Report
Share
Recommended
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
Viewers also liked
Viewers also liked (20)
Similar to Bp regulation
Similar to Bp regulation (20)
Maintaining homeostatic mean arterial blood pressure

Maintaining homeostatic mean arterial blood pressure
Physiological Regulation of Arterial Blood Pressure.pptx

Physiological Regulation of Arterial Blood Pressure.pptx
More from DrChintansinh Parmar
More from DrChintansinh Parmar (20)
Bp regulation
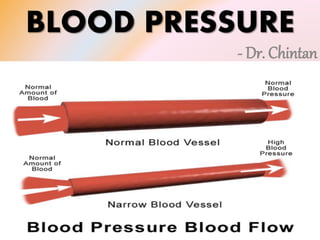
- 1. BLOOD PRESSURE - Dr. Chintan
- 2. Regulation of BP• Short term (seconds to minutes) • Baroreceptor • Chemoreceptor • CNS ischemic response • Intermediate term (minutes to hours) • Capillary fluid shift • Stress relaxation • Long term (days to years) • Renal body fluid mechanism • Renin – angiotensin system
- 3. Short term Regulation • Baroreceptors – aortic arch (10th), carotid sinus (9th) • 60 – 200 mmHg range of MBP • stretch-sensitive mechanoreceptors • Hypertension - the baroreceptor reflex mechanism is reset at a higher level to maintain BP at elevated level
- 7. Short term Regulation • Chemoreceptors – aortic body(10th), carotid body(9th) • 40 – 100 mmHg range of MBP • They respond to the chemicals mainly • a) Hypoxia ( ↓ pO2) • b) Hypercapnia ( ↑ pCO2) • c) Acidosis ( ↑ H+)
- 10. Short term Regulation • CNS ischemic response • 15 – 50 mmHg range of MBP when blood flow to VMC becomes decreased severely enough to cause cerebral ischemia ↓ The VMC respond directly to the ischemia and become strongly excited ↓ sympathetic vasoconstriction • whenever blood flow to the brain decreases dangerously close to the lethal level - the “last ditch stand”
- 11. Cushing’s Reflex Increased intracranial pressure ↓ Cerebral hypoxia and Hypercapnia ↓ Direct effect on VMC ↓ SNS action increases ↓ Vasoconstriction ↓ Increased BP ↓ Reflex bradycardia via baroreceptors
- 12. Intermediate term • Capillary fluid shift • When capillary pressure falls too low → fluid is absorbed through the capillary membranes from the tissues into the circulation → building up the blood volume and increasing the pressure • when the capillary pressure rises too high → fluid is lost out of the circulation into the tissues → reducing the blood volume as well as the pressure
- 13. Intermediate term • Stress relaxation & reverse Stress relaxation When the pressure in the blood vessels becomes too high ↓ They become stretched and keep on stretching more and more for minutes or hours; ↓ the pressure in the vessels falls toward normal
- 16. Long term regulation• Renal body fluid mechanism When the body contains too much ECF ↓ the blood volume and arterial pressure rise ↓ direct effect to cause the kidneys to excrete the excess ECF (pressure naturesis, pressure diuresis) ↓ returning the pressure back toward normal
- 17. Long term regulation• Renin-Angiotensin System
- 20. THANQ…
