = 13600 kg m-3 and density of water = 1000 kg m-3. 1 atm = __10.336___ m of water Barometer is an instrument to measure atmospheric pressure. There are 2 types of barometer: (a) .... barometer aneroid....... (is made of a partially vacuum sealed metal box). (b) … simple barometer …. (is made of a long glass tube about 1 meter in length fully filled with mercury and then inverted (turned upside down) into a bowl of mercury). 3-11
- 12. Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 3 – Forces & Pressure GCKL 2011 Example 1: The atmospheric pressure is 760 mm Hg. What is the value of the atmospheric pressure in Pascal? [ Density of mercury, ρ (Hg) = 13 600 kg m-3 ] h = 760 mm = 76 cm = 0.76 m Atmospheric pressure, Patm = h ρ g = (0.76)(13600)(9.8) = …103360 …. Pa Manometer PA = PB = Patm = 76 cm Hg PC = PA + PHg PD = PA + PHg 1 = (76 + 4) cm Hg = 79 cm Hg = 80 cm Hg ρHg = 13600 kg m-3 ; ρwater = 1000 kg m-3 h PA = PB = Patm = 76 cm Hg 2 PC = PA + PHg PD = Pc = 80 cm Hg = (76 + 4) cm Hg = 1088 cm water = 80 cm Hg PA = Patm = 76 cm Hg PC = PA + PHg 3 = (76 + 4) cm Hg = 80 cm Hg Pgas = PD = Pc = 80 cm Hg 3-12
- 13. Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 3 – Forces & Pressure GCKL 2011 Simple Barometer 1. Figure shows apparatus set up which is used to measure atmospheric pressure. [Mercury density = 1.36 x 104 kg m- 3 ] Calculate the pressure at point Q in Pa. 2. If the atmospheric pressure is 76 cm Hg, what is the pressure of the trapped air P? Applications of 1.Siphon …………………………………. atmospheric pressure. ………………………………….. ………………………………….. ………………………………….. 2. Vacuum cleaner …………spm 2009…… ………………………………….. ………………………………….. ………………………………….. 3-13
- 14. Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 3 – Forces & Pressure GCKL 2011 Exercise ( g = 9.8 m s-2 ; ρHg = 13.6 x 103 kg m-3 ) 1. What is the pressure of the gas 2. Which instruments is meant for trapped inside the J-tube, in Pa unit? measuring atmospheric pressure? A. Carburettor B. Siphon C. Fortin’s Barometer D. Hydrometer 3. Which of the following is not true about atmospheric pressure? A. Atmospheric pressure acts in all A. 1.19 x 105 Pa directions. B. 1.90 x 105 Pa B. Atmospheric pressure decreases with C. 2.19 x 105 Pa distance from Earth’s surface. D. 2.90 x 105 Pa C. Atmospheric pressure can only measure in Pa or N m-2. 3 Diagram below shows a set up of apparatus for measuring atmospheric pressure. Diagram shows a set up of apparatus for measuring atmospheric pressure. (a) What is the name for the instrument? … Simple Barometer …………………………………………………………………… (b) Determine the atmospheric pressure as measured by the instrument , (i) in the cm Hg unit (ii) in the Pa unit 76 cm Hg = 0.76 x 13600 x 9.8 = 101292.8 Pa (c) State the change of length of the mercury column above the mercury surface (i) The tube is raised by 10cm ...…… unchanged …………………………………. (ii) The surrounding temperature increases ………… decrease ………………….. (iii) The instrument is brought to the peak of a mountain …… decrease ………….. (iv) Water vapor is brought to the vacuum region ……… decrease ..…………… 3-14
- 15. Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 3 – Forces & Pressure GCKL 2011 3.4 P A S C A L ’ S P R I N C I P L E Definition Pascal’s Principle state that pressure exerted on an … enclosed …fluid is transmitted …… equally in all direction …. to every part of the fluid. Water spurts out at the _ same ______ speed because the pressure act at all the point are …same…. Pascal’s Principle A B Pressure at both side are same, PA = PB Remember, So that ; FA = FB P=F AA AB A a) When 20 N of force is applied at piston A, FB produced is FB = FA AB = 20 x 8.0 FB = _400 N ___ AA 0.47 b) When piston A is moved downward for 2 m, how far the load has been move up. Volume of liquid transmitted from A to B are equal. VA = VB ; where as V = Ah AAhA = ABhB hB = __0.1 m __ 3-15
- 16. Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 3 – Forces & Pressure GCKL 2011 Application Gather information about ; of Pascal’s Principle 1. Hydraulic brake system 2. Automobile hydraulic lift. Exercise 1. Figure below shows a hydraulic jack. 2. Which of the following device is Piston A and piston B have cross- based on the Pascal’s Principle of sectional areas 5 cm2 and 100 cm2 pressure transmission? respectively. If mass of 3kg is placed A. Hydrometer on piston A, what is the maximum B. Car’s hydraulic brake weight that can be lifted by piston B? C. Bunsen burner D. Fire extinguisher 3. The input piston of hydraulic press is pushed down 2.0 cm from the original position. If the cross sectional area of input piston is 5.0 cm2 and of the output piston is 50 cm2 , how much A. 300N B. 600N will the load be raised up? C. 800N D. 900N A. 0.2 cm B. 1.0 cm C. 1.5 cm D. 1.8 cm 4 A hydraulic jack which is used for lifting a car at a service centre for motor vehicles. The hydraulic jack made up of two pistons X and Y of cross-sectional area 0.02 m2 and 18 m2 respectively. When the compressor is switched on, a force of 200 N acts on piston X. (a) Name the physics principle applied in the hydraulic jack. __ Pascal’s principle _______________________________________ (b) Explain how the car is lifted __when piston X is pushed down. The pressure exerted is transmitted equally to the piston Y. the big force produced then push the car upward._________ 3-16
