Pth and ca
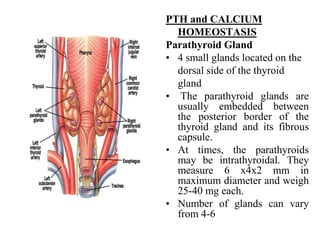
- 1. PTH and CALCIUM HOMEOSTASIS Parathyroid Gland • 4 small glands located on the dorsal side of the thyroid gland • The parathyroid glands are usually embedded between the posterior border of the thyroid gland and its fibrous capsule. • At times, the parathyroids may be intrathyroidal. They measure 6 x4x2 mm in maximum diameter and weigh 25-40 mg each. • Number of glands can vary from 4-6
- 2. History Sir Richard Owen, the curator of the British Museum of Natural History, discovered the parathyroid glands in 1852 while dissecting a rhinoceros that had died in the London Zoo. However, credit for discovery of the human parathyroid glands usually is given to Sandstrom, a Swedish medical student who published an anatomical report in 1890. In 1891, von Recklinghausen reported a new bone disease, which he termed "osteitis fibrosa cystica," which Askanazy subsequently described in a patient with a parathyroid tumor in 1904. The glands were rediscovered a decade later by Gley, who determined the effects of their extirpation with the thyroid. Vassale and Generali then successfully removed only the parathyroids and noted that tetany, convulsions, and death quickly followed unless calcium was given postoperatively
- 3. Unique properties of PTH PTH secretion responds to small alterations in plasma Ca2+ within seconds. A unique calcium receptor within the parathyroid cell plasma membrane senses changes in the extracellular fluid concentration of Ca2+. This is a typical G-protein coupled receptor that activates phospholipase C and inhibits adenylate cyclase—result is increase in intracellular Ca2+ via generation of inositol phosphates and decrease in cAMP which prevents exocytosis of PTH from secretory granules PTH secretion also is stimulated by, low levels of 1,25- dihydroxy vitamin D, catecholamines, and hypomagnesemia. PTH is synthesized in the parathyroid gland as a precursor hormone, preproparathyroid hormone, which is cleaved first to proparathyroid hormone and then to the final 84-amino-acid PTH. Secreted PTH has a half-life of 2 to 4 minutes
- 4. Role of PTH in Calcium Homeostasis
- 5. Parathyroid “C” Cells PTH Calcitonin Inhibit Inhibit Bone Bone Kidney Kidney Intestine [Ca++] [Ca++] In plasma In plasma
- 6. Control of bone formation and resorption • Bone resorption of Ca++ by two mechanims: osteocytic osteolysis is a rapid and transient effect and osteoclasitc resorption which is slow and sustained. • Both are stimulated by PTH. • Does not merely extract calcium, it destroys entire matrix of bone and diminishes bone mass. • Cell responsible for resorption is the osteoclast.
- 7. Bone remodeling • Endocrine signals to resting osteoblasts generate paracrine signals to osteoclasts and precursors. • Osteoclasts resorb an area of mineralized bone. • Local macrophages clean up debris. • Process reverses when osteoblasts and precursors are recruited to site and generate new matrix. • New matrix is minearilzed. • New bone replaces previously resorbed bone.
- 8. Osteoclasts and Ca++ resorption
- 9. Calcium, bones and osteoporosis • The total bone mass of humans peaks at 25-35 years of age. • Men have more bone mass than women. • A gradual decline occurs in both genders with aging, but women undergo an accelerated loss of bone due to increased resorption during perimenopause. Bone resorption exceeds formation. • Reduced bone density and mass: osteoporosis • Susceptibility to fracture. Earlier in life for women than men but eventually both genders succumb. • How to reduce risk? Inc in calcium in the diet habitual exercise avoidance of smoking and alcohol intake avoid drinking carbonated soft drinks
- 10. Hormonal control of Ca2+ • Three principal hormones regulate Ca++ and three organs that function in Ca++ homeostasis. • Parathyroid hormone (PTH), 1,25-dihydroxy Vitamin D3 (Vitamin D3), and Calcitonin, regulate Ca++ resorption, reabsorption, absorption and excretion from the bone, kidney and intestine. In addition, many other hormones effect bone formation and resorption.
- 11. Hyperparathyroidism • Calcium homeostatic loss due to excessive PTH secretion • Due to excess PTH secreted from adenomatous or hyperplastic parathyroid tissue • Hypercalcemia results from combined effects of PTH-induced bone resorption, intestinal calcium absorption and renal tubular reabsorption • Pathophysiology related to both PTH excess and concomitant excessive production of 1,25-(OH)2-D.
- 12. Hypoparathyroidism • Hypocalcemia occurs when there is inadequate response of the Vitamin D-PTH axis to hypocalcemic stimuli • Hypocalcemia is often multifactorial • Hypocalcemia is invariably associated with hypoparathyroidism • PTH-deficient hypoparathyroidism – Reduced or absent synthesis of PTH – Often due to inadvertent removal of excessive parathyroid tissue during thyroid or parathyroid surgery • PTH-ineffective hypoparathyroidism – Synthesis of biologically inactive PTH