Report
Share
Download to read offline
Recommended
Recommended
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
IP Infusion Application Note for 4G LTE Fixed Wireless Access

IP Infusion Application Note for 4G LTE Fixed Wireless Access
Similar to Inter as cisco1
Similar to Inter as cisco1 (20)
Ipv6 application in 5G bearer network--C&T RF Antennas Inc

Ipv6 application in 5G bearer network--C&T RF Antennas Inc
PLNOG15: BGP New Advanced Features - Piotr Wojciechowski

PLNOG15: BGP New Advanced Features - Piotr Wojciechowski
OpenNebulaConf2018 - Scalable L2 overlay networks with routed VXLAN / BGP EVP...

OpenNebulaConf2018 - Scalable L2 overlay networks with routed VXLAN / BGP EVP...
Rafał Szarecki - PIM-tunnels and MPLS P2MP as Multicast data plane in IPTV a...

Rafał Szarecki - PIM-tunnels and MPLS P2MP as Multicast data plane in IPTV a...
Recently uploaded
Recently uploaded (20)
TrustArc Webinar - Unified Trust Center for Privacy, Security, Compliance, an...

TrustArc Webinar - Unified Trust Center for Privacy, Security, Compliance, an...
Continuing Bonds Through AI: A Hermeneutic Reflection on Thanabots

Continuing Bonds Through AI: A Hermeneutic Reflection on Thanabots
Navigating Identity and Access Management in the Modern Enterprise

Navigating Identity and Access Management in the Modern Enterprise
WSO2 Micro Integrator for Enterprise Integration in a Decentralized, Microser...

WSO2 Micro Integrator for Enterprise Integration in a Decentralized, Microser...
Choreo: Empowering the Future of Enterprise Software Engineering

Choreo: Empowering the Future of Enterprise Software Engineering
The Zero-ETL Approach: Enhancing Data Agility and Insight

The Zero-ETL Approach: Enhancing Data Agility and Insight
Stronger Together: Developing an Organizational Strategy for Accessible Desig...

Stronger Together: Developing an Organizational Strategy for Accessible Desig...
Decarbonising Commercial Real Estate: The Role of Operational Performance

Decarbonising Commercial Real Estate: The Role of Operational Performance
Tales from a Passkey Provider Progress from Awareness to Implementation.pptx

Tales from a Passkey Provider Progress from Awareness to Implementation.pptx
Six Myths about Ontologies: The Basics of Formal Ontology

Six Myths about Ontologies: The Basics of Formal Ontology
API Governance and Monetization - The evolution of API governance

API Governance and Monetization - The evolution of API governance
Cloud Frontiers: A Deep Dive into Serverless Spatial Data and FME

Cloud Frontiers: A Deep Dive into Serverless Spatial Data and FME
The Ultimate Prompt Engineering Guide for Generative AI: Get the Most Out of ...

The Ultimate Prompt Engineering Guide for Generative AI: Get the Most Out of ...
Repurposing LNG terminals for Hydrogen Ammonia: Feasibility and Cost Saving

Repurposing LNG terminals for Hydrogen Ammonia: Feasibility and Cost Saving
UiPath manufacturing technology benefits and AI overview

UiPath manufacturing technology benefits and AI overview
ChatGPT and Beyond - Elevating DevOps Productivity

ChatGPT and Beyond - Elevating DevOps Productivity
Portal Kombat : extension du réseau de propagande russe