- 17. Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 3 – Forces & Pressure GCKL 2011 (c) State two advantages of using oil as the hydraulic fluid of water. __cannot be compress ; reduce friction. _____________ (d) Calculate the pressure exerted on piston Y. 10 000 Pa (e) Calculate the maximum weight of a load that can be lifted by piston Y. 180 000 N (f) If piston X move down by 45 cm, what is the distance moved by piston Y? 0.05 cm 5. Cross section area of piston A and piston B are 4000 cm2 and 6 000 cm2 respectively. i) Calculate the ratio of the force acting on piston A with the force acting on piston B 2:3 ii) If the piston B lifts a car 2.50 m high, how far to the right should piston A move? 3.75 m iii) Why the system less effective when there is air bubbles in the piston. … some force are used to press the air bubbles.……. 6. Given that the cross-sectional area of smaller piston and larger piston are 20 cm2 and 60 cm2 respectively. If the smaller piston is pushed with a force of 15 N. Calculate; a) i) Pressure exerted on smaller piston. ii) Pressure exerted on larger piston -2 15 / 20 = 0.75 N cm PL = Ps = 0.75 N cm-2 b) the ratio of pressure acted on the smaller piston and larger piston 1:1 c) the force experienced by the larger piston FL = 0.75 x 60 = 45 N 3-17
- 18. Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 3 – Forces & Pressure GCKL 2011 3.5 A R C H I M E D E S ’ P R I N C I P L E Definition Archimedes’ Principle: When an object is __ fully __ or __partially __ immersed in a fluid, the upthrust or ___buoyancy __ on it is equal to the __weight __ of fluid displaced. Relationship Simple activity to show the presence of buoyant force between ; 1. Determine the actual weight of plasticine and the apparent weight of the plasticine in water. Actual weight = ……………………… 1. FB with liquid Apparent weight = …………………. displaced (The weight of plasticine in water) Loss in weight = ……………………. Weight of = Buoyant force Water Displaced 2. FB with Weight of floating Volume of liquid displaced = Volume of _ object immersed object 2. Floating object F W Floating Buoyant force = weight of object Buoyancy FB = buoyant force (N) Force, FB FB = Wliquid displaced ; W = mg ; m = V ρ ρ = density (kgm-3) g = 10 ms-2 FB = __ Vρg __ V = volume (m3) Example 1. An object of density, 40 g cm-3 and mass 500 g is immersed in a liquid of density 2 g cm-3. Calculate; a) the volume of liquid displaced b) the mass of the liquid displaced 3-18
- 19. Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 3 – Forces & Pressure GCKL 2011 V = 500 / 40 = 12.5 cm3 m = 2 x 12.5 = 6.25 g c) the buoyant force experienced by the object (g =10 m s-2) FB = 0.0625 N Application 1. Submarine of Archimedes’ Principle 2. Hot Air Ballon 3. Hydrometer Exercise 1. A ship of mass 80000 kg floats on the 2. The diagram shows an object partly floated and sea surface. If the density of the sea immersed in a liquid. What was the mass of the water is 1250 kg m-3, what is the object. ( g = 10 m s-2 ) volume of the displaced sea water? A. 6.4 m3 B. 64 m3 3 C. 640 m D. 800 m3 A. 2.0 N B. 20 N C. 0.020 kg D. 200 g 3. The diagram shows an object immersed 4. A body of density 800 kg m-3 floats in liquid A in two liquids of different densities. and liquid B as shown. If the density of liquid B is 1000 kg m-3 , what is the possible density of liquid A? A. 790 kg m-3 B. 905 kg m-3 Which of the following related F1 and F2 C. 1000 kg m-3 correctly? D. 1050 kg m-3 A. F1 < F2 B. F1 = F2 C. F1 > F2 3-19
- 20. Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 3 – Forces & Pressure GCKL 2011 5. (a) A fisherman finds that his boat is at different levels in the sea and in the river, although the boat carries the same load. The density of sea water is 1 025 kg m-3 and of river water is 1 000 kg m-3. Figure 1 and 2 illustrate the situation of the boat in the sea and in the river. (i) What is meant by density? ___________________________________________________________________ (ii) Using Figure 1 and 2, compare the levels of the boat and the volumes of water displaced by the boat. ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………….. ……………………………………………………………………………………….. ……………………………………………………………………………………….. ……………………………………………………………………………………….. Relating the mass of the boat with its load, the volume of water displaced and the density of the water, deduce a relevant physics concept. ………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………… (iii) Name the physics principle that explains the above situation. ……………………………………………………………………………………………. b) A submarine can sail on the sea surface and under the sea. Explain how a submarine on the surface submerges. 3-20
- 21. Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 3 – Forces & Pressure GCKL 2011 (3 marks) c) Figures 3.5(c) and 3.5(d) below illustrate the working principle of a hydrometer. The depth to which the test tube sinks depends on its surrounding liquid. Draw a diagram that shows the design of your hydrometer and in your explanation, emphasis the following aspects: (i) the stability of the hydrometer (ii) the sensitivity of the hydrometer (iii) the ability to measure a wide range of densities of liquids (iv) the calibration of the hydrometer. [10m] 3-21
- 22. Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 3 – Forces & Pressure GCKL 2011 3.6 B E R N O U L L I ’ S P R I N C I P L E Definition In a steady flow of fluid, the _ pressure __in the fluid is _decreases__ when the velocity of the fluid is high and vice versa. Reminder : 1. Bernoulli’s Principle is obeyed only for moving fluid . 2. Fluid will move from high pressure into the low pressure. AEROFOIL Figure below shows an __ aerofoil__ The upper region of the aerofoil has _ higher _ air velocity than the lower region of the aerofoil. By Bernoulli’s principle, the lower region has __higher ___ pressure than the upper region of the aerofoil. This causes a __lifting force act____ on the aerofoil. Situation 1. that Water flows through a uniform tube involved from _ higher __ pressure to a __lower __ with pressure area. Fluid pressure decreases Bernoulli’s linearly; Principle PA > PB > PC VA < VB < VC Therefore hA > hB > hC 3-22
- 23. Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 3 – Forces & Pressure GCKL 2011 Water flows through a non uniform tube, 2. Venturi tube the velocity of the fluid; VB > VC > V A VC is the highest because water is forces to flow through a constriction at A, hence it speed up. 3. When the of fluid; flowing the pressure is Pressure air is not same at everyPA > PC >When the air is point. PB allowed to flow in, the velocity of the fluid; Therefore; hA > >C > hBV V hV > B C A Because the cross-sectional area at B is the smallest. Pressure of fluid; PA > PC > PB Therefore; hB > hC > hA 4. Water flows around the ping pong ball at _ high__ speed through the filter. Higher atmospheric pressure produces a __ upward force_ which is larger than __downward force __ of ping pong ball. Ping pong ball is pushed __ upward __ by upward force and does not drop. Exercise 1. If the height of the fluid in tube L is h1, 2. Aeroplane wingsact as aerofoils. What is the and that is tube M is h2, which of the funtion of an aerofoil? following is true? A. h1 > h2 because v1 > v2 B. h1 < h2 because v1 < v2 A. To raise up the aeroplane. C. h1 > h2 because v1 < v2 B. To increase the speed of air flow at the surface D. h1 < h2 because v1 > v2 of wing. C. To reduce the air resistance and the drag force. 3-23
- 24. Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 3 – Forces & Pressure GCKL 2011 3. Which of the following instruments is not 4. Which of the following relates two quantities in based on Bernoulli’s principle? Bernoulli’s principle? A. Bunsen burner A. Velocity and force B. Car carburettor B. Pressure and momentum C. Hydraullic jack C. Velocity and pressure D. Flight of an airplane D. Force and momentum 5. A boy standing by the road side. When a big lorry passed in front of him, the boy feels a pull towards the lorry. This phenomenon can be explained by A. Pascal’s principle B. Bernoulli’s principle C. Archimedes’ principle 6. As a researcher in a boat manufacturing company. , you are assigned to study metal characteristics used to make the boat. You are given four choices of metals P, Q, R and S. The table below shows the characteristics for the four metals. Metal Shape Density Specific Heat Strength 3 Capacity Kgm P Streamlined 900 Low High Q Oval 452 High High R Circle 387 Low High S Streamlined 500 High High Table 1 Based on table 1 i) Explain the suitable characteristics of the metal to be used as the material to make the boat. ( 8 marks) ii) Determine the most suitable metal to be used as the material to make the boat and give your reasons. ( 2 marks) 3-24
- 25. Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 3 – Forces & Pressure GCKL 2011 7. 3-25