Portal Kombat : extension du réseau de propagande russe
Inter as cisco1
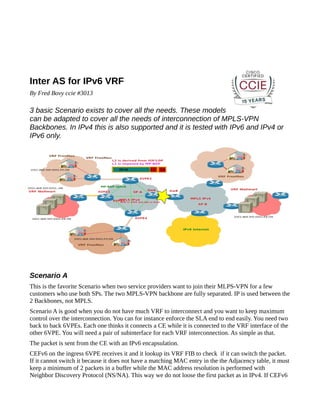
- 1. Inter AS for IPv6 VRF By Fred Bovy ccie #3013 3 basic Scenario exists to cover all the needs. These models can be adapted to cover all the needs of interconnection of MPLS-VPN Backbones. In IPv4 this is also supported and it is tested with IPv6 and IPv4 or IPv6 only. Scenario A This is the favorite Scenario when two service providers want to join their MLPS-VPN for a few customers who use both SPs. The two MPLS-VPN backbone are fully separated. IP is used between the 2 Backbones, not MPLS. Scenario A is good when you do not have much VRF to interconnect and you want to keep maximum control over the interconnection. You can for instance enforce the SLA end to end easily. You need two back to back 6VPEs. Each one thinks it connects a CE while it is connected to the VRF interface of the other 6VPE. You will need a pair of subinterface for each VRF interconnection. As simple as that. The packet is sent from the CE with an IPv6 encapsulation. CEFv6 on the ingress 6VPE receives it and it lookup its VRF FIB to check if it can switch the packet. If it cannot switch it because it does not have a matching MAC entry in the the Adjacency table, it must keep a minimum of 2 packets in a buffer while the MAC address resolution is performed with Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NS/NA). This way we do not loose the first packet as in IPv4. If CEFv6
- 2. find that the route is recursive it applies a stack of label. Then when we have the MAC Address packet is sent. The Internal label is the MP-BGP label which has been allocated by the Egress 6VPE MP-BGP (Gateway A) and sent with the IPv6 Route to the Ingress 6VPE. The external label is matching the local Gateway A 6VPE /32 loopback address. Then on Gateway B CEFv6 allocates the external label which are allocated by the neighbor P routers and is most of the time a POP label to reach the egress 6VPE. The IPv6 VRF Address is advertised by the MP-BGP packet to all the others 6VPE directly or mostly via a Route-Reflector. The Packet goes from the ingress 6VPE to the Internal Gateway A as if it was the destination. Then it is forwarded to the Ingress 6VPE which will forward it toward the Egress 6VPE. Illustration 1: InterAS Scenario A It gives maximum control on the data and isolates the networks so there is no MPLS on the interconnection. MPLS-VPN parameters can be completely different: RD, RT as long as it leads to the correct egress 6VPE.
- 3. Scenario B The Scenario needs two dedicated gateway with an MP-eBGP + Labels session in between. This way all the vpnv6 routes are exchanged between the two 6VPEs with all the VRF routing info to reach the destination. First we must disable the automatic dropping of all the path which are not imported by any VRF. We are not going to configure all the VRF on the Gateways. “no default BGP routetarget filter” command within the BGP address-family vpnv6 configuration With this method we advertise all the paths. Also, it requires two big dedicated routers. A Big difference with the previous, we have MPLS running between the two gateways instead of IPv6. As we use multihop MP-eBGP between the Gateways, the next-hop for the inter VRF communication will be the advertising Gateway itself. The next-hop self is needed for SP A to be the next hop for any destination going to SP B. The packet can cross the link between GwA and GwB thanks to a route and a label advertized by a MPeBGP vpnv6 multihop configuration. When Gateway B receives the packet it has the two labels needed to encapsulate the packet to the egress 6VPE. This solution does not allow the same granularity of control as previous but is much more scalable if you have 2 big networks to interconnect for the same customer. In this scenario the VRF parameters: RD and RT must be consistent. This is a good solution if one of the 2 networks don't use BGP Route Reflector otherwise prefer solution C.
- 4. Illustration 2: Scenario B Scenario C In this solution we interconnect the Route-Reflectors of the two MSPL-VPN networks so all the vpnv6 routes will be learned with a MP-eBGP session between the RR. As we connect the two RR of the two MSPL-VPN Networks have different AS so the next hop should not be changed by the BGP Route Reflectors. Between the two gateways we need to configure ipv4 routing for SP A to know a route and a label for each 6VPE loopback and the opposite. eBGPv4 + Label can be used to leak the 6VPE loopback addresses to the other SP.
- 5. The Next-hop for the ingress 6VPE will be the Egress 6VPE loopback /32 address, that's why we need LSP between all 6VPE of both Service Providers. Each SP must know a route and a label for each remote 6VPE Loopback. Illustration 3: Scenario C